Ase Mitral Regurgitation, often referred to as mitral insufficiency, is a heart condition where the mitral valve doesn’t close tightly, allowing blood to flow backward into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts. This backflow can lead to various symptoms and complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Ase Mitral Regurgitation?
Several factors can contribute to ase mitral regurgitation, ranging from congenital heart defects to acquired conditions. Some common causes include:
- Mitral Valve Prolapse: This occurs when the leaflets of the mitral valve bulge back into the left atrium during the heart’s contraction.
- Rheumatic Fever: This inflammatory disease can damage the mitral valve, leading to regurgitation.
- Infective Endocarditis: An infection of the heart’s inner lining can affect the mitral valve.
- Heart Attack: Damage to the heart muscle can disrupt the normal function of the mitral valve.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle can weaken the heart’s ability to pump effectively, leading to mitral regurgitation.
See the ASE guidelines for native valvular regurgitation for more in-depth information.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Ase Mitral Regurgitation
In the early stages, ase mitral regurgitation may not cause any noticeable symptoms. As the condition progresses, individuals might experience:
- Shortness of Breath: This is often the first and most common symptom.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak, even with minimal exertion.
- Heart Palpitations: A rapid, fluttering, or irregular heartbeat.
- Swelling in the Ankles and Feet: Due to fluid buildup.
- Persistent Cough: Especially when lying down.
Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent the progression of the condition and minimize potential complications.
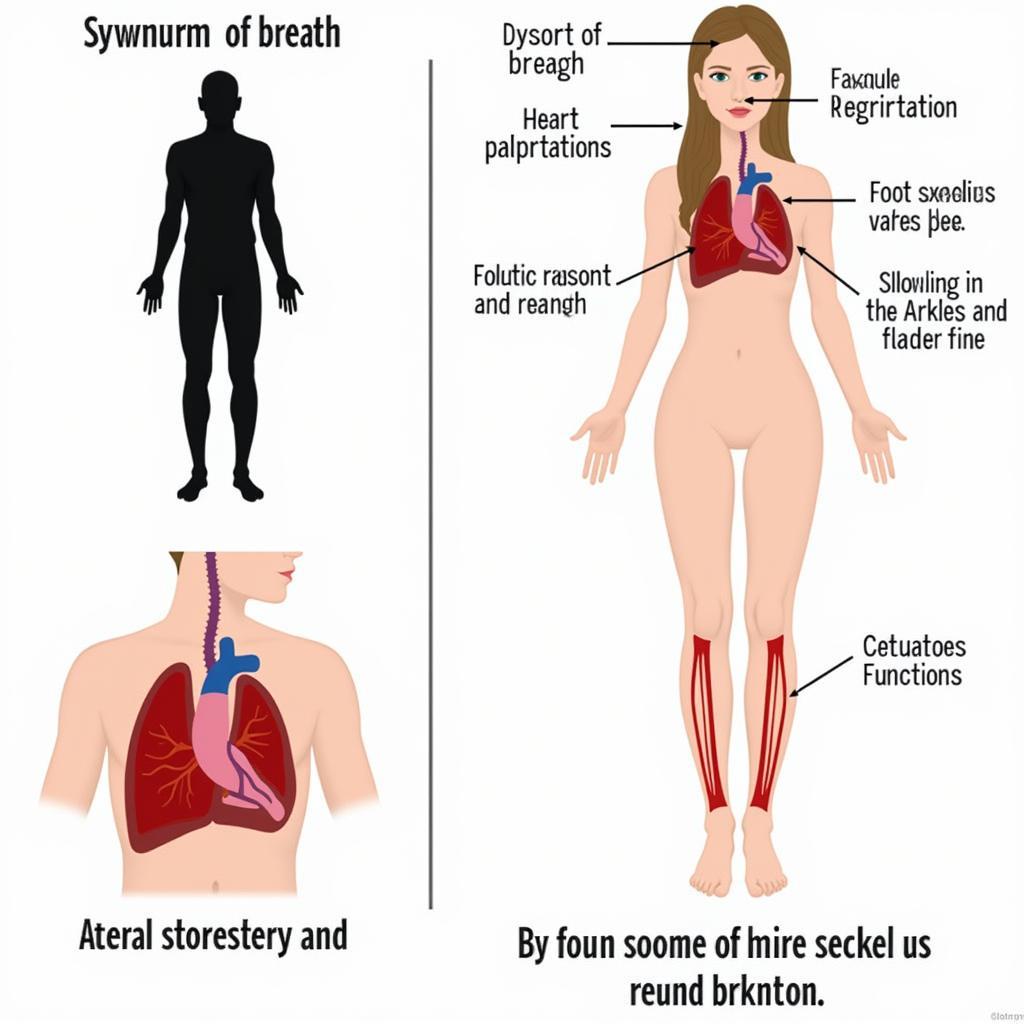 Common Symptoms of Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Common Symptoms of Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Diagnosing Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Diagnosing ase mitral regurgitation involves a combination of physical examination and diagnostic tests. A physician will listen to the heart with a stethoscope for a characteristic heart murmur. Further tests may include:
- Echocardiogram: This uses ultrasound to create images of the heart, showing the structure and function of the mitral valve.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This records the electrical activity of the heart.
- Chest X-Ray: This can reveal an enlarged heart or fluid in the lungs.
- Cardiac MRI or CT Scan: These provide detailed images of the heart and surrounding structures.
You can find more information regarding guidelines for this condition in the ASE mitral valve regurgitation guidelines.
Treating Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Treatment options for ase mitral regurgitation depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Options range from medications to manage symptoms to surgical interventions to repair or replace the mitral valve.
- Medications: These may include diuretics to reduce fluid buildup, vasodilators to relax blood vessels, and medications to control heart rate and rhythm.
- Lifestyle Modifications: These may include regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking.
- Mitral Valve Repair: This surgical procedure involves repairing the damaged mitral valve.
- Mitral Valve Replacement: This involves replacing the damaged valve with a mechanical or biological valve.
For other valve related issues, refer to the ASE valve guidelines 2014.
 Treatment Options for Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Treatment Options for Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Living with Ase Mitral Regurgitation
Managing ase mitral regurgitation effectively involves regular follow-up with a cardiologist, adhering to prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications, and attending regular cardiac rehabilitation programs. By actively participating in their care, individuals with ase mitral regurgitation can significantly improve their quality of life and long-term prognosis.
Conclusion
Ase mitral regurgitation is a serious heart condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for individuals living with this condition. By seeking medical attention and following recommended treatment plans, individuals can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing serious complications and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
FAQs
- What is the difference between mitral regurgitation and mitral stenosis?
- What are the long-term complications of untreated ase mitral regurgitation?
- Is ase mitral regurgitation hereditary?
- Can exercise help manage ase mitral regurgitation?
- What is the recovery time after mitral valve surgery?
- How often should I see a cardiologist if I have ase mitral regurgitation?
- Are there any dietary restrictions for individuals with ase mitral regurgitation?
Other Questions to Consider:
- What are the newest technological advancements in treating ase mitral regurgitation?
- How can I find a qualified cardiologist specializing in mitral valve disorders?
- What are the latest research findings regarding ase mitral regurgitation?
Explore More
- You can also refer to our article on ASE pulmonary hypertension guidelines for related information.
- For information about echo guidelines relating to Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs), please see the ASE LVAD echo guidelines.
When you need assistance, please contact us. Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected]. Our address is: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.

