Ase Soil Extraction, or Accelerated Solvent Extraction, is a revolutionary technique used to isolate target compounds from solid and semi-solid environmental samples like soil. It offers a faster, more efficient, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods, making it a crucial tool in various scientific fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ASE soil extraction, exploring its applications, benefits, and future potential.
What is ASE Soil Extraction?
ASE soil extraction utilizes a combination of elevated temperature and pressure to accelerate the extraction process. By subjecting the sample to these specific conditions, target analytes are quickly and efficiently partitioned into the solvent. This process dramatically reduces extraction time compared to traditional methods like Soxhlet extraction, which can take hours or even days. ASE utilizes smaller solvent volumes, minimizing waste and reducing the environmental impact. The method’s automation further enhances its efficiency, allowing for unattended operation and freeing up valuable lab time.
After this introductory section, we can dive into a specific aspect of ASE.
accelerated solvent extractor ase 200
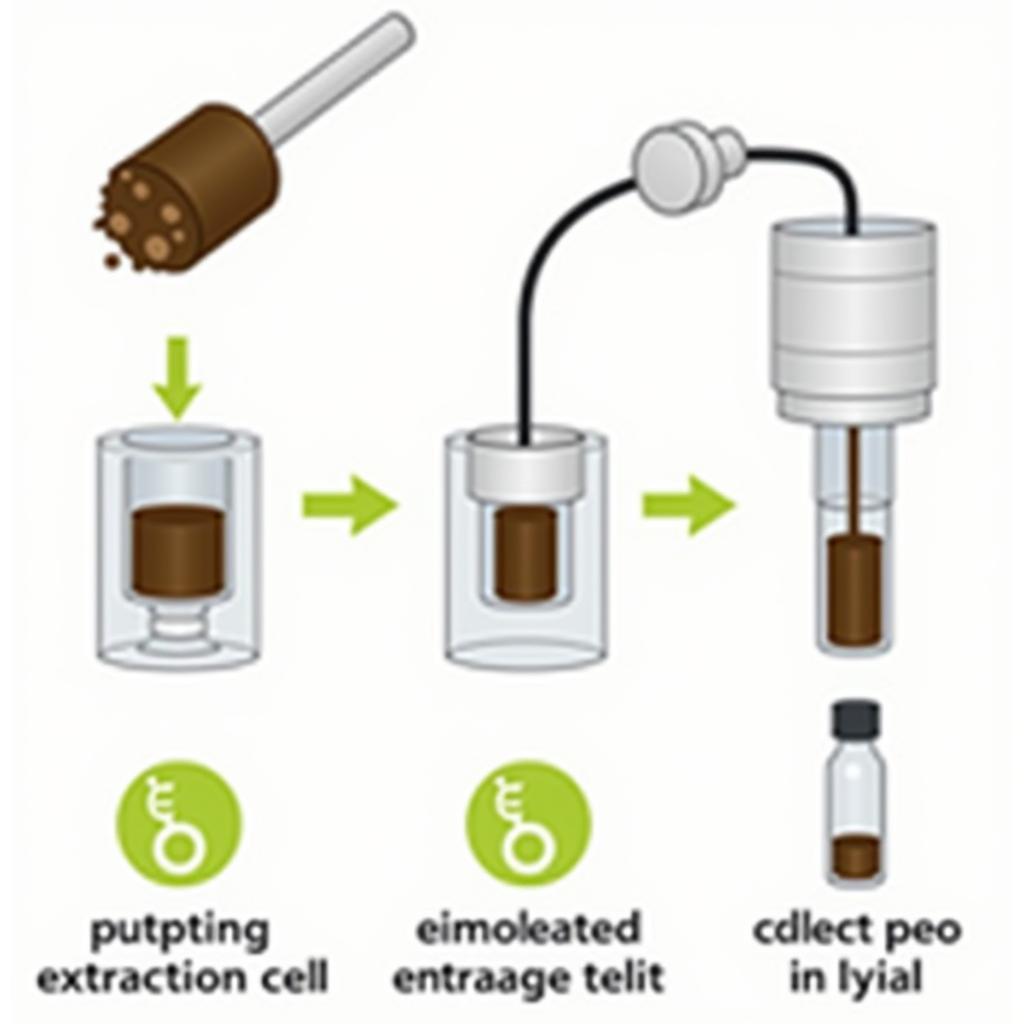 ASE Soil Extraction Process in Lab
ASE Soil Extraction Process in Lab
Benefits of Using ASE for Soil Analysis
ASE soil extraction offers several distinct advantages. It significantly reduces extraction time, leading to increased sample throughput. The reduced solvent consumption minimizes waste and lowers costs, promoting a more sustainable lab environment. ASE’s automated nature improves precision and reproducibility by minimizing human error. Moreover, it effectively extracts a wide range of analytes, including persistent organic pollutants (POPs), pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
Enhanced Accuracy and Precision with ASE
The controlled and automated nature of ASE leads to enhanced accuracy and precision in soil analysis. The precise control over temperature and pressure minimizes variations in extraction conditions, resulting in more consistent results. This is particularly crucial for environmental monitoring and regulatory compliance, where accurate and reliable data is paramount.
Applications of ASE Soil Extraction
The versatility of ASE makes it applicable in various fields. It’s widely used in environmental monitoring to analyze soil contamination, assess environmental risks, and ensure regulatory compliance. In agriculture, ASE helps determine pesticide residues in soil, contributing to food safety and sustainable farming practices. The pharmaceutical industry utilizes ASE for drug discovery and development by extracting target compounds from soil microorganisms.
ASE in Environmental Remediation
ASE plays a vital role in environmental remediation projects. By accurately identifying and quantifying contaminants in soil, ASE guides remediation strategies and helps monitor the effectiveness of cleanup efforts. This contributes to the restoration of contaminated sites and the protection of human health and the environment.
Common Questions about ASE Soil Extraction
What types of solvents are used in ASE? ASE utilizes a variety of solvents depending on the target analytes and the nature of the soil matrix. Common solvents include methanol, acetone, and hexane.
How does temperature affect ASE extraction efficiency? Elevated temperature increases the solubility and diffusion rate of analytes, leading to higher extraction efficiency.
accelerated solvent extraction ase market
 ASE Soil Extraction in Environmental Monitoring
ASE Soil Extraction in Environmental Monitoring
Choosing the Right ASE System
Several factors influence the selection of an appropriate ASE system. The type and volume of samples being processed, the target analytes, and the budget are crucial considerations. Consulting with experts and reviewing available options can help determine the most suitable system for specific needs.
“ASE’s ability to deliver rapid and reliable results is invaluable in our environmental monitoring work,” says Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a leading environmental chemist. “It allows us to make informed decisions and respond quickly to environmental challenges.”
Future Directions of ASE
ASE continues to evolve, driven by the demand for faster, more efficient, and sustainable analytical techniques. Advancements in automation, solvent selection, and data analysis are shaping the future of ASE, promising even greater precision, sensitivity, and versatility.
“The future of soil analysis lies in innovative techniques like ASE,” adds Dr. Tran Van Hao, a soil scientist. “Its ability to provide comprehensive data is essential for sustainable environmental management.”
Conclusion
ASE soil extraction is a powerful technique that has revolutionized the way we analyze environmental samples. Its efficiency, precision, and versatility make it an invaluable tool in various fields, contributing to a safer and more sustainable future. ASE offers a clear path forward for tackling complex environmental challenges.
FAQ
- Is ASE soil extraction environmentally friendly?
- What are the limitations of ASE?
- How does ASE compare to other extraction techniques?
- What are the cost considerations for ASE implementation?
- What safety precautions should be taken when using ASE?
- How is data analyzed after ASE extraction?
- What types of soils are suitable for ASE extraction?
For further information related to solvent extraction, please explore our resources on Accelerated Solvent Extractor ASE 200.
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.