Ase Embedded Die technology is a cutting-edge packaging technique used in the semiconductor industry to integrate multiple dies (individual semiconductor chips) into a single package. This innovative approach offers several benefits, including reduced size, improved electrical performance, and enhanced design flexibility.
What is ASE Embedded Die Technology?
Unlike traditional packaging methods where dies are placed next to each other, ASE embedded die technology embeds one or more dies within the substrate or interposer layer of the package. This arrangement minimizes the distance between components, reducing signal path lengths and parasitic capacitance. As a result, embedded die technology enables faster data transfer rates, lower power consumption, and improved overall performance.
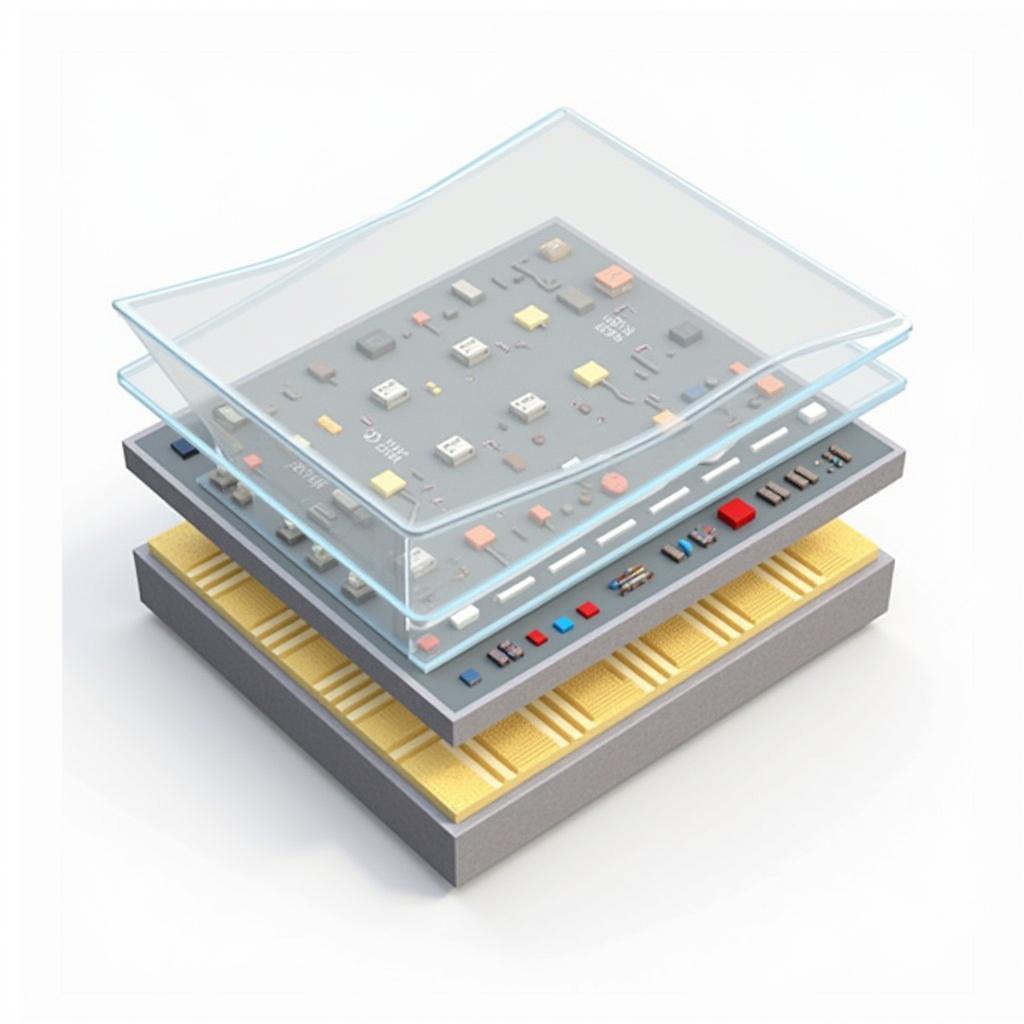 ASE Embedded Die Packaging
ASE Embedded Die Packaging
Advantages of ASE Embedded Die Technology
The adoption of ASE embedded die technology offers numerous advantages for various applications:
-
Increased Design Flexibility: Designers can combine multiple dies with different functionalities, such as processors, memory, and wireless communication modules, into a compact package. This flexibility enables the development of highly integrated and feature-rich electronic devices.
-
Enhanced Performance: The reduced interconnect lengths minimize signal propagation delays and crosstalk, leading to faster data transfer speeds, lower power consumption, and improved signal integrity.
-
Smaller Form Factor: Embedding dies within the package substrate allows for a significant reduction in overall package size compared to conventional side-by-side die placement. This miniaturization is crucial for space-constrained applications like mobile devices and wearables.
-
Improved Thermal Management: The close proximity of dies to the substrate or interposer facilitates efficient heat dissipation, improving thermal management and ensuring optimal operating temperatures for enhanced device reliability.
Applications of ASE Embedded Die Technology
ASE embedded die technology finds applications in a wide range of electronic devices and systems:
-
Smartphones and Tablets: Embedded die packaging enables the integration of high-performance processors, memory, and other components into compact mobile devices, resulting in thinner and lighter designs with extended battery life.
-
Networking and Data Centers: High-speed networking equipment and data center servers benefit from the enhanced signal integrity and reduced latency offered by embedded die technology, enabling faster data processing and transmission rates.
-
Automotive Electronics: Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and other automotive electronics require high levels of integration and reliability. ASE embedded die technology provides a robust solution for integrating multiple sensors, processors, and control units within a single package.
 Applications of ASE Embedded Die Technology
Applications of ASE Embedded Die Technology
Challenges and Future Trends
While ASE embedded die technology offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges:
-
Manufacturing Complexity: The process of embedding dies within the substrate requires advanced manufacturing techniques and precise alignment, which can be complex and costly.
-
Thermal Management: Efficient heat dissipation remains a critical consideration, particularly as the number of embedded dies increases and power densities rise.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts focus on addressing these limitations and further advancing embedded die technology:
-
2.5D and 3D Packaging: Extending embedded die concepts to 2.5D and 3D packaging architectures enables even higher levels of integration and performance.
-
Advanced Materials: Research into new substrate and interposer materials with improved electrical and thermal properties will further enhance the capabilities of embedded die technology.
Conclusion
ASE embedded die technology is a game-changer in the semiconductor industry, enabling the development of smaller, faster, and more power-efficient electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, we can expect wider adoption of embedded die solutions across various industries, driving innovation and shaping the future of electronics.