ASE noise, or Amplified Spontaneous Emission noise, is an inherent factor in optical amplification systems that utilize Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs). While EDFAs are crucial for long-haul optical communication, effectively managing ASE noise is paramount for achieving optimal system performance. This article delves into the intricacies of ASE noise, its impact on EDFA systems, and strategies for mitigation.
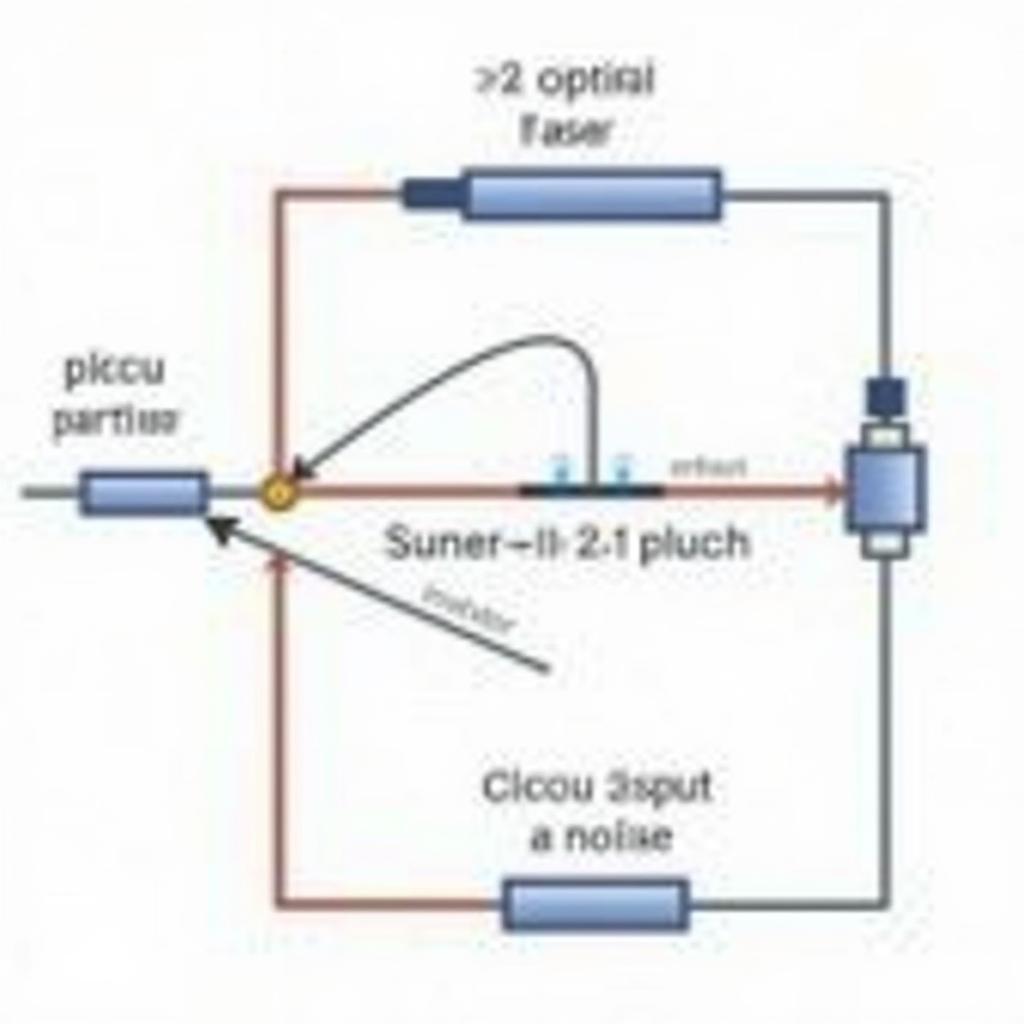 EDFA System Schematic
EDFA System Schematic
What is ASE Noise in EDFA?
At the heart of an EDFA lies an optical fiber doped with erbium ions. When these ions absorb energy from a pump laser, they transition to an excited state. Upon returning to their ground state, the erbium ions emit photons, amplifying the optical signal passing through the fiber. However, this process isn’t perfectly efficient. Some excited erbium ions spontaneously emit photons in random directions and at random wavelengths, even without an incoming signal photon to stimulate the emission. This spontaneous emission, when amplified along with the signal, manifests as ASE noise.
The Impact of ASE Noise on Optical Signals
The random nature of ASE noise adds a broadband background noise to the amplified signal. This noise floor can significantly degrade the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the optical signal, ultimately limiting the system’s performance in several ways:
- Reduced Sensitivity: ASE noise can mask weak optical signals, making it challenging for the receiver to distinguish between the signal and the noise floor. This reduced sensitivity translates to a shorter transmission distance or lower bit rates for a given performance level.
- Increased Bit Error Rate (BER): As ASE noise interferes with the signal, it increases the likelihood of errors in the received data stream. A higher BER implies a greater probability of data corruption, requiring more robust error correction mechanisms and potentially impacting data integrity.
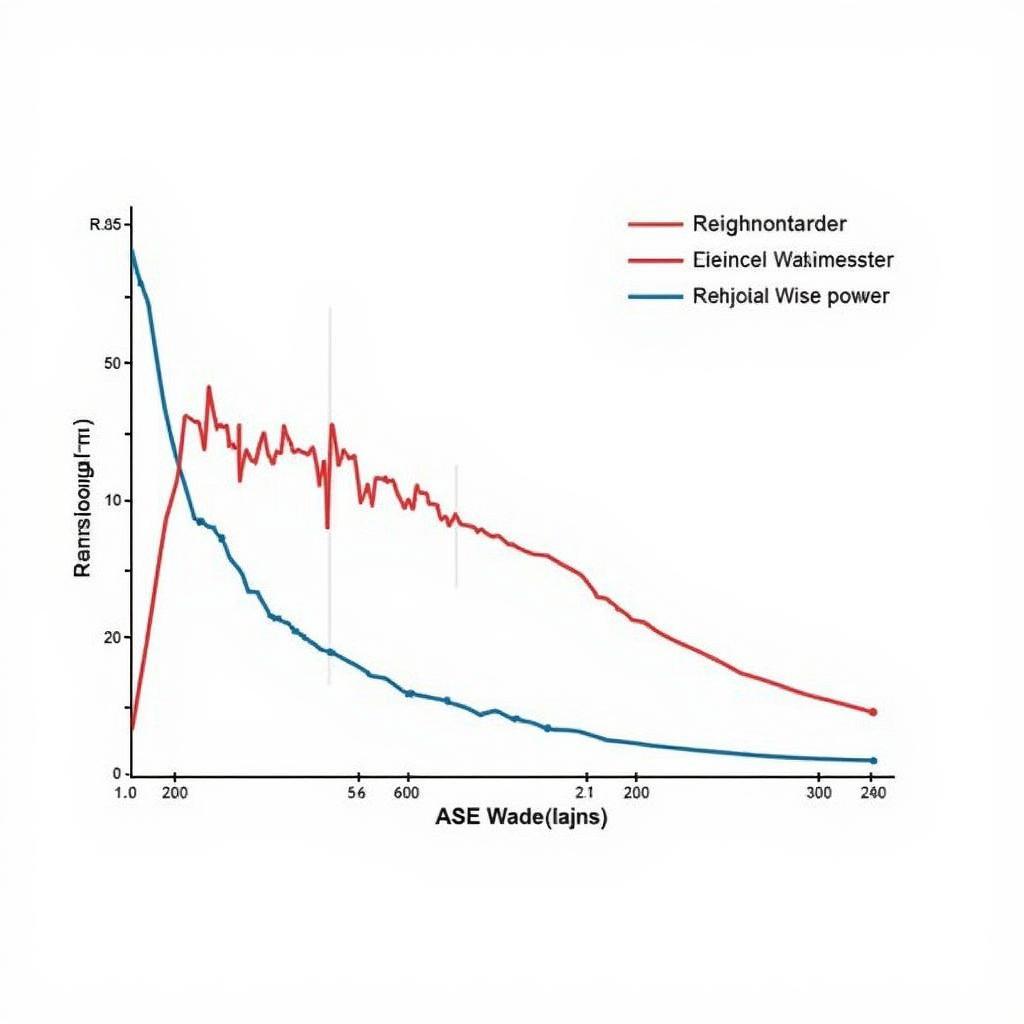 ASE Noise Spectrum
ASE Noise Spectrum
Techniques for Minimizing ASE Noise
Given its detrimental effects on system performance, mitigating ASE noise is crucial in EDFA-based optical systems. Several techniques have been developed to combat ASE noise:
1. Optical Filtering
Since ASE noise has a broader optical spectrum compared to the signal, optical filters can selectively attenuate the noise while allowing the signal to pass through. These filters are typically placed at the output of the EDFA, effectively narrowing the optical bandwidth and improving the SNR.
2. Optimal EDFA Design and Operation
The amount of ASE noise generated is influenced by various EDFA parameters, including fiber length, erbium doping concentration, and pump power. Optimizing these parameters can significantly reduce ASE noise generation. For instance, using shorter fiber lengths and lower pump powers can help lower the overall noise level.
3. Forward Error Correction (FEC)
While not directly addressing the noise source, FEC techniques can enhance the system’s resilience to ASE noise. By adding redundant bits to the data stream, FEC allows the receiver to detect and correct errors caused by noise, improving the overall BER.
FAQs: ASE Noise in EDFA Systems
1. What is the typical wavelength range of ASE noise in EDFA systems?
ASE noise typically spans a range of wavelengths around the signal wavelength, which is typically in the C-band (1530-1565 nm) or L-band (1565-1625 nm) for optical communication systems.
2. How does the gain of the EDFA affect ASE noise?
Higher EDFA gain generally leads to higher ASE noise levels. This is because the amplification process that boosts the signal also amplifies the spontaneous emission, leading to a higher noise floor.
3. Can ASE noise be completely eliminated in EDFA systems?
No, ASE noise is an inherent characteristic of the spontaneous emission process in EDFAs and cannot be entirely eliminated. However, the techniques discussed above can effectively mitigate its impact on system performance.
Need Help with Your EDFA System?
For expert guidance on optimizing your EDFA system, mitigating ASE noise, or addressing other technical challenges, our team of specialists at Asean Media is here to assist you. Contact us at 0369020373 or email us at [email protected]. We’re dedicated to providing you with the technical expertise and support you need, 24/7. You can also visit us at our office located in Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam.
