Southeast Asia, a region brimming with cultural dynamism and economic potential, is home to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). This diverse coalition of 10 countries boasts a unique blend of natural resources, skilled labor forces, and strategic geographical locations. But what are the specific resources that give each ASEAN member state its competitive edge? Let’s delve into the treasure trove of advantages that each nation brings to the table.
Brunei: An Abode of Energy Riches
Brunei, a small but affluent nation on the island of Borneo, enjoys a wealth of oil and natural gas reserves. These energy resources have been the cornerstone of Brunei’s economy, propelling it to become one of the highest per capita income nations globally.
Cambodia: Where Ancient History Meets Fertile Lands
Cambodia, renowned for its magnificent temples of Angkor, possesses fertile land ideal for agriculture. Rice, the country’s staple crop, thrives in these fertile plains. In recent years, Cambodia has also emerged as a key player in the garment industry, leveraging its competitive labor costs.
Indonesia: The Archipelago of Opportunities
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago, boasts a diverse range of resources. From vast deposits of coal, nickel, and tin to fertile volcanic soil perfect for palm oil and coffee production, the archipelago is a treasure trove of natural wealth. Indonesia’s burgeoning digital economy and young, dynamic population further add to its competitive edge.
Laos: Harnessing the Power of Water and Minerals
Laos, a landlocked nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, is rich in hydropower potential. The Mekong River, flowing through its heart, provides ample opportunities for hydroelectric power generation. Laos is also endowed with mineral resources like gold and copper, attracting significant foreign investment in its mining sector.
Malaysia: A Hub for Manufacturing and Technology
Malaysia has successfully transitioned from an agricultural economy to a manufacturing powerhouse. Its electronics, automotive, and palm oil industries are globally recognized. Malaysia’s strategic location along major shipping routes and its investment in high-tech industries solidify its position as a key player in the region.
Myanmar: Untapped Potential Waiting to be Unleashed
Myanmar, also known as Burma, possesses significant untapped natural resources. From vast reserves of natural gas and precious stones like jade and rubies to fertile land suitable for agriculture, the nation holds immense economic potential. However, political and economic reforms are crucial to unlock this potential and attract foreign investment.
Philippines: A Service Sector Powerhouse with Natural Bounty
The Philippines stands out for its strong service sector, particularly in business process outsourcing (BPO) and IT. English proficiency, a young and talented workforce, and competitive labor costs have made it a global BPO hub. Alongside its service industry strength, the Philippines is blessed with abundant marine resources and mineral deposits.
Singapore: A Global Financial and Innovation Hub
Singapore, despite its small size and lack of natural resources, has emerged as a global economic powerhouse. Its strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and highly skilled workforce have transformed it into a global financial, trade, and innovation hub. Singapore’s commitment to research and development and its pro-business environment continue to attract global businesses and talent.
Thailand: The Land of Smiles and Industrial Prowess
Thailand, known for its warm hospitality and vibrant culture, is a manufacturing hub for automobiles, electronics, and food processing. Its tourism industry, renowned for its beautiful beaches, ancient temples, and delicious cuisine, is a significant contributor to the economy. Thailand’s fertile central plains make it a leading exporter of rice and agricultural products.
Vietnam: A Rising Star in Manufacturing and Export
Vietnam has emerged as a major manufacturing and export hub in recent years. Its low labor costs, strategic location, and government incentives have attracted significant foreign investment. Vietnam is a leading exporter of textiles, footwear, and electronics. The nation’s long coastline and fertile Mekong Delta also contribute to its agricultural prowess.
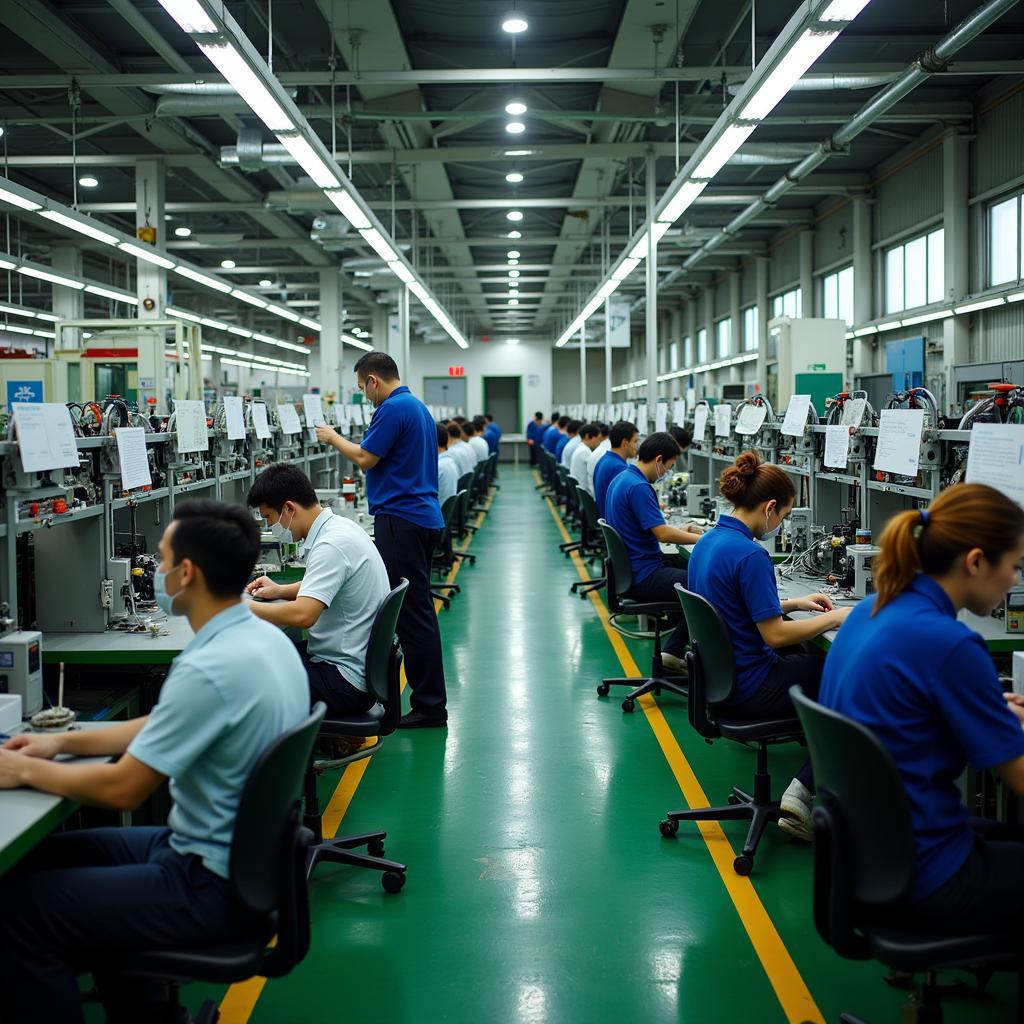 Thriving Manufacturing Sector in Vietnam
Thriving Manufacturing Sector in Vietnam
Conclusion: ASEAN’s Collective Strength
Each ASEAN member state possesses unique resources and competitive advantages, contributing to the region’s dynamic economic landscape. As ASEAN nations continue to integrate their economies, cooperate on infrastructure development, and invest in education and technology, the region is poised for continued growth and prosperity. ASEAN’s diverse strengths, working in harmony, make it a formidable force in the global economy.
FAQs:
- What is the most abundant resource in ASEAN?
Southeast Asia is rich in a variety of resources, including oil and natural gas, fertile land for agriculture, and a young and dynamic workforce. - Which ASEAN country is the richest?
Brunei, with its significant oil and gas reserves, boasts the highest per capita income in ASEAN. - What is the main export of most ASEAN countries?
ASEAN countries export a diverse range of products, including electronics, textiles, agricultural goods, and natural resources.
Need More Information on ASEAN’s Resources?
Contact us! Our team at Asean Media is here to help.
Phone: +84 369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
We are available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide insights into Southeast Asia’s dynamic business landscape.