The term “ASEAN 10+6” signifies a significant framework for economic cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region. It refers to the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and six dialogue partners: Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand. This collaboration seeks to deepen economic integration and foster sustainable growth across these sixteen nations.
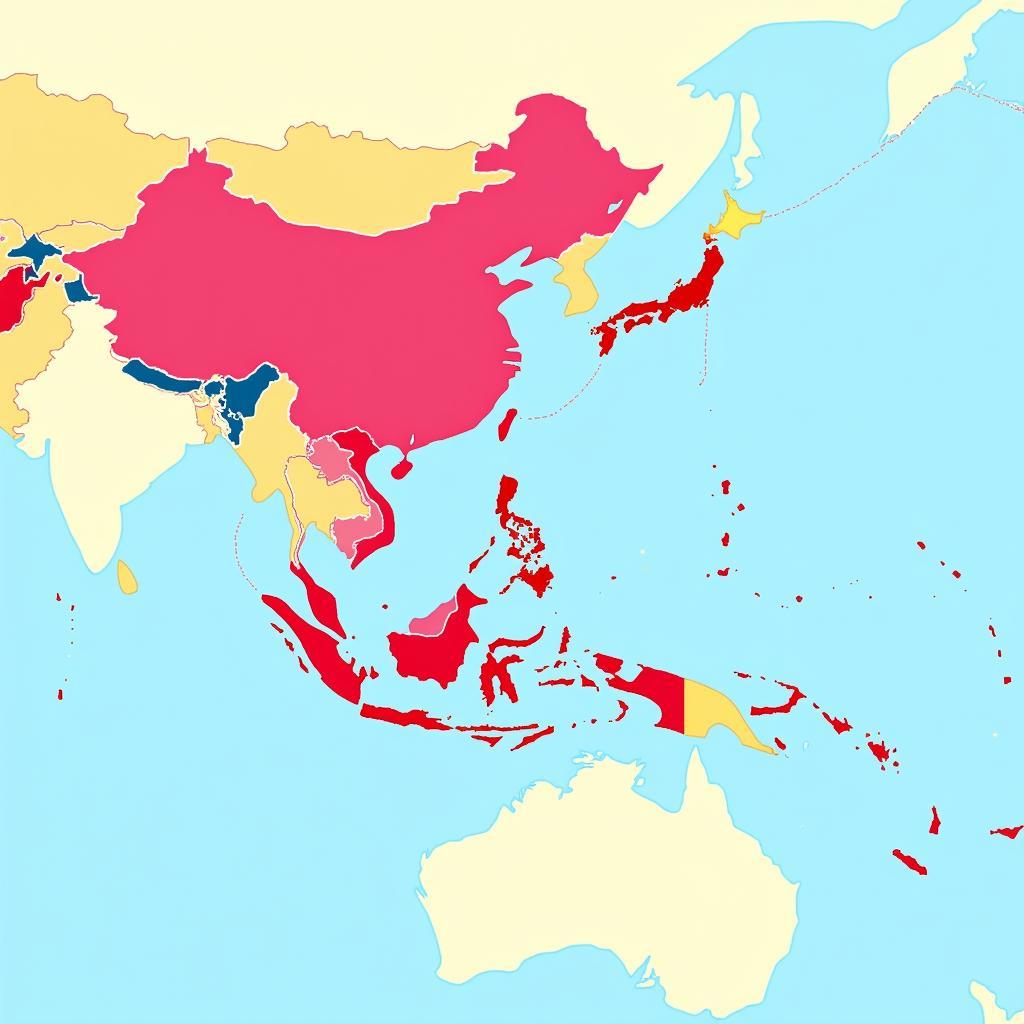 Map of ASEAN 10+6 Countries
Map of ASEAN 10+6 Countries
A Foundation for Regional Integration
The ASEAN 10+6 framework represents a crucial step toward broader regional integration. It builds upon the existing ASEAN Plus Three (APT) mechanism, which includes China, Japan, and South Korea. By incorporating Australia, India, and New Zealand, the 10+6 format encompasses a wider range of economic powerhouses and fosters a more inclusive approach to regional development.
This expanded dialogue partnership aims to tackle common challenges, enhance trade and investment flows, and promote financial stability. The ultimate goal is to establish a vast East Asia Free Trade Area (EAFTA) that would create one of the world’s largest trading blocs.
Key Areas of Cooperation
ASEAN 10+6 collaboration spans a wide array of sectors, with a particular focus on:
- Trade and Investment: The framework seeks to reduce trade barriers, harmonize customs procedures, and promote investment opportunities among member nations. This includes negotiations on the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), a mega-trade agreement that encompasses all 16 countries.
- Financial Cooperation: ASEAN 10+6 promotes financial stability and integration through initiatives like the Chiang Mai Initiative Multilateralisation (CMIM). This regional financial safety net provides financial support during times of economic crisis.
- Food Security: Recognizing the importance of food security for regional stability, the framework encourages cooperation in areas like agricultural research, technology transfer, and disaster management.
- Energy Security: With growing energy demands across Asia, ASEAN 10+6 facilitates dialogue and collaboration on energy efficiency, renewable energy sources, and infrastructure development.
Benefits and Challenges of ASEAN 10+6
The ASEAN 10+6 framework offers significant potential benefits, including:
- Increased Trade and Investment: By reducing trade barriers and promoting investment, the framework can unlock new markets and boost economic growth across the region.
- Enhanced Regional Integration: Collaboration in key areas like finance, food security, and energy strengthens regional ties and promotes a sense of shared purpose.
- Improved Competitiveness: A more integrated regional economy can enhance the global competitiveness of participating countries.
However, challenges remain:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disagreements or conflicts between member states, particularly in areas like territorial disputes, can hinder cooperation.
- Development Gaps: Significant economic disparities between countries may pose challenges in achieving equitable outcomes.
- Implementation Challenges: Translating agreements into concrete action and ensuring effective implementation of initiatives is crucial for success.
Looking Ahead: The Future of ASEAN 10+6
The ASEAN 10+6 framework represents a bold vision for regional economic integration in Asia. While challenges exist, the potential benefits for participating countries are immense. As the global landscape continues to evolve, strengthening cooperation and dialogue within this framework will be crucial for navigating shared challenges and seizing new opportunities for sustainable and inclusive growth.
 Container Ship at a Busy Port
Container Ship at a Busy Port
FAQs about ASEAN 10+6
1. What is the main goal of ASEAN 10+6?
The primary goal is to enhance economic cooperation and integration between the ten ASEAN member states and six dialogue partners: Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand.
2. How does ASEAN 10+6 differ from ASEAN Plus Three (APT)?
ASEAN 10+6 expands upon APT by including Australia, India, and New Zealand. This creates a broader platform for dialogue and cooperation.
3. What are some of the key areas of focus for ASEAN 10+6?
Key areas include trade and investment, financial cooperation, food security, and energy security.
4. What are some of the potential benefits of ASEAN 10+6?
Benefits include increased trade and investment, enhanced regional integration, and improved global competitiveness for participating countries.
5. What are some of the challenges facing ASEAN 10+6?
Challenges include geopolitical tensions between member states, development gaps, and the need for effective implementation of agreements.
For further information on ASEAN 10+6 and related topics, you can explore the following resources on our website:
- 2010-2016 asea scrap imports table
- asean 10 plus 6
- 10.1002 ase.1697
- ase l3 statistics
- 2010-2016 stats on asea scrap imports table
Need support? Contact us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our customer service team is available 24/7.