ASE, or Atomic Spectrometry, plays a crucial role in analyzing furan, a volatile organic compound (VOC) often found in heated foods. This article explores the significance of using Ase For Furan analysis, delving into its benefits and providing a comprehensive overview of the process.
The Importance of Analyzing Furan with ASE
Furan is a known carcinogen found in various common food items, particularly those subjected to heat treatments like canning, jarring, and roasting. Monitoring furan levels is essential to ensure food safety and mitigate potential health risks. ASE provides a sensitive and reliable method for accurate furan quantification. This technique utilizes atomic absorption or emission to measure the concentration of furan, offering advantages over other analytical methods in terms of speed and sensitivity.
Benefits of Using ASE for Furan Analysis
- High Sensitivity: ASE can detect even trace amounts of furan, enabling accurate measurements in complex food matrices.
- Rapid Analysis: The automated nature of ASE significantly reduces analysis time compared to traditional methods.
- Reduced Solvent Consumption: ASE utilizes minimal solvent, making it an environmentally friendly option.
- Improved Reproducibility: The standardized procedure ensures consistent results across different laboratories and analyses.
- Versatility: ASE can be applied to a wide range of food samples, from coffee and baby food to canned goods and baked products.
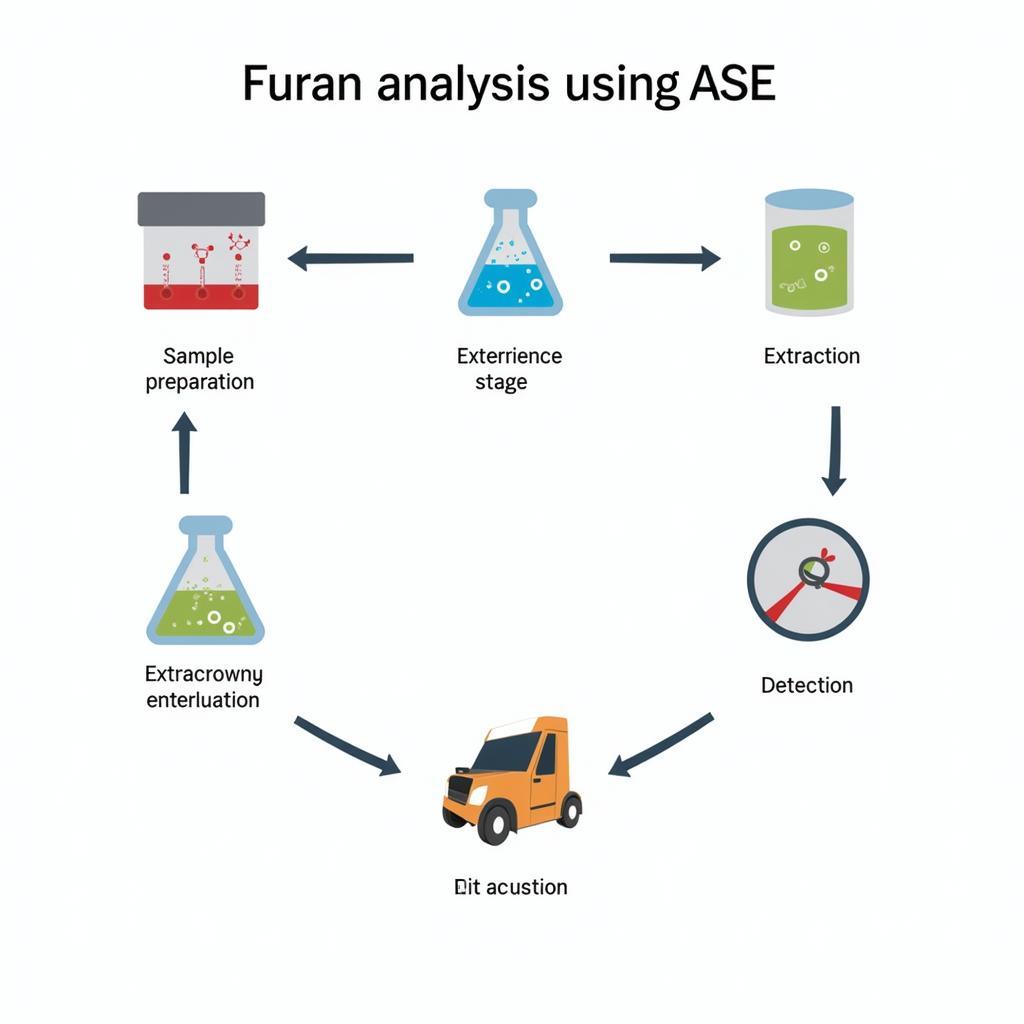 ASE Furan Analysis Process
ASE Furan Analysis Process
How ASE Works for Furan Detection
The process begins with sample preparation, which involves homogenizing and weighing the food item. The prepared sample is then placed in an extraction cell with a specific solvent. The cell is pressurized and heated, facilitating the extraction of furan from the food matrix into the solvent. The extract is then analyzed using an atomic spectrometer, which measures the absorption or emission of light at specific wavelengths characteristic of furan. The resulting signal is proportional to the furan concentration in the sample.
Understanding the Chemistry Behind ASE for Furan
The chemical principles underlying ASE for furan detection involve the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with furan molecules. When the extract is introduced into the atomic spectrometer, the furan molecules absorb light at specific wavelengths. This absorption is measured and used to quantify the furan concentration. The technique’s effectiveness lies in its ability to isolate and measure furan even in complex mixtures, making it a vital tool for food safety analysis.
Ensuring Accurate Furan Analysis with ASE
Several factors contribute to accurate furan analysis using ASE. Proper sample preparation, appropriate solvent selection, and optimized instrument parameters are crucial for reliable results. Regular calibration and quality control measures are also essential to maintain accuracy and precision.
“Accurate furan analysis is crucial for protecting public health. ASE provides a robust and reliable method for achieving this, enabling us to monitor and minimize the presence of this carcinogen in our food supply,” states Dr. Amelia Chen, a leading food safety expert.
Addressing Common Challenges in ASE for Furan Analysis
Despite its advantages, certain challenges can arise during ASE for furan analysis. Matrix effects from complex food samples can sometimes interfere with the measurement. However, these challenges can be addressed through careful method optimization and the use of appropriate internal standards.
“While challenges exist, the advantages of ASE, particularly its sensitivity and speed, make it an invaluable tool in furan analysis,” adds Dr. Chen.
 ASE Furan Challenges and Solutions
ASE Furan Challenges and Solutions
Conclusion
ASE offers a powerful and efficient method for analyzing furan in food. Its high sensitivity, rapid analysis time, and reduced solvent consumption make it an ideal choice for food safety monitoring. By understanding the principles and addressing potential challenges, we can effectively utilize ASE to ensure the safety and quality of our food supply, ultimately minimizing the risks associated with furan exposure.
FAQ
- What is the acceptable limit of furan in food? (Regulatory limits vary depending on the food type and jurisdiction.)
- What are the alternatives to ASE for furan analysis? (GC-MS is another common method.)
- How can I minimize furan formation during cooking? (Avoid overheating food and ensure proper ventilation.)
- Is ASE suitable for all types of food samples? (While versatile, certain sample matrices may require specific modifications to the ASE method.)
- What are the long-term health implications of furan exposure? (Long-term exposure to high levels of furan is linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.)
- Where can I find more information on furan and food safety? (Several reputable organizations, like the FDA and EFSA, provide valuable resources.)
- How can I access ASE testing for furan analysis? (Specialized food testing laboratories offer ASE analysis services.)
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit our office at Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.