The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, is a dynamic intergovernmental organization composed of 11 members. Founded in 1967, ASEAN plays a crucial role in fostering political, economic, and socio-cultural cooperation among its member states. This article delves into the unique characteristics, contributions, and aspirations of each member, highlighting the vibrant tapestry that is Southeast Asia.
A Glimpse into the ASEAN Identity: Who are the 11 Members?
The 11 Members Of Asean, diverse in geography, culture, and history, are united by their shared commitment to regional peace, stability, and prosperity. They are:
- Brunei Darussalam
- Cambodia
- Indonesia
- Laos
- Malaysia
- Myanmar
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
From Founding Fathers to New Entrants: A Timeline of ASEAN Expansion
ASEAN’s journey began with five founding members: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Over time, the organization expanded to embrace the diversity of Southeast Asia. Vietnam joined in 1995, followed by Laos and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999. Timor-Leste, though not yet a full member, actively participates in ASEAN forums and initiatives.
The ASEAN Way: Navigating Cooperation and Consensus
ASEAN operates on the principle of consensus-based decision-making, emphasizing dialogue, consultation, and mutual respect. This approach, often referred to as “the ASEAN Way,” allows member states to address challenges and pursue common goals while respecting national sovereignty and sensitivities.
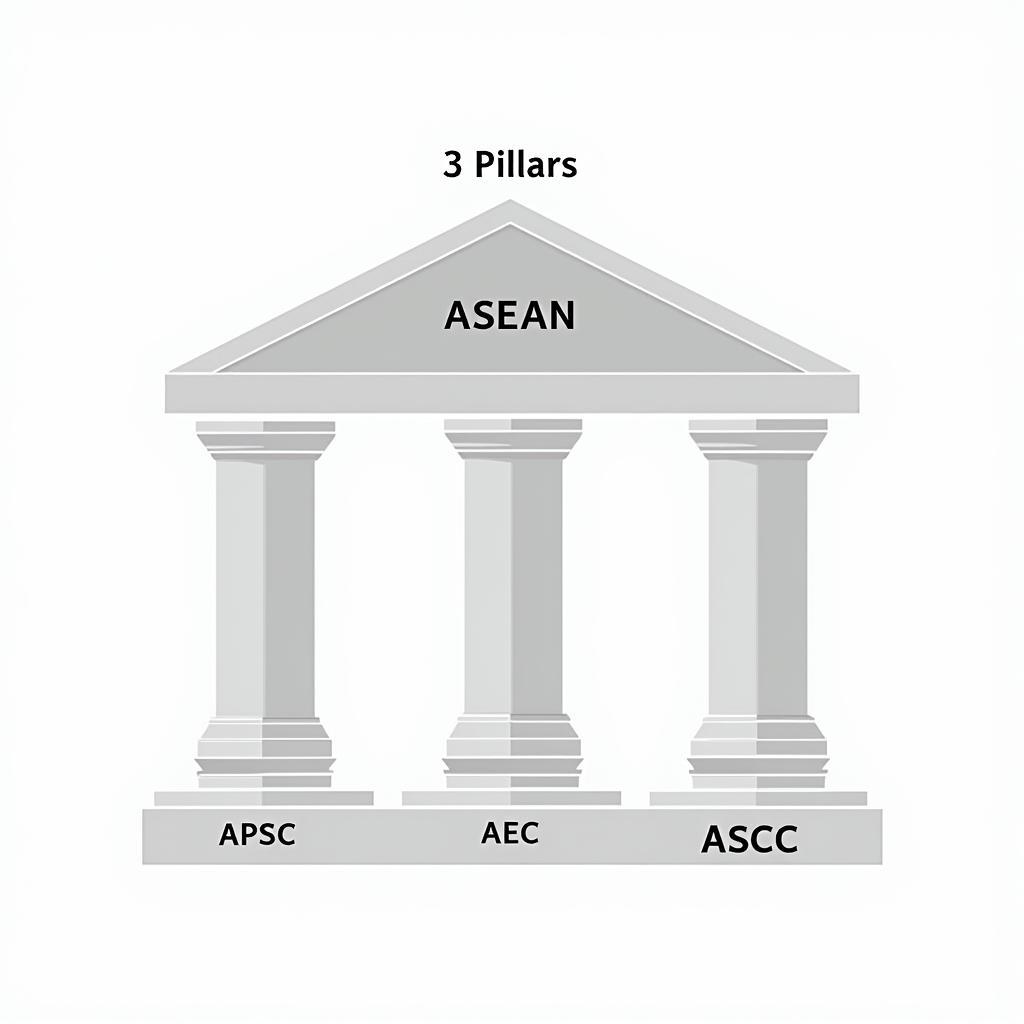
Pillars of Progress: The Three Pillars of the ASEAN Community
To achieve its vision of an integrated, peaceful, and prosperous region, ASEAN focuses on three key pillars:
-
ASEAN Political-Security Community: This pillar aims to promote peace, security, and stability in the region through dialogue, confidence-building measures, and preventive diplomacy.
-
ASEAN Economic Community: This pillar envisions a single market and production base with free flow of goods, services, investment, and skilled labor. It strives to enhance ASEAN’s competitiveness and integrate the region into the global economy.
-
ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community: This pillar seeks to build a people-centered ASEAN that promotes human development, social justice, and cultural understanding. It emphasizes initiatives in education, health, culture, and environmental protection.
ASEAN in the 21st Century: Navigating a Complex World
In an era of globalization, technological advancements, and emerging challenges, ASEAN continues to adapt and evolve. The organization is actively engaged in addressing issues such as climate change, cybersecurity, and transnational crime. ASEAN also plays a vital role in promoting regional connectivity through initiatives like the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity 2025.
11 Nations, One Vision: The Future of ASEAN
The 11 members of ASEAN, despite their differences, share a common destiny. By working together, they strive to build a more integrated, prosperous, and resilient Southeast Asia. As a dynamic and influential regional bloc, ASEAN is poised to play an even greater role on the global stage, promoting peace, stability, and cooperation in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about the 11 Members of ASEAN
1. What are the official languages of ASEAN?
While ASEAN recognizes the diversity of languages spoken within the region, its official working language is English.
2. What is the significance of the ASEAN flag?
The ASEAN flag, with its blue, red, white, and yellow colors, symbolizes peace, dynamism, purity, and prosperity. The ten stalks of rice represent the unity and solidarity of the member states.
3. Does ASEAN have a common currency?
No, ASEAN does not have a common currency. Each member state retains its own monetary policy and currency.
4. How does ASEAN address human rights issues?
ASEAN established the ASEAN Intergovernmental Commission on Human Rights (AICHR) to promote and protect human rights in the region.
5. What are some of the challenges faced by ASEAN?
ASEAN faces challenges such as territorial disputes, non-traditional security threats, and socioeconomic disparities within and between member states.
Need More Information?
For further insights into the 11 members of ASEAN, explore these related articles:
Contact Us
For any inquiries or assistance, please reach out to our dedicated team at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.
Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.