Asean Artinya, in Indonesian, translates to “ASEAN means.” This seemingly simple phrase opens the door to understanding a complex and dynamic organization – the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. ASEAN plays a crucial role in fostering political, economic, and socio-cultural cooperation amongst its ten member states. From promoting peace and stability to driving economic growth and preserving cultural heritage, ASEAN’s impact on Southeast Asia and the global stage is undeniable.
What Does ASEAN Artinya Really Signify?
Beyond a literal translation, understanding ASEAN artinya requires delving into the organization’s core principles and objectives. It signifies a commitment to regional solidarity, a shared vision for prosperity, and a platform for dialogue and collaboration. ASEAN artinya embodies the spirit of unity in diversity, recognizing the unique identities of each member state while striving for collective progress.
The Pillars of ASEAN Artinya: Exploring the Three Community Pillars
The true meaning of ASEAN artinya is best understood through its three pillars: the Political-Security Community, the Economic Community, and the Socio-Cultural Community. These pillars represent the interconnected and multifaceted nature of ASEAN’s work.
-
Political-Security Community: This pillar focuses on maintaining peace and stability within the region. It promotes conflict resolution, diplomacy, and cooperation on security challenges.
-
Economic Community: This pillar aims to create a single market and production base, facilitating the free flow of goods, services, investment, and skilled labor.
-
Socio-Cultural Community: This pillar emphasizes the importance of cultural exchange, education, and social development to foster a sense of shared identity and regional belonging.
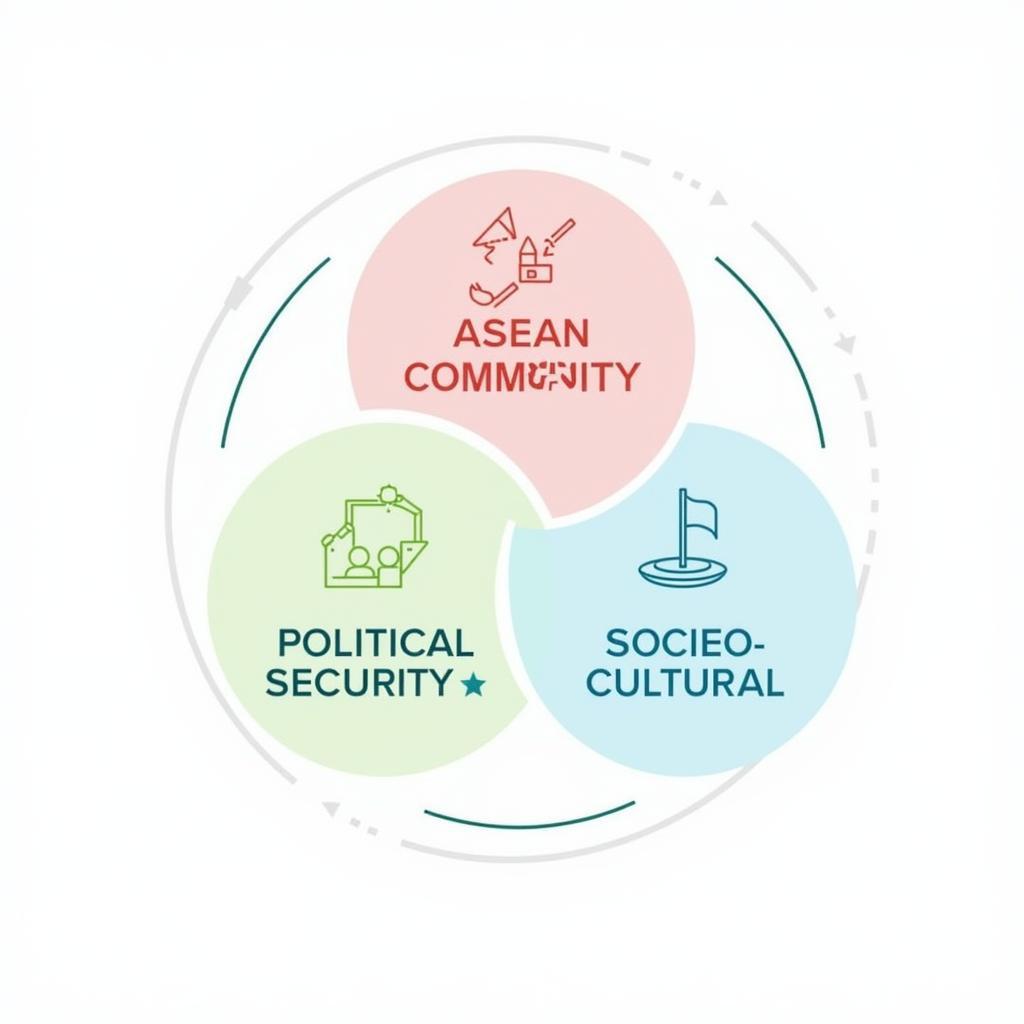 ASEAN Community Pillars: Political-Security, Economic, and Socio-Cultural
ASEAN Community Pillars: Political-Security, Economic, and Socio-Cultural
ASEAN Artinya in Action: Real-World Examples
Understanding ASEAN artinya is not just about theory; it’s about witnessing its impact on the lives of people across Southeast Asia. From disaster relief efforts to educational exchange programs and the simplification of visa procedures for ASEAN citizens, the organization’s work translates into tangible benefits for the region.
ASEAN’s Role in Regional Development
ASEAN has been instrumental in promoting economic development within its member states. Through initiatives like the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), the organization has reduced trade barriers and fostered greater economic integration.
-
Free Trade Agreements: ASEAN has actively pursued free trade agreements with other countries, expanding market access for its member states.
-
Infrastructure Development: ASEAN supports infrastructure projects that connect the region, facilitating trade and transportation.
-
Skills Development: ASEAN promotes skills development and education to prepare its workforce for the challenges and opportunities of a globalized economy.
ASEAN Artinya and the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
While ASEAN has achieved significant progress, it also faces challenges such as navigating geopolitical complexities, addressing economic disparities, and ensuring environmental sustainability. The future of ASEAN hinges on its ability to adapt to a changing global landscape and effectively address these issues.
Navigating a Complex World: ASEAN’s Role in Global Affairs
ASEAN’s growing influence extends beyond the region, playing an increasingly important role in international forums. The organization’s commitment to multilateralism and dialogue makes it a valuable partner in addressing global challenges.
-
Promoting Dialogue: ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation between major powers, promoting peace and stability in the region and beyond.
-
Addressing Global Issues: ASEAN engages in discussions and initiatives related to climate change, cybersecurity, and other global concerns.
“ASEAN’s strength lies in its ability to bring diverse nations together to address common challenges. It’s a model for regional cooperation that can inspire other parts of the world,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Southeast Asian Studies.
 ASEAN Future Outlook: Global Partnerships and Regional Cooperation
ASEAN Future Outlook: Global Partnerships and Regional Cooperation
Conclusion
ASEAN artinya, therefore, encompasses more than just a translation; it represents a vision for a united, prosperous, and peaceful Southeast Asia. Understanding its meaning requires looking beyond the acronym and appreciating the complex interplay of factors that shape this dynamic organization. From its three community pillars to its impact on regional development and its role in global affairs, ASEAN continues to strive for a better future for its people and the world.
FAQ
- What are the 10 member states of ASEAN?
- When was ASEAN established?
- What is the ASEAN Charter?
- How does ASEAN promote economic cooperation?
- What is ASEAN’s role in maintaining regional security?
- How can I learn more about ASEAN initiatives?
- What are the future challenges facing ASEAN?
For further information or assistance, please contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer service team available to assist you. You may also be interested in exploring other articles related to ASEAN’s history, economy, and culture on our website.
“ASEAN’s future depends on the continued commitment of its member states to work together and address the challenges that lie ahead. The organization’s success will be measured by its ability to improve the lives of its citizens and contribute to a more peaceful and prosperous world,” adds Dr. Sharma.
“ASEAN’s cultural richness and diversity are truly remarkable. The organization provides a platform for celebrating these unique traditions while fostering a sense of shared identity among its people,” shares Mr. Kenji Tanaka, Cultural Attache at the Embassy of Japan in Indonesia.