ASEAN woodlands, a vibrant tapestry of biodiversity, hold immense ecological and cultural significance. From the lush rainforests of Borneo to the mangrove forests of Vietnam, these wooded landscapes provide habitats for countless species, support local communities, and contribute to the region’s rich natural heritage. This article delves into the fascinating world of ASEAN woodlands, exploring their unique characteristics, the challenges they face, and the ongoing efforts to conserve these vital ecosystems.
The Diverse Ecosystems of ASEAN Woodlands
ASEAN woodlands encompass a wide range of forest types, each with its own distinct flora and fauna. These include tropical rainforests, montane forests, mangrove forests, and peat swamp forests. The region’s diverse topography and climate create a mosaic of habitats, supporting an astonishing array of plant and animal life. Tropical rainforests, such as those found in Malaysia and Indonesia, are renowned for their towering trees, dense canopies, and incredible biodiversity. These forests are home to iconic species like orangutans, tigers, and elephants. Mangrove forests, found along the coastlines of countries like Thailand and the Philippines, play a crucial role in protecting coastal communities from erosion and storms. They also provide vital breeding grounds for fish and other marine life.
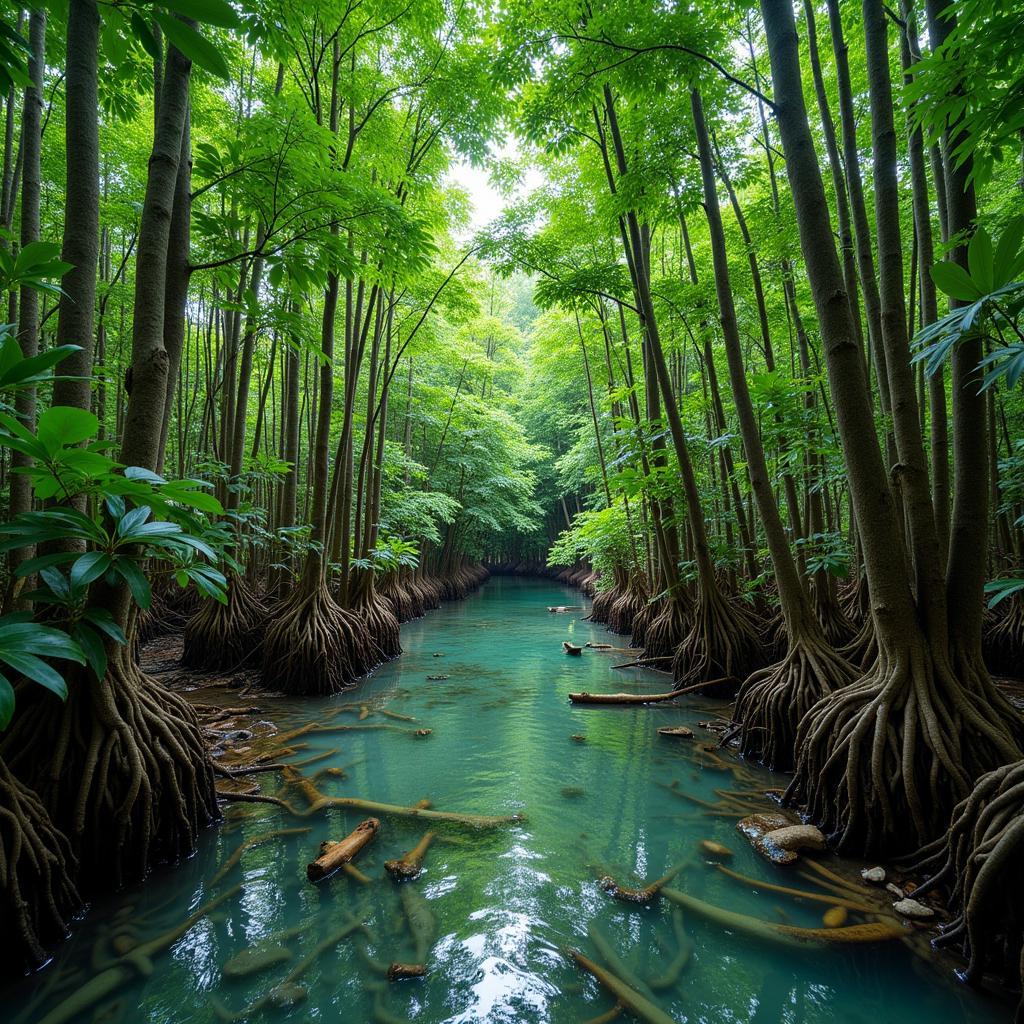 Thriving Mangrove Forest Ecosystem in ASEAN
Thriving Mangrove Forest Ecosystem in ASEAN
Montane forests, located in the higher elevations of countries like Vietnam and Laos, harbor unique species adapted to cooler temperatures and higher rainfall. These forests are often shrouded in mist, creating a mystical and enchanting atmosphere. Peat swamp forests, found in areas like Indonesia and Brunei, are characterized by waterlogged soils rich in organic matter. While they may appear desolate, these forests are vital carbon sinks, playing a critical role in mitigating climate change.
Threats to ASEAN Woodlands
Unfortunately, ASEAN woodlands face numerous threats, primarily driven by human activities. Deforestation due to logging, agriculture, and urban expansion is a major concern. Illegal wildlife trade also poses a significant threat to many endangered species. The increasing demand for palm oil and other agricultural commodities has led to widespread deforestation, particularly in Indonesia and Malaysia.
 The Devastating Impact of Deforestation on ASEAN Woodlands
The Devastating Impact of Deforestation on ASEAN Woodlands
Climate change also presents a growing challenge, with rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns impacting forest health and increasing the risk of forest fires. These threats not only endanger the region’s biodiversity but also threaten the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on forests for their sustenance and cultural heritage.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Practices
Recognizing the importance of ASEAN woodlands, governments, NGOs, and local communities are working together to protect and conserve these vital ecosystems. Sustainable forestry practices, such as selective logging and reforestation, are being promoted to minimize the impact of logging on forest ecosystems. Protected areas and national parks are being established to safeguard biodiversity hotspots and provide refuge for endangered species. Community-based conservation programs are empowering local communities to manage and protect their forests, recognizing their traditional knowledge and practices.
What are the key initiatives to protect ASEAN woodlands?
Key initiatives include establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable forestry practices, and empowering local communities through community-based conservation programs.
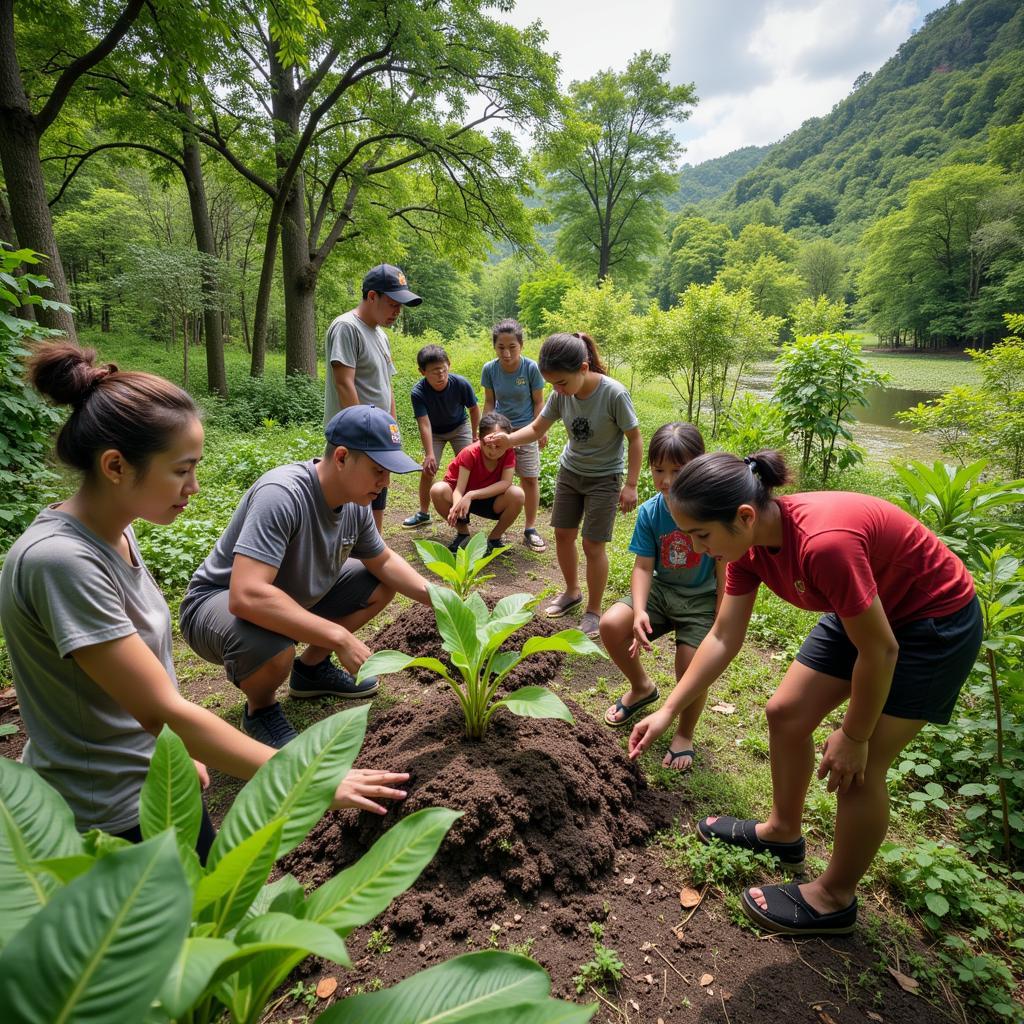 Community-Based Conservation Efforts in ASEAN Woodlands
Community-Based Conservation Efforts in ASEAN Woodlands
Conclusion
ASEAN woodlands are a treasure trove of biodiversity, providing invaluable ecological and cultural benefits. Protecting these forests is crucial not only for the region’s future but also for the global environment. By working together to implement sustainable practices and address the threats facing ASEAN woodlands, we can ensure that these precious ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come. Let us all play our part in preserving the beauty and biodiversity of ASEAN woodlands.
FAQs
- What are the main types of forests found in ASEAN? Tropical rainforests, montane forests, mangrove forests, and peat swamp forests are among the main types.
- Why are ASEAN woodlands important? They are crucial for biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of millions of people.
- What are the biggest threats to these forests? Deforestation, illegal wildlife trade, and climate change are major threats.
- What is being done to protect ASEAN woodlands? Conservation efforts include sustainable forestry, protected areas, and community-based conservation.
- How can I contribute to the conservation of ASEAN woodlands? Supporting sustainable products, raising awareness, and donating to conservation organizations are ways to help.
- What are some examples of sustainable forestry practices? Selective logging and reforestation are examples of sustainable practices.
- How do local communities contribute to forest conservation? Their traditional knowledge and active participation are vital for effective conservation efforts.
Need further assistance? Contact us at Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you.