Ase 350 is a widely used technique for extracting analytes from solid and semi-solid samples. This method is faster, more efficient, and uses less solvent compared to traditional extraction methods. Let’s explore the ins and outs of ASE 350, its applications, advantages, and how it compares to other extraction techniques.
What is ASE 350 Accelerated Solvent Extraction?
ASE 350 Accelerated Solvent Extraction is a technique that uses high temperature and pressure to extract analytes from a variety of matrices. The process involves loading a sample into an extraction cell, which is then pressurized and heated with a solvent. The elevated temperature and pressure increase the efficiency of the extraction, resulting in faster extraction times and higher analyte recoveries.
The “350” in ASE 350 refers to the maximum sample capacity of the instrument, which is 350 mL. This makes it suitable for a wide range of sample sizes, from milligrams to grams.
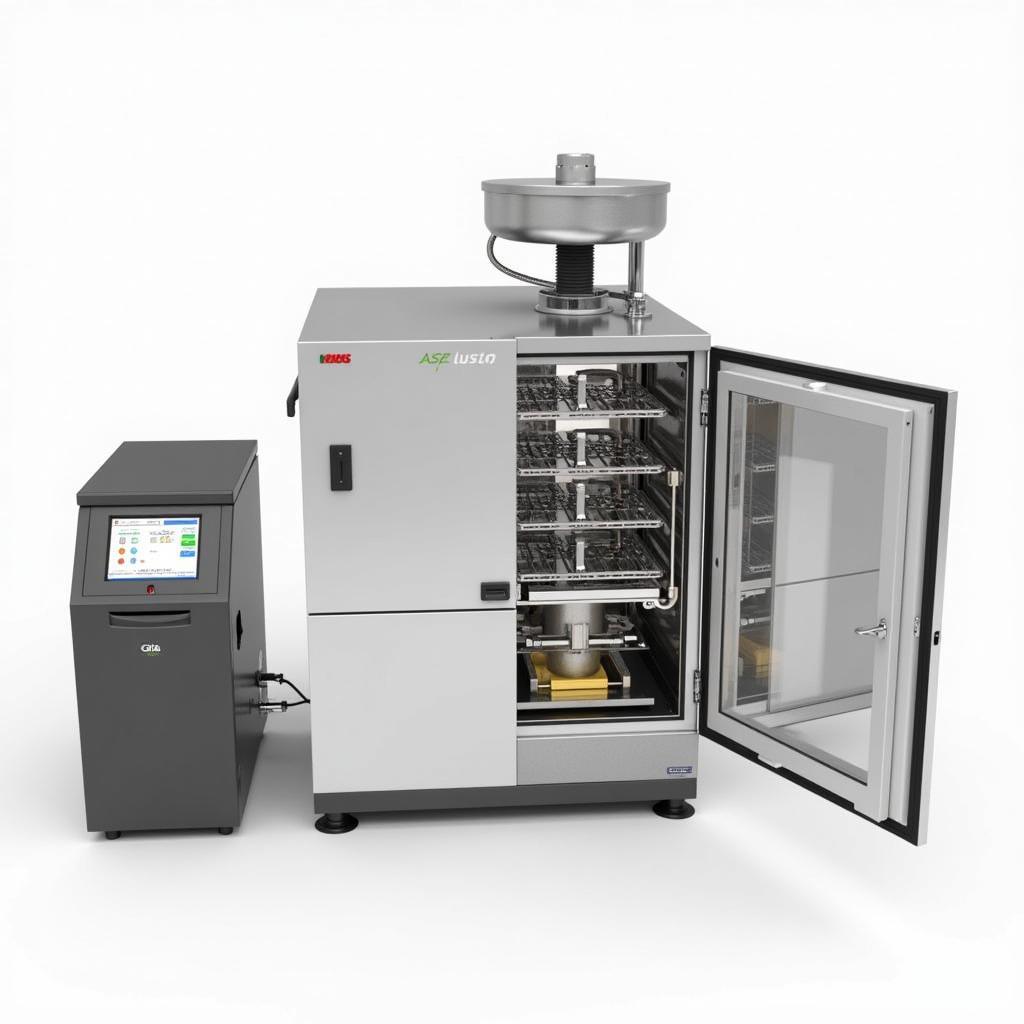 ASE 350 System
ASE 350 System
How Does ASE 350 Work?
The ASE 350 extraction process typically involves the following steps:
- Sample Preparation: The sample is ground, weighed, and loaded into an extraction cell.
- Solvent Addition: The chosen solvent is added to the extraction cell containing the sample.
- Heating and Pressurization: The extraction cell is heated to a specific temperature (typically between 50-200°C) and pressurized (typically 100-200 bar).
- Extraction: The solvent, under high temperature and pressure, penetrates the sample matrix and dissolves the target analytes.
- Flushing: After a set extraction time, the cell is flushed with fresh solvent to remove any remaining analytes.
- Collection: The extract is collected in a vial for further analysis.
Advantages of Using ASE 350
ASE 350 offers several advantages over traditional extraction methods:
- Faster Extraction Times: ASE 350 significantly reduces extraction times from hours to minutes, increasing lab productivity.
- Reduced Solvent Consumption: ASE 350 utilizes significantly less solvent compared to traditional methods, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
- Higher Extraction Efficiency: The use of elevated temperature and pressure leads to higher analyte recoveries and improved reproducibility.
- Automation: ASE 350 systems are typically automated, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing human error.
Applications of ASE 350 Extraction
ASE 350 is a versatile technique with numerous applications across various fields:
- Environmental Analysis: Extracting pollutants from soil, sediment, and water samples.
- Food Science: Analyzing pesticide residues, contaminants, and additives in food products.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Extracting active ingredients from plant materials and analyzing drug formulations.
- Polymer and Material Science: Extracting additives, plasticizers, and other compounds from polymers and composite materials.
ASE 350 vs. Other Extraction Techniques
Compared to other extraction techniques like Soxhlet extraction and sonication, ASE 350 offers several advantages:
- Speed: ASE 350 is considerably faster than Soxhlet extraction, which can take several hours or even days.
- Solvent Consumption: ASE 350 uses significantly less solvent than Soxhlet extraction, making it more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Automation: ASE 350 is more amenable to automation than sonication, leading to better reproducibility and reduced labor costs.
Choosing the Right ASE 350 System
When choosing an ASE 350 system, consider the following factors:
- Sample Capacity: Determine the maximum sample size you’ll be working with.
- Number of Samples: Consider the number of samples you need to process per day.
- Solvent Compatibility: Ensure the system is compatible with the solvents required for your applications.
- Automation Features: Look for features that enhance automation and data analysis capabilities.
Conclusion
ASE 350 is a powerful and efficient extraction technique revolutionizing various industries. Its speed, efficiency, and environmental friendliness make it a preferred choice for extracting analytes from diverse matrices. If you’re looking for an extraction technique that offers high throughput, reduced solvent consumption, and improved analyte recovery, ASE 350 is a valuable tool to consider.
FAQs
1. What types of solvents can be used with ASE 350?
ASE 350 is compatible with a wide range of organic solvents, including but not limited to, hexane, acetone, dichloromethane, and methanol. The choice of solvent depends on the analyte’s polarity and the sample matrix.
2. What is the typical temperature and pressure range used in ASE 350?
The temperature and pressure used in ASE 350 vary depending on the analyte and matrix properties. However, typical temperature ranges are between 50-200°C, and pressure ranges are between 100-200 bar.
3. Can ASE 350 be used for quantitative analysis?
Yes, ASE 350 can be used for quantitative analysis. Proper method validation is essential to ensure accurate and precise results.
4. What are some common maintenance requirements for an ASE 350 system?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the extraction cells, replacing seals and filters, and checking the pressure system.
5. Are there any safety concerns associated with ASE 350?
As with any laboratory equipment, safety precautions should be taken when operating an ASE 350 system. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Need more information about ASE 350 extraction cells, prices, or the technique itself? Explore our other articles:
- ASE 350 extraction cells
- Accelerated solvent extraction ASE 350
- ASE 350 accelerated solvent extraction
- ASE 350 extractor
- ASE 350 price
Have other questions or need expert advice?
Contact us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.