Ase Pericardial Tamponade is a serious medical condition where fluid accumulates in the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart. This pressure buildup restricts the heart’s ability to fill with blood, compromising its function and potentially leading to life-threatening complications. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment is crucial for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Cardiac tamponade can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, infections, cancer, and certain medical procedures. One of the challenges in diagnosing cardiac tamponade is that its symptoms can often mimic other conditions, such as heart attack or pneumonia. These symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Accurate and prompt diagnosis is essential for effective management of ASE pericardial tamponade. For more information on pericardial disease in general, see our ASE guidelines pericardial disease.
What are the Key Symptoms of ASE Pericardial Tamponade?
Recognizing the symptoms is the first step towards getting appropriate medical attention. While some symptoms can be vague, others are more specific and indicative of cardiac tamponade. Key symptoms include:
- Chest pain: This pain is often described as sharp and may worsen with deep breaths or lying down.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing is a common symptom as the heart struggles to pump effectively.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause these symptoms.
- Rapid heart rate: The heart beats faster to compensate for the decreased blood volume.
- Low blood pressure: The restricted heart function can lead to a drop in blood pressure.
- Muffled heart sounds: As fluid builds up, it can make it harder to hear the heart sounds clearly.
How is ASE Pericardial Tamponade Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of ASE pericardial tamponade involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests. These tests can include:
- Echocardiogram: This is the most important test for diagnosing cardiac tamponade, as it can visualize the fluid around the heart and assess its impact on heart function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can show changes in the heart’s electrical activity.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray may reveal an enlarged heart silhouette.
- Cardiac catheterization: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel and threading it to the heart to measure pressures within the heart chambers.
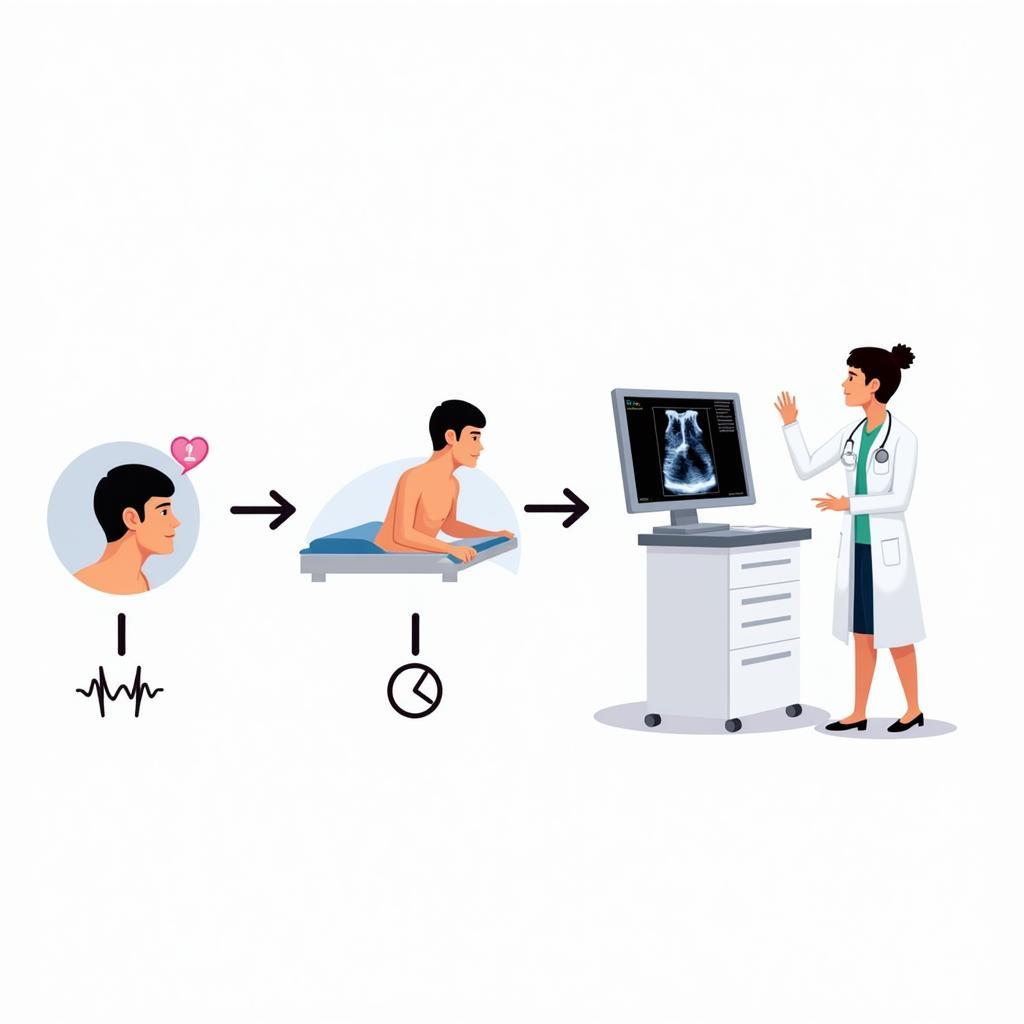 ASE Pericardial Tamponade Diagnosis Process
ASE Pericardial Tamponade Diagnosis Process
Treatment Options for ASE Pericardial Tamponade
Treatment for ASE pericardial tamponade focuses on relieving the pressure on the heart. This can be achieved through several methods:
- Pericardiocentesis: This procedure involves inserting a needle into the pericardium to drain the excess fluid. This is often the first-line treatment in emergency situations.
- Pericardial window: A small surgical opening is created in the pericardium to allow the fluid to drain.
- Medications: Medications may be used to support heart function and manage symptoms.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the underlying cause of the tamponade.
For a quick overview of ASE Tamponade, see our resource on ASE tamponade.
What are the Long-Term Effects of ASE Pericardial Tamponade?
The long-term effects of ASE pericardial tamponade can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to minimize potential long-term complications. Some patients may recover fully with no lasting effects, while others may experience ongoing heart problems.
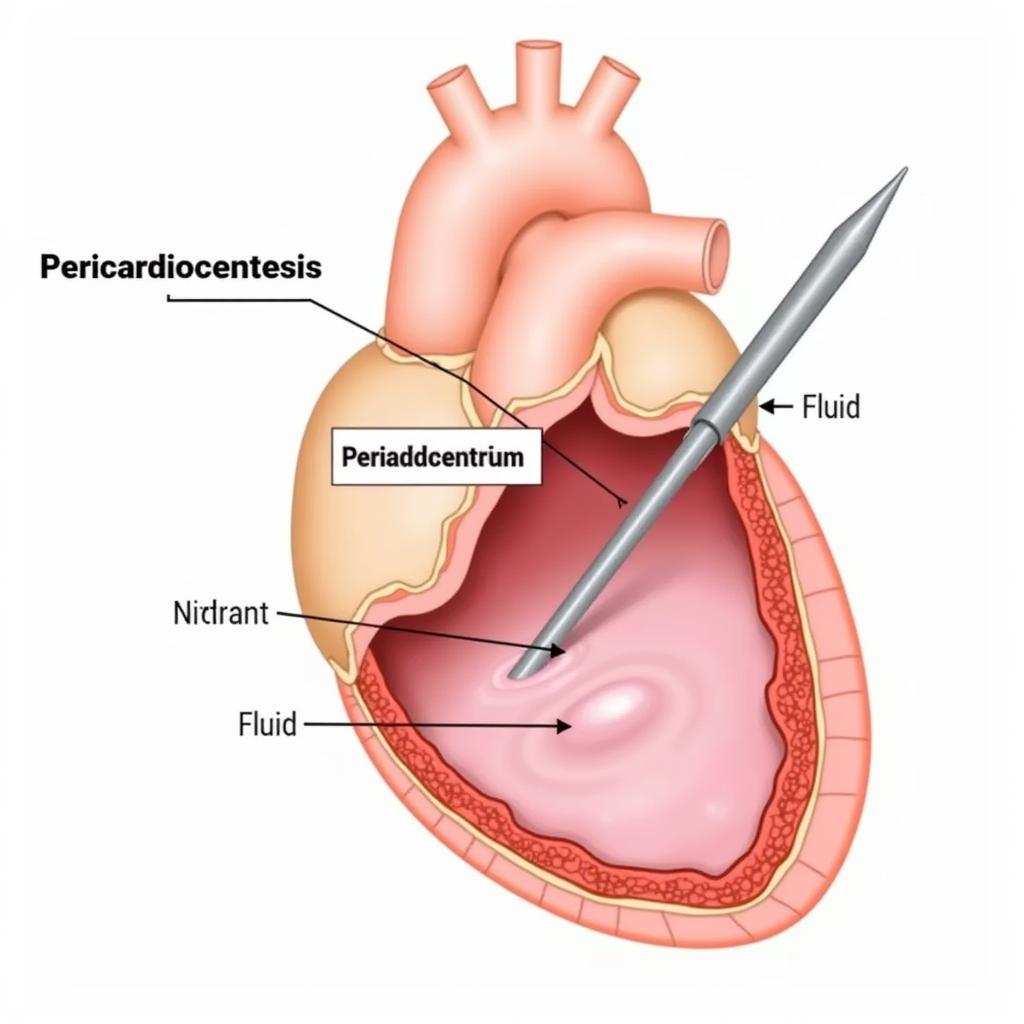 Treating ASE Pericardial Tamponade
Treating ASE Pericardial Tamponade
“Early recognition and treatment are paramount in managing pericardial tamponade. The faster we intervene, the better the chances of a positive outcome,” says Dr. Anisa Rahman, a leading cardiologist at the National Heart Institute in Kuala Lumpur.
Preventing ASE Pericardial Tamponade
While not all cases of pericardial tamponade are preventable, some measures can help reduce the risk, such as promptly treating infections and seeking medical attention for chest injuries.
“Prevention is key, especially in cases related to infection or trauma,” adds Dr. Nguyen Van Thanh, a thoracic surgeon at Cho Ray Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City. “Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of developing tamponade.” For further information on treatment guidelines, you can refer to our ASE tamponade guidelines.
 Preventing ASE Pericardial Tamponade Strategies
Preventing ASE Pericardial Tamponade Strategies
In conclusion, ASE pericardial tamponade is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Understanding the causes, diagnostic procedures, and available treatments is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals. For a broader understanding of pericardial diseases, see ASE pericardial disease.
FAQ
- What is the most common cause of pericardial tamponade?
- How quickly does pericardial tamponade develop?
- Can pericardial tamponade be fatal?
- What are the chances of recurrence after treatment?
- Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent pericardial tamponade?
- What is the difference between pericarditis and pericardial tamponade?
- What should I do if I suspect someone has pericardial tamponade?
For further assistance, please contact us: Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit our office at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.