The ASE transition marks a pivotal shift in the economic landscape of Southeast Asia. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key aspects of this transition, providing insights, challenges, and opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. We will explore the implications across various sectors, the role of technology, and the broader impact on the ASEAN community.
Understanding the ASE Transition
The ASE transition, short for “ASEAN Single Economy,” represents a multifaceted initiative by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to establish a highly integrated and globally competitive economic region. This transition aims to eliminate barriers to trade, enhance regional connectivity, and foster a more conducive environment for investment and economic growth.
Key Pillars of the ASE Transition
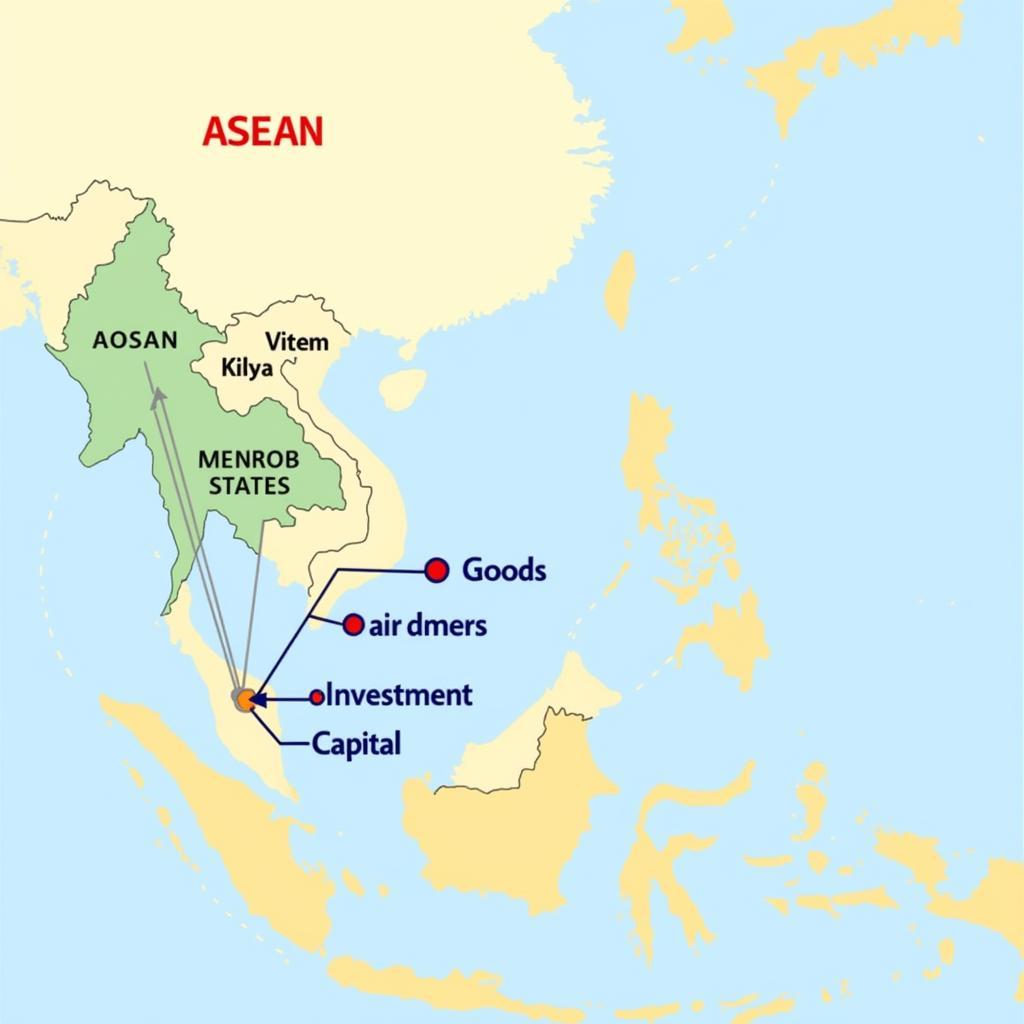
The ASE transition is built upon four key pillars:
- Free flow of goods: ASEAN aims to create a single market and production base by reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers to trade between member states.
- Free flow of services: Facilitating the cross-border movement of professionals and skilled labor within ASEAN to enhance service sector competitiveness.
- Free flow of investment: Creating a more attractive investment climate for both regional and foreign investors by streamlining investment procedures and harmonizing regulations.
- Freer flow of capital: Promoting greater mobility of capital within ASEAN to support economic growth and development across the region.
 ASEAN Economic Integration
ASEAN Economic Integration
Opportunities Arising from the ASE Transition
The ASE transition presents a multitude of opportunities for businesses and individuals in Southeast Asia and beyond:
- Market Expansion: Businesses can tap into a larger consumer base of over 650 million people with rising disposable incomes.
- Lower Production Costs: Access to a wider range of raw materials, lower tariffs, and a more competitive labor market can significantly reduce production costs.
- Increased Investment: The harmonization of regulations and investment procedures makes ASEAN a more attractive destination for foreign direct investment.
- Job Creation: The economic integration and growth driven by the ASE transition are expected to create numerous job opportunities across various sectors.
Challenges in the ASE Transition
While the ASE transition holds immense potential, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Infrastructure Development: Improving infrastructure connectivity, particularly in transportation and logistics, is crucial for seamless trade and economic integration.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Discrepancies in regulations and standards among member states can hinder trade and investment flows.
- Skills Gap: Addressing the skills gap and equipping the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in a more competitive environment is vital.
- SMEs Integration: Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to participate in and benefit from the ASE transition is essential.
Technology’s Role in the ASE Transition
Technology plays a transformative role in accelerating the ASE transition:
- E-commerce: Digital platforms facilitate cross-border trade, connecting businesses and consumers across ASEAN.
- Fintech: Financial technology innovations streamline payment systems and improve access to financial services, particularly for SMEs.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Technology optimizes logistics and supply chain management, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Digital Skills Development: Technology enables access to online learning platforms and resources, bridging the skills gap.
 Technology Driving ASEAN Growth
Technology Driving ASEAN Growth
The Impact of the ASE Transition on ASEAN People
The ASE transition is not just about economic integration; it is also about creating a more inclusive and prosperous ASEAN community:
- Improved Living Standards: Economic growth and job creation are expected to lead to higher incomes and improved living standards for people across ASEAN.
- Access to Opportunities: The free flow of goods, services, investment, and skilled labor creates new opportunities for individuals to work, study, and live in different parts of ASEAN.
- Cultural Exchange: Increased interaction among people from different ASEAN countries fosters cultural exchange and understanding.
Conclusion
The ASE transition represents a defining moment for Southeast Asia. By embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges, ASEAN can unlock its full economic potential and emerge as a global economic powerhouse. This transition will shape the future of the region, bringing about increased prosperity, connectivity, and opportunities for all.
FAQs
1. What is the timeframe for the full implementation of the ASE transition?
ASEAN has set a target of achieving significant progress towards economic integration by 2025. However, the full realization of the ASE is an ongoing process with no fixed deadline.
2. How will the ASE transition benefit consumers?
Consumers will benefit from a wider choice of goods and services at competitive prices due to increased competition and reduced trade barriers.
3. What is ASEAN doing to support SMEs in the ASE transition?
ASEAN has implemented various initiatives to enhance SME competitiveness, including capacity building programs, access to finance, and trade facilitation measures.
Need More Information?
For further assistance and guidance on navigating the ASE transition, please contact our team at:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to address your queries and provide tailored support. You can also visit us at our office located in Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We are committed to empowering you with the knowledge and resources to succeed in the dynamic ASEAN landscape.

