ASEAN stress echo guidelines for non-ischemic cases provide a crucial framework for diagnosing and managing various heart conditions. These guidelines, tailored for the diverse ASEAN population, address the use of stress echocardiography in evaluating non-ischemic cardiomyopathies, valvular heart disease, and other cardiac abnormalities where reduced blood flow isn’t the primary concern. Understanding these guidelines is essential for healthcare professionals across Southeast Asia in providing optimal patient care.
Understanding Non-Ischemic Stress Echocardiography
Non-ischemic stress echocardiography helps assess the heart’s function under stress when the cause isn’t related to blocked arteries. It utilizes various stressors, such as exercise or medication, to increase the heart’s workload and reveal underlying functional limitations not apparent at rest. This technique plays a vital role in diagnosing conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, and valvular heart diseases.
Types of Stressors Used in Non-Ischemic Cases
Several stressors can be used for non-ischemic stress echocardiography, each with its benefits and limitations. Dobutamine, a medication that mimics the effects of exercise, is commonly used. Exercise stress testing, using a treadmill or stationary bike, is another option, particularly for assessing exercise capacity.
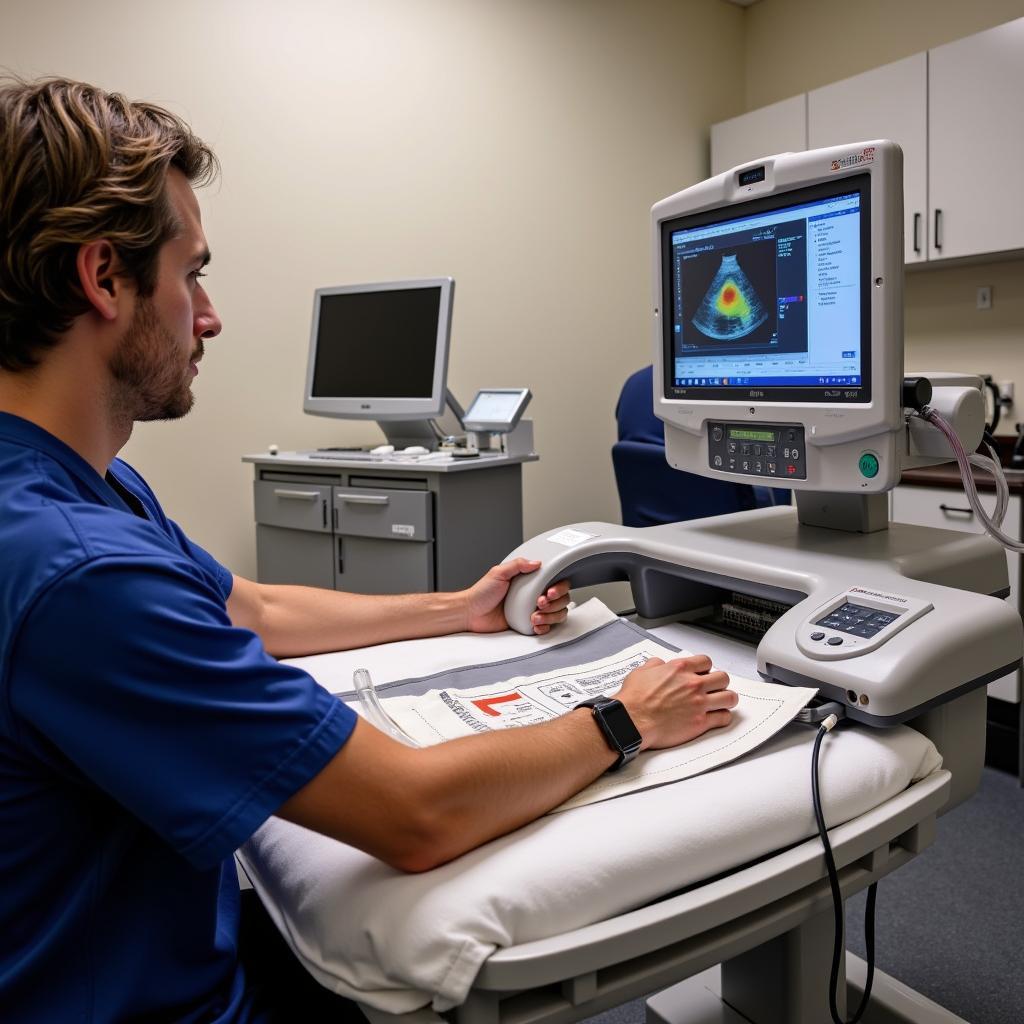 Dobutamine Infusion for Stress Echo
Dobutamine Infusion for Stress Echo
ASEAN Guidelines for Specific Non-Ischemic Conditions
The ASEAN guidelines provide specific recommendations for various non-ischemic conditions. For instance, in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, stress echo can help assess the severity of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. In valvular heart disease, it can evaluate the impact of the valve abnormality on cardiac function under stress.
Interpreting the Results of a Non-Ischemic Stress Echo
Interpreting the results requires expertise. The key parameters assessed include changes in wall motion, left ventricular function, and valve function during stress. Any abnormalities detected can indicate underlying pathology and guide treatment decisions.
The Importance of Regional Expertise within ASEAN
The diverse demographics and healthcare landscape within ASEAN necessitate regional expertise in interpreting stress echo results. Factors like ethnicity and prevalence of specific conditions can influence the interpretation and application of the guidelines.
Clinical Applications and Patient Benefits
Non-ischemic stress echo offers significant benefits for patients, enabling early diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. It helps determine the prognosis and guide management decisions in various cardiac conditions.
Improving Patient Outcomes in Southeast Asia
By adhering to the ASEAN guidelines, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy of diagnosis and tailor treatment plans, ultimately improving patient outcomes across Southeast Asia.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research focuses on refining stress echo techniques and expanding their applications in non-ischemic heart disease. This includes developing new stressors and improving image quality for more precise assessments.
“Accurate interpretation of non-ischemic stress echo is crucial for effective management of various cardiac conditions,” says Dr. Nguyen Thi Phuong Mai, a leading cardiologist at the National Heart Institute in Vietnam. “The ASEAN guidelines provide valuable guidance for healthcare professionals in the region.”
How does a non-ischemic stress echo differ from a regular echocardiogram?
A regular echocardiogram assesses the heart at rest, while a stress echo evaluates its function under stress, revealing potential issues not apparent at rest.
What are the common indications for a non-ischemic stress echo?
Common indications include evaluating suspected hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, and valvular heart disease.
Conclusion
The ASEAN stress echo guidelines for non-ischemic cases are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of various heart conditions. By adhering to these guidelines and utilizing the expertise within the ASEAN region, healthcare providers can improve patient care and outcomes. These guidelines play a critical role in advancing cardiovascular health across Southeast Asia.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of a non-ischemic stress echo? To assess heart function under stress when the issue isn’t related to blocked arteries.
- What are the common stressors used in this procedure? Dobutamine and exercise.
- How are the results interpreted? By analyzing changes in wall motion, left ventricular function, and valve function.
- Why are regional guidelines important? To account for diverse demographics and specific disease prevalence.
- How does this test benefit patients? Enables early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and better outcomes.
- What is the role of ongoing research? To refine techniques and expand applications.
- Where can I find more information about these guidelines? Consult with your cardiologist or refer to the ASEAN Society of Cardiology.
When you need assistance, please contact Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.