Diastolic dysfunction, often referred to as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), is a complex condition affecting the heart’s ability to relax and fill with blood. The Ase Diastolic Dysfunction Algorithm, developed by the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE), provides a structured approach to diagnosing and classifying this often-misunderstood form of heart failure. This article will delve into the intricacies of the ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm, exploring its components, application, and significance in managing heart health.
Decoding the ASE Diastolic Dysfunction Algorithm: A Step-by-Step Guide
The ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm utilizes a combination of echocardiographic parameters to assess diastolic function. This involves evaluating various measurements, including the E/A ratio, E/e’ ratio, and left atrial volume index (LAVI). These measurements help clinicians determine the severity and type of diastolic dysfunction. Understanding these parameters is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Key Parameters and Their Significance in the Algorithm
- E/A Ratio: This ratio compares the early (E) and late (A) diastolic mitral inflow velocities, reflecting the relative contributions of active relaxation and atrial contraction to ventricular filling. Changes in this ratio can indicate impaired relaxation.
- E/e’ Ratio: This ratio, derived from the mitral inflow E velocity and the early diastolic mitral annular velocity (e’), provides an estimate of left ventricular filling pressure. Elevated E/e’ suggests increased filling pressures, a hallmark of diastolic dysfunction.
- Left Atrial Volume Index (LAVI): An enlarged left atrium can be a consequence of chronic elevated filling pressures. LAVI helps assess the degree of left atrial remodeling and provides further evidence of diastolic dysfunction.
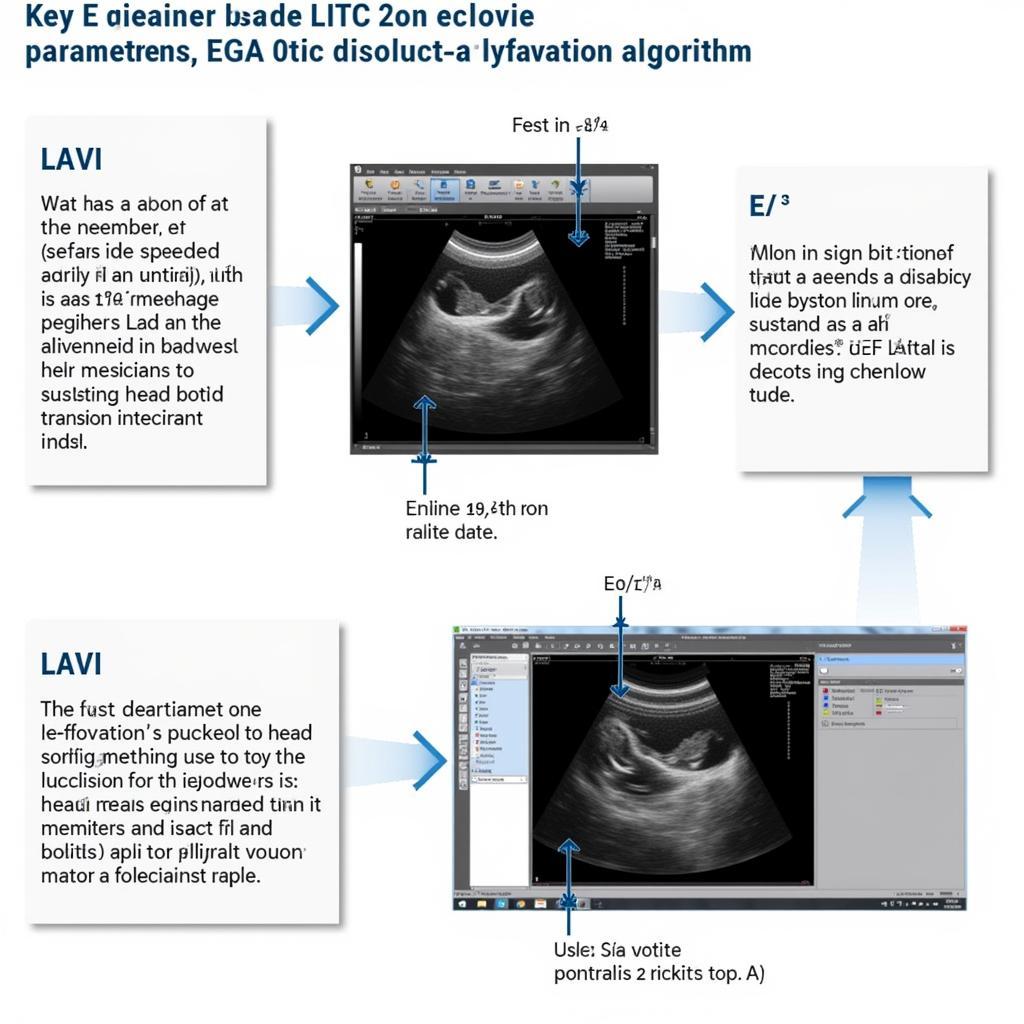 ASE Diastolic Dysfunction Algorithm: Key Parameters
ASE Diastolic Dysfunction Algorithm: Key Parameters
Applying the ASE Diastolic Dysfunction Algorithm in Clinical Practice
The ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm utilizes a stepwise approach, integrating the aforementioned parameters to classify diastolic function into grades: normal, grade 1 (impaired relaxation), grade 2 (pseudonormal), and grade 3 (restrictive). This graded classification helps clinicians tailor treatment strategies based on the severity of dysfunction. 2016 diastolic dysfunction ase provides more in-depth information.
Understanding the Implications of Diastolic Dysfunction
Diastolic dysfunction can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and exercise intolerance. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to prevent disease progression and improve patient outcomes.
The Role of Echocardiography in Diagnosing Diastolic Dysfunction
Echocardiography plays a pivotal role in evaluating diastolic function. It provides a non-invasive method to assess cardiac structure and function, enabling clinicians to visualize the heart chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns. This information is crucial for applying the ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm and arriving at an accurate diagnosis.
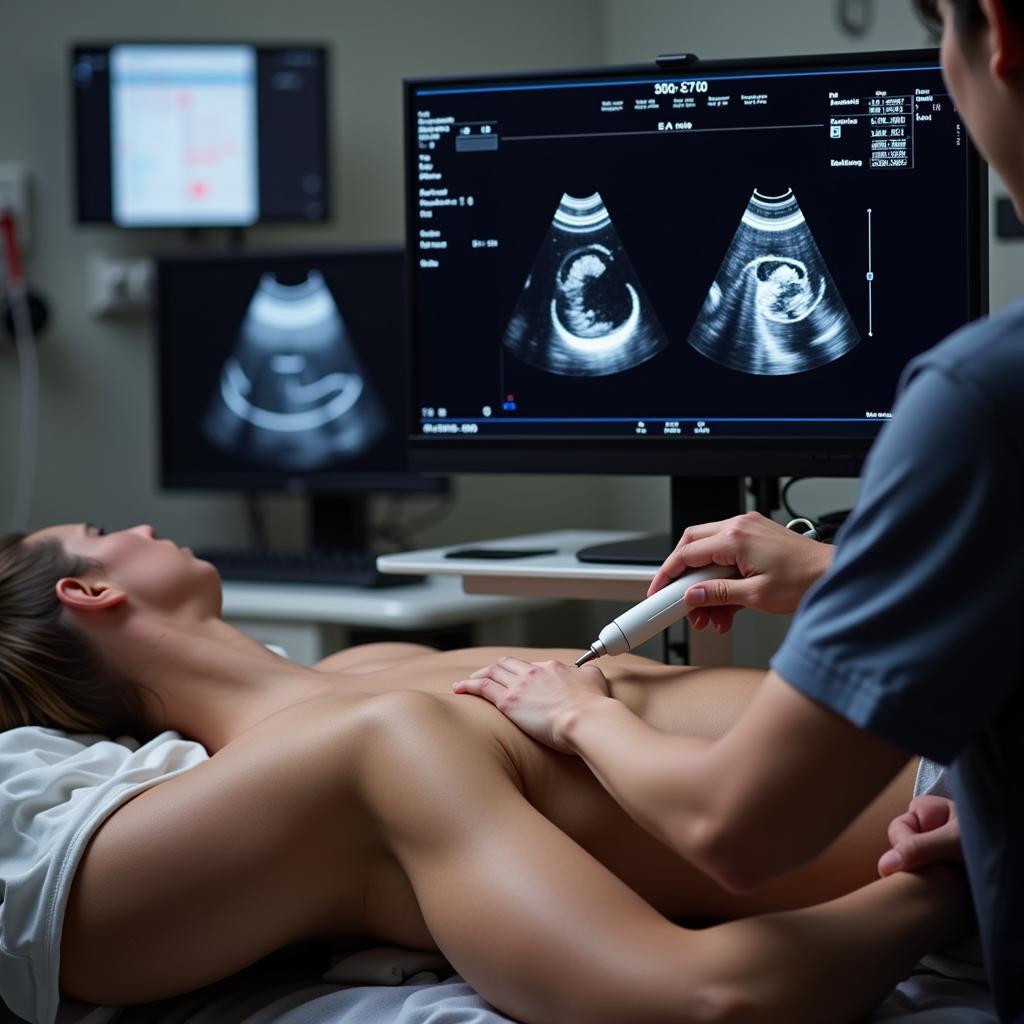 Echocardiography in Diastolic Dysfunction Diagnosis
Echocardiography in Diastolic Dysfunction Diagnosis
“Accurate assessment of diastolic function is paramount for managing patients with heart failure,” says Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a leading cardiologist at the National Heart Centre Singapore. “The ASE algorithm provides a standardized framework for evaluating diastolic parameters and guiding treatment decisions.”
2016 diastolic dysfunction ase
Living with Diastolic Dysfunction: Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing diastolic dysfunction requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, can significantly improve symptoms and overall health.
Lifestyle Changes for Improved Heart Health
- Diet: A balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats can help manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing strain on the heart.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves cardiovascular fitness and helps manage weight, both of which are beneficial for individuals with diastolic dysfunction.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate heart conditions. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help manage stress levels and improve heart health.
 Lifestyle Modifications for Diastolic Dysfunction
Lifestyle Modifications for Diastolic Dysfunction
“Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing diastolic dysfunction,” adds Dr. Nguyen. “These changes empower patients to take control of their health and improve their quality of life.” 2016 diastolic dysfunction ase
In conclusion, the ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm provides a valuable tool for diagnosing and classifying diastolic dysfunction. By understanding its components and application, clinicians can effectively manage patients with this complex condition. Early diagnosis, combined with appropriate lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, can significantly improve patient outcomes and enhance their overall well-being. Remember, understanding your heart health is key to a healthier, happier life.
FAQ
- What is diastolic dysfunction?
- What are the symptoms of diastolic dysfunction?
- How is diastolic dysfunction diagnosed?
- What is the ASE diastolic dysfunction algorithm?
- What are the treatment options for diastolic dysfunction?
- What lifestyle changes can help manage diastolic dysfunction?
- What is the prognosis for individuals with diastolic dysfunction?
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit us at: Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam.

