The South China Sea dispute is a complex geopolitical issue with significant implications for ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations). This article delves into the intricacies of the dispute, examining its historical context, legal frameworks, and the various perspectives of the involved parties. We will explore ASEAN’s role in managing the tensions and promoting peaceful resolutions while navigating the challenges presented by this multifaceted maritime dispute.
Historical Context and Territorial Claims
The South China Sea, a strategically vital waterway, has been a source of contention for decades due to overlapping territorial claims. China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan all assert sovereignty over various islands, reefs, and their surrounding waters.
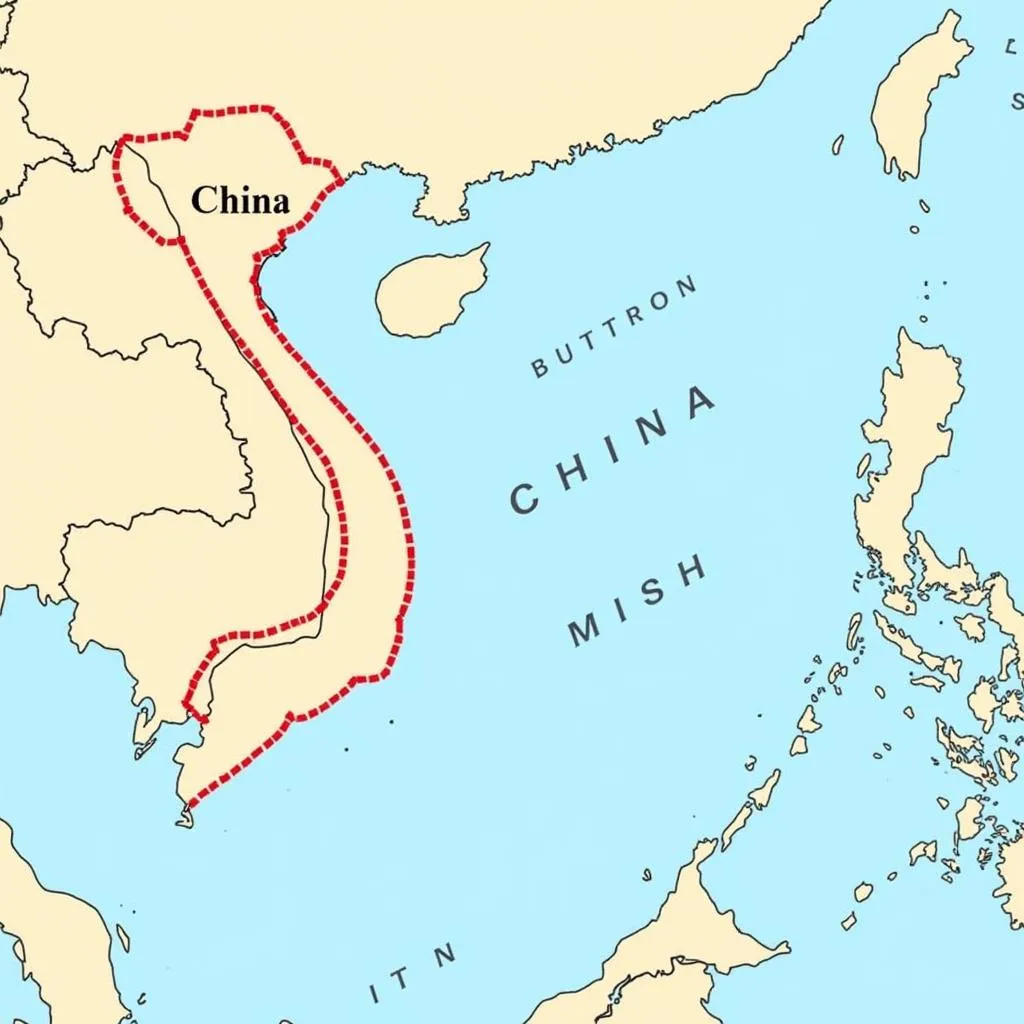 Map of South China Sea with disputed areas
Map of South China Sea with disputed areas
These claims are often rooted in historical narratives, with some countries pointing to centuries-old maps and records to support their positions. China’s “nine-dash line” claim, encompassing a vast swathe of the sea, has been a particular point of contention.
Legal Frameworks and International Law
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) serves as the primary legal framework governing maritime disputes. UNCLOS establishes rules for maritime zones, including territorial waters, exclusive economic zones (EEZs), and the continental shelf. However, interpreting and applying these rules to the specific circumstances of the South China Sea dispute has proven challenging.
 Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling on the South China Sea dispute
Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling on the South China Sea dispute
A landmark 2016 ruling by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague invalidated the legal basis of China’s nine-dash line claim. While this ruling was hailed by some as a victory for international law, China has rejected the tribunal’s jurisdiction and continues to assert its claims.
ASEAN’s Role and Regional Diplomacy
ASEAN, as a regional bloc, plays a crucial role in managing tensions and promoting dialogue in the South China Sea. The organization has consistently advocated for peaceful resolutions through dialogue, cooperation, and adherence to international law.
Key ASEAN Initiatives:
-
Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea (DOC): Signed in 2002, the DOC serves as a non-binding agreement to promote cooperation and restraint in the disputed waters.
-
Negotiations for a Code of Conduct (COC): ASEAN and China have been engaged in lengthy negotiations to establish a more comprehensive and legally binding COC to govern activities in the South China Sea.
Challenges and Opportunities for ASEAN:
- Maintaining unity and a cohesive approach among its member states, some of whom have closer ties with China than others.
- Balancing economic engagement with China while upholding its commitment to international law and regional stability.
- Leveraging its convening power to facilitate dialogue and confidence-building measures between the claimant states.
Economic and Strategic Significance
The South China Sea holds immense economic and strategic importance, making the stakes in the dispute particularly high.
- Rich fishing grounds: The sea provides a vital source of livelihood for millions of people in the region.
- Energy resources: The area is believed to hold significant reserves of oil and natural gas.
- Shipping lanes: The South China Sea is a crucial artery for global trade, with trillions of dollars worth of goods passing through its waters annually.
Looking Ahead: Navigating a Complex Future
The South China Sea dispute is likely to remain a persistent challenge in the region. Finding a lasting and peaceful resolution requires continued diplomacy, adherence to international law, and a commitment to dialogue and cooperation among all involved parties.
Expert Insights:
“The South China Sea is not just a regional issue, but one with global implications. It is in everyone’s interest to find a peaceful and sustainable solution that respects the rights and interests of all parties involved,” says Dr. [Expert Name 1], a leading scholar of Southeast Asian security issues.
” ASEAN’s role as a mediator and facilitator of dialogue is crucial. By promoting cooperation and confidence-building measures, ASEAN can help to reduce tensions and create a more conducive environment for a negotiated settlement,” adds [Expert Name 2], a senior analyst at a prominent think tank.
FAQs about ASEAN and the South China Sea Dispute:
1. What is ASEAN’s official position on the South China Sea dispute?
ASEAN, as an organization, maintains neutrality on the specific territorial claims in the South China Sea. However, it strongly advocates for peaceful resolutions through dialogue, cooperation, and adherence to international law, particularly UNCLOS.
2. What is the significance of the Code of Conduct (COC)?
The COC aims to establish a more comprehensive and legally binding framework to govern activities in the South China Sea. It is intended to prevent misunderstandings, manage incidents, and promote peaceful cooperation among the claimant states.
3. How does the South China Sea dispute impact ASEAN-China relations?
The dispute presents both challenges and opportunities for ASEAN-China relations. While it has the potential to create tensions, it also encourages dialogue and cooperation on managing the dispute.
4. What role can external actors play in resolving the dispute?
External actors can play a constructive role by supporting ASEAN-led mechanisms, encouraging adherence to international law, and promoting dialogue and diplomacy among the claimant states.
5. What are the potential consequences of an escalation of tensions in the South China Sea?
An escalation of tensions could have severe consequences for regional stability, economic prosperity, and international security. It is crucial to prioritize peaceful resolutions and avoid any actions that could further escalate the situation.
For further information and resources on ASEAN and the South China Sea dispute, please refer to:
Need Support?
Contact us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.

