The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia. However, the phrase “Asean 11 Countries” often pops up, causing some confusion. This article will explore the current 10 members of ASEAN, delve into the potential 11th member, and examine the bloc’s impact on the region and the world.
Understanding ASEAN Membership
Founded in 1967, ASEAN comprises 10 member states: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. These nations share a common goal of promoting peace, stability, and economic growth in the region.
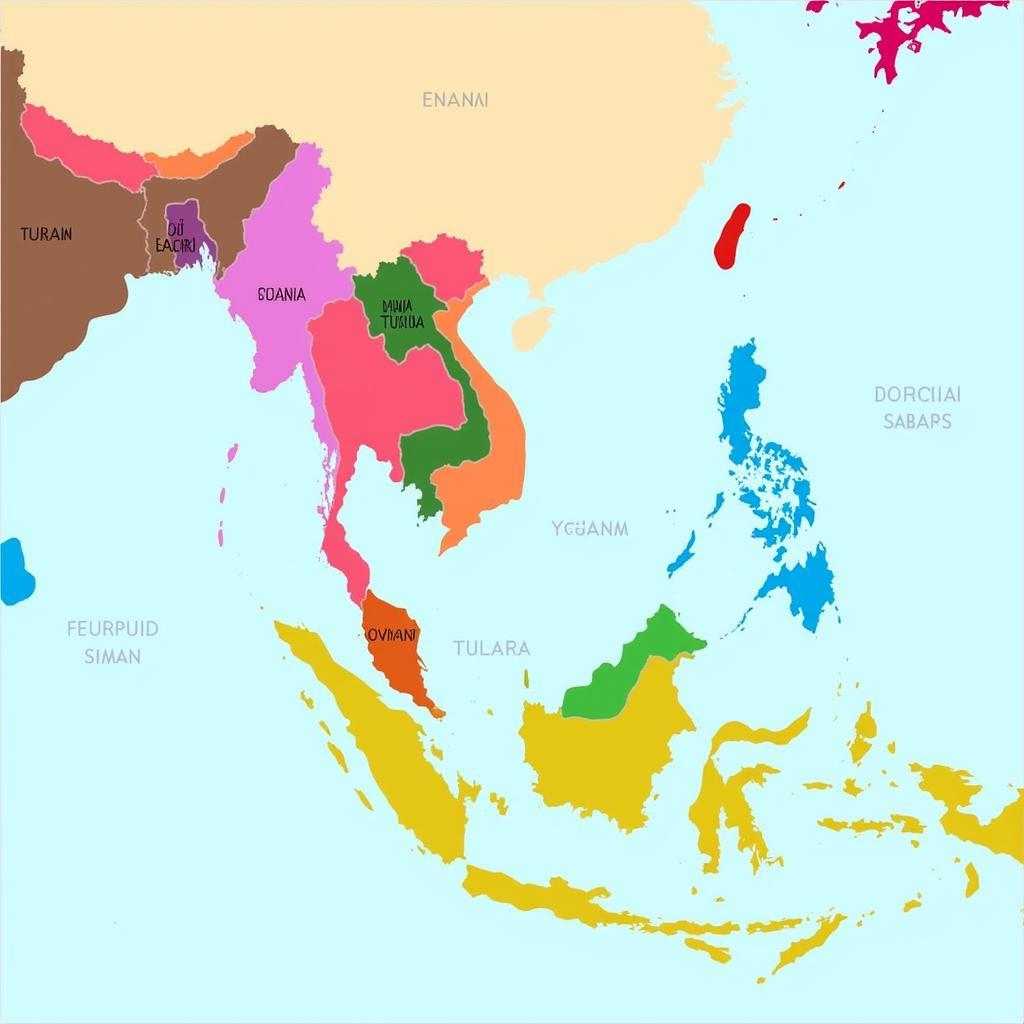 Map of ASEAN Countries
Map of ASEAN Countries
The concept of “ASEAN 11 countries” stems from the potential inclusion of Timor-Leste (East Timor). Having gained independence in 2002, Timor-Leste applied for ASEAN membership in 2011 and has been actively engaged in the accession process.
Timor-Leste: The Potential 11th Member
Timor-Leste’s inclusion in ASEAN holds significant geopolitical and economic implications. Located on the island of Timor, it bridges Southeast Asia and the Pacific, offering strategic importance. Its youthful population and largely untapped natural resources make it a potential economic powerhouse.
While Timor-Leste’s accession is widely anticipated, it faces several challenges. These include strengthening its economy, improving infrastructure, and meeting ASEAN’s political and security criteria.
 Timor-Leste Flag Waving
Timor-Leste Flag Waving
“Timor-Leste’s inclusion will not only strengthen ASEAN’s geopolitical footprint but also provide a much-needed boost to the country’s own development trajectory,” says Dr. Maya Kian, a Southeast Asian political analyst.
ASEAN’s Impact and Influence
Despite consisting of diverse cultures, languages, and political systems, ASEAN has made remarkable strides in fostering regional integration. The bloc has played a crucial role in:
- Promoting peace and stability: ASEAN has established mechanisms for dialogue and cooperation, helping to prevent conflicts and maintain regional stability.
- Boosting economic growth: The ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) has facilitated trade and investment, turning the region into a global economic powerhouse.
- Enhancing social and cultural exchange: ASEAN promotes people-to-people contact through educational programs, cultural exchanges, and tourism initiatives.
ASEAN in a Globalized World
As a key player in the Asia-Pacific region, ASEAN plays an active role in shaping the global landscape. The bloc has forged strategic partnerships with major powers like China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union.
ASEAN’s growing influence is evident in its initiatives like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the world’s largest free trade agreement.
Conclusion
While ASEAN currently comprises 10 member states, the potential addition of Timor-Leste as the 11th member underlines the bloc’s dynamism and continued evolution. ASEAN’s commitment to regional integration, economic growth, and peaceful cooperation has positioned it as a vital force in the global arena. As ASEAN continues to grow and evolve, it will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in shaping the future of Southeast Asia and beyond.
FAQs
1. What does ASEAN stand for?
ASEAN stands for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
2. How many countries are currently in ASEAN?
There are currently 10 member states in ASEAN.
3. Why is Timor-Leste considered a potential 11th member?
Timor-Leste has officially applied for ASEAN membership and is undergoing the accession process.
4. What are the main goals of ASEAN?
ASEAN aims to promote peace, stability, and economic growth in Southeast Asia.
5. How does ASEAN impact the global economy?
ASEAN’s economic integration and trade agreements, like AFTA and RCEP, have made it a significant player in the global market.
For support, contact us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
We have a 24/7 customer support team.