The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a political and economic union of 10 Southeast Asian countries. Established on August 8, 1967, by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand, ASEAN promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration among its members and other Asian states. Since its formation, ASEAN has expanded to include Brunei, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), and Vietnam.
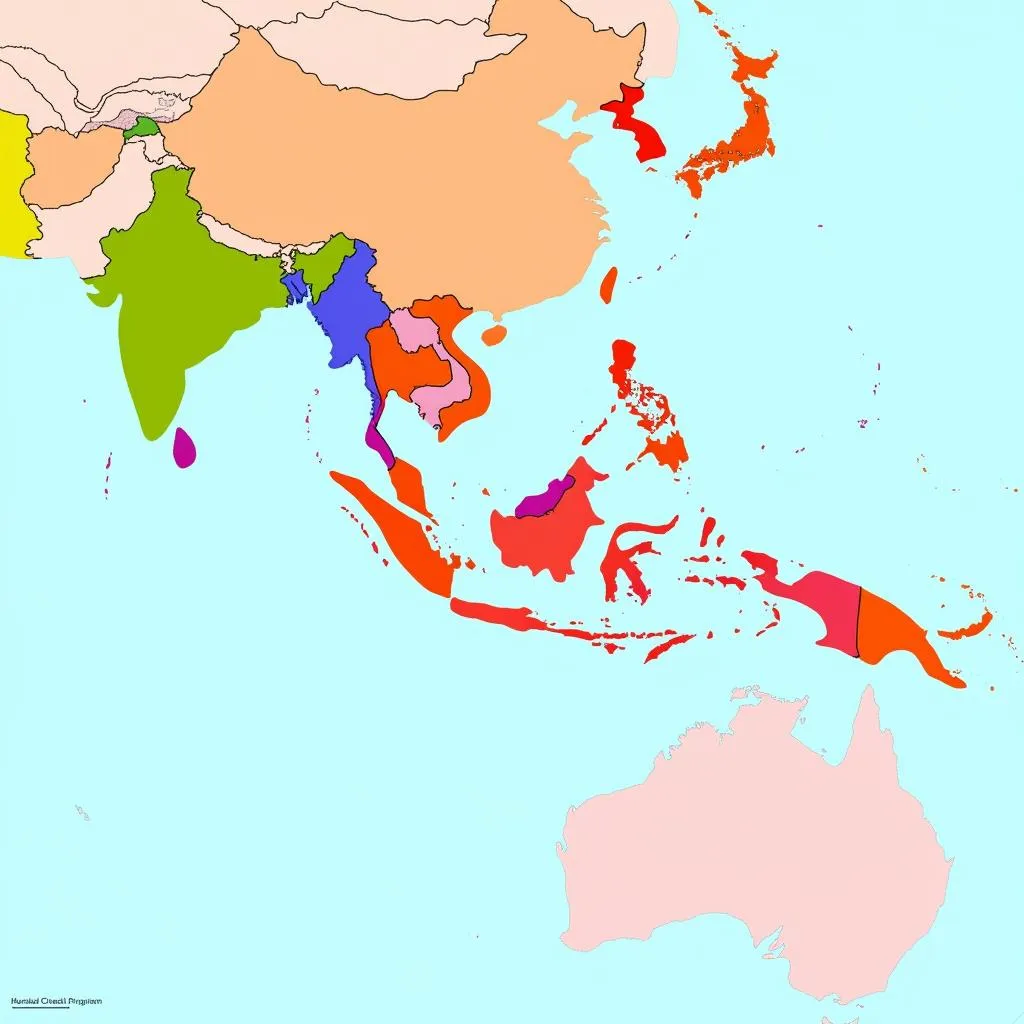 Southeast Asia map with ASEAN countries highlighted
Southeast Asia map with ASEAN countries highlighted
A Closer Look at the 10 Countries Included in ASEAN:
1. Brunei
Known formally as the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace, this small but wealthy country is located on the north coast of Borneo. Its economy is heavily reliant on oil and natural gas exports.
2. Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in Southeast Asia. Its landscape spans low-lying plains, the Mekong delta, mountains, and Thailand’s coastline. Cambodia has a rich history and culture and is known for the majestic temples of Angkor.
3. Indonesia
The Republic of Indonesia is the world’s largest island country, with over 17,000 islands. It is the fourth most populous country in the world and has the world’s largest population of Muslims. Indonesia is a significant player on the global stage with a mixed economy that includes tourism, manufacturing, and agriculture.
4. Laos
The Lao People’s Democratic Republic is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is known for its mountainous terrain, French colonial architecture, Buddhist monasteries, and stunning natural landscapes.
5. Malaysia
Malaysia is a Southeast Asian country whose territory comprises two regions: Peninsular Malaysia (West Malaysia) and East Malaysia, separated by the South China Sea. Malaysia is known for its beaches, rainforests, and mix of Malay, Chinese, Indian, and European cultural influences.
6. Myanmar
Officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, this Southeast Asian country is bordered by Bangladesh, India, China, Laos, and Thailand. It is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups. Myanmar is also known for its numerous pagodas and Buddhist monasteries.
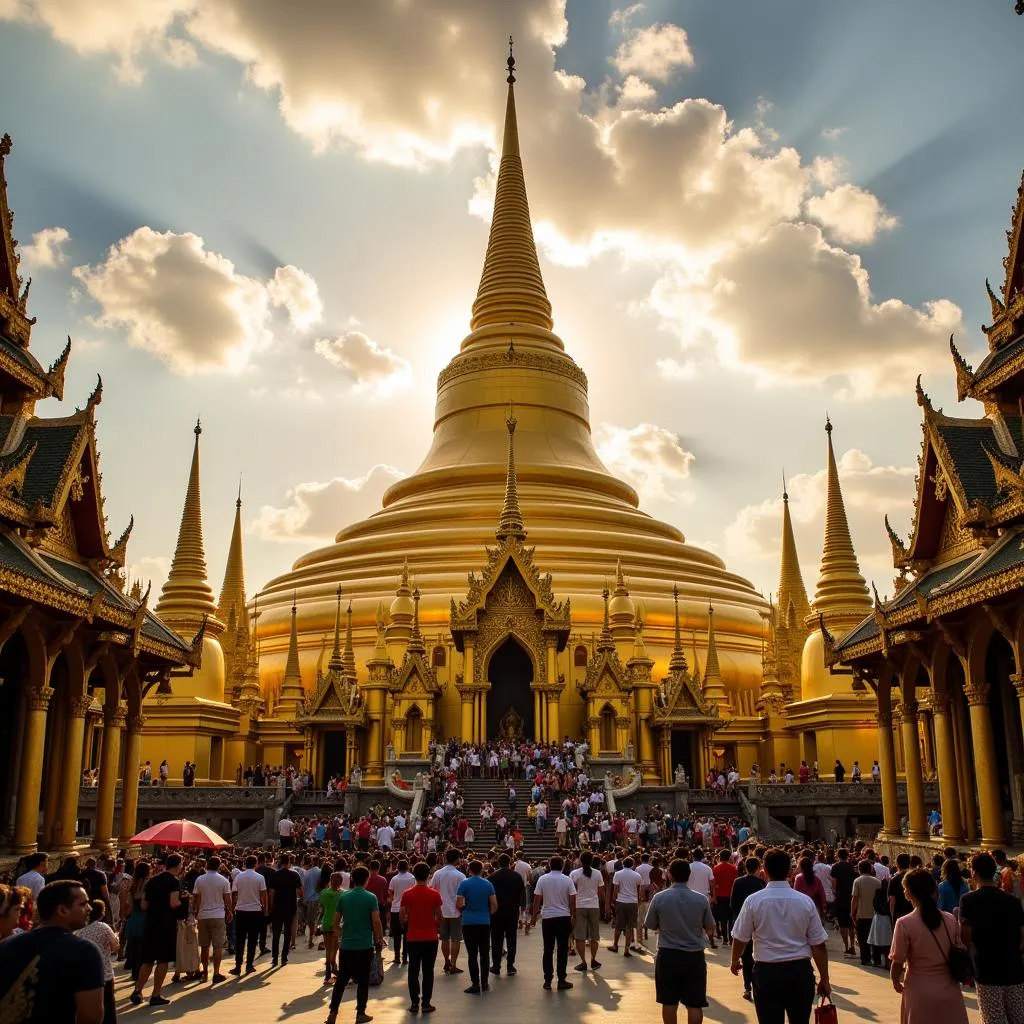 Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon, Myanmar
Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon, Myanmar
7. The Philippines
The Republic of the Philippines is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is composed of some 7,641 islands categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is known for its stunning beaches, diving spots, and diverse marine life.
8. Singapore
The Republic of Singapore is an island city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It is a global hub for finance, trade, and transportation. This vibrant nation is a melting pot of cultures and ethnicities, renowned for its cleanliness, efficiency, and modern cityscape.
9. Thailand
The Kingdom of Thailand is a country in Southeast Asia. Thailand is known for its tropical beaches, opulent royal palaces, ancient ruins, and ornate temples displaying figures of Buddha. It is a popular tourist destination and a significant economic hub in Southeast Asia.
10. Vietnam
The Socialist Republic of Vietnam is a country located in Southeast Asia. From bustling cities to tranquil rice paddies, Vietnam offers diverse landscapes. It is known for its rich history, delicious cuisine, and stunning natural beauty.
What is the Purpose of ASEAN?
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, was formed in 1967 with a common goal: to foster peace and stability in a region still grappling with the aftermath of colonialism and threatened by the rise of communist movements. ASEAN aimed to achieve this by:
- Accelerating economic growth: ASEAN encourages collaboration and free trade among its members, aiming to create a single market and production base. This integration helps attract foreign investment, boosts trade, and improves living standards.
- Promoting social progress: ASEAN works on improving education, healthcare, and social welfare within its member states. This involves sharing best practices, implementing regional programs, and promoting human rights and social justice.
- Promoting cultural development: Recognizing the rich cultural diversity of the region, ASEAN promotes cultural exchanges, understanding, and cooperation. This strengthens regional identity and fosters a sense of community within ASEAN.
- Maintaining regional peace: ASEAN provides a platform for dialogue and conflict resolution. The organization promotes peaceful settlement of disputes, upholding regional stability, and fostering a spirit of cooperation and understanding among member countries.
Why is ASEAN Important?
ASEAN has gained increasing global recognition and has become a vital player in the Asia-Pacific region. The organization plays a crucial role in:
- Boosting economic growth: By promoting free trade and economic cooperation among its member states, ASEAN has become a driving force for economic development in the region and globally.
- Enhancing regional security: ASEAN serves as a forum for dialogue and cooperation on security issues such as transnational crime, terrorism, and maritime security. This collaboration helps address common threats and maintain stability.
- Promoting regional integration: ASEAN promotes closer ties between its member states in various sectors, including trade, investment, tourism, and people-to-people exchanges. This integration fosters a sense of community and shared destiny within the region.
 ASEAN Summit: Leaders shaking hands
ASEAN Summit: Leaders shaking hands
What are some challenges faced by ASEAN?
Despite its achievements, ASEAN faces numerous challenges, including:
- Economic disparities: Significant economic gaps exist between member states. Bridging this development gap and ensuring inclusive growth remains a priority.
- Territorial disputes: Overlapping maritime territorial claims in the South China Sea continue to pose challenges and could potentially escalate into conflicts.
- Political instability: Domestic political situations in some member states and the rise of nationalism pose risks to ASEAN’s unity and effectiveness.
- Non-interference principle: ASEAN’s commitment to non-interference in the internal affairs of member states is sometimes viewed as an obstacle to addressing serious issues like human rights violations and democratic backsliding.
Conclusion
ASEAN’s ten member countries represent a diverse and dynamic region with immense potential. The organization has played a pivotal role in promoting regional peace, stability, and prosperity. As ASEAN celebrates over five decades of existence, its role in navigating a complex geopolitical landscape, addressing regional challenges, and seizing new opportunities will be more critical than ever. By fostering cooperation, dialogue, and integration, ASEAN can continue to contribute to a more peaceful, prosperous, and interconnected Southeast Asia.
FAQ
1. What does ASEAN stand for?
ASEAN stands for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
2. When was ASEAN established?
ASEAN was established on August 8, 1967.
3. Where is the ASEAN secretariat located?
The ASEAN Secretariat is located in Jakarta, Indonesia.
4. What is the ASEAN Charter?
The ASEAN Charter, adopted in 2007, provides a legal framework for ASEAN and outlines its goals, principles, and organizational structure.
5. How can I learn more about ASEAN?
You can visit the official ASEAN website or refer to publications from reputable institutions like the ASEAN Secretariat, ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute, and the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS).
Need Support?
Contact us at:
Phone Number: +84 369 020 373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.
Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.
