The ASEAN acronym stands for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, a political and economic alliance of 10 member states in Southeast Asia. This organization plays a crucial role in fostering collaboration, promoting peace, and driving economic growth in one of the world’s most dynamic regions. Understanding what ASEAN stands for is key to unlocking the potential and complexities of this diverse and vibrant area.
What Does ASEAN Stand For and Why Does It Matter?
ASEAN represents a collective force in the global landscape, wielding considerable influence in trade, diplomacy, and cultural exchange. The ASEAN acronym, while seemingly simple, embodies a rich history and a shared vision for a prosperous future. For businesses, investors, and anyone interested in Southeast Asia, understanding what ASEAN stands for is crucial for navigating the region’s opportunities and challenges. From its founding principles to its current initiatives, ASEAN’s impact is undeniable. The association strives to create a unified and harmonious region, promoting peace, stability, and shared prosperity among its member nations.
A Deep Dive into the ASEAN Acronym
The full form of the ASEAN acronym – Association of Southeast Asian Nations – clearly outlines the organization’s geographical scope and primary objective: to unite the nations of Southeast Asia. But it’s more than just a name; it’s a symbol of unity, resilience, and a commitment to shared progress. Each word in the ASEAN acronym carries weight: “Association” signifying collaboration, “Southeast Asian” defining its geographical focus, and “Nations” highlighting the importance of state sovereignty within the collective.
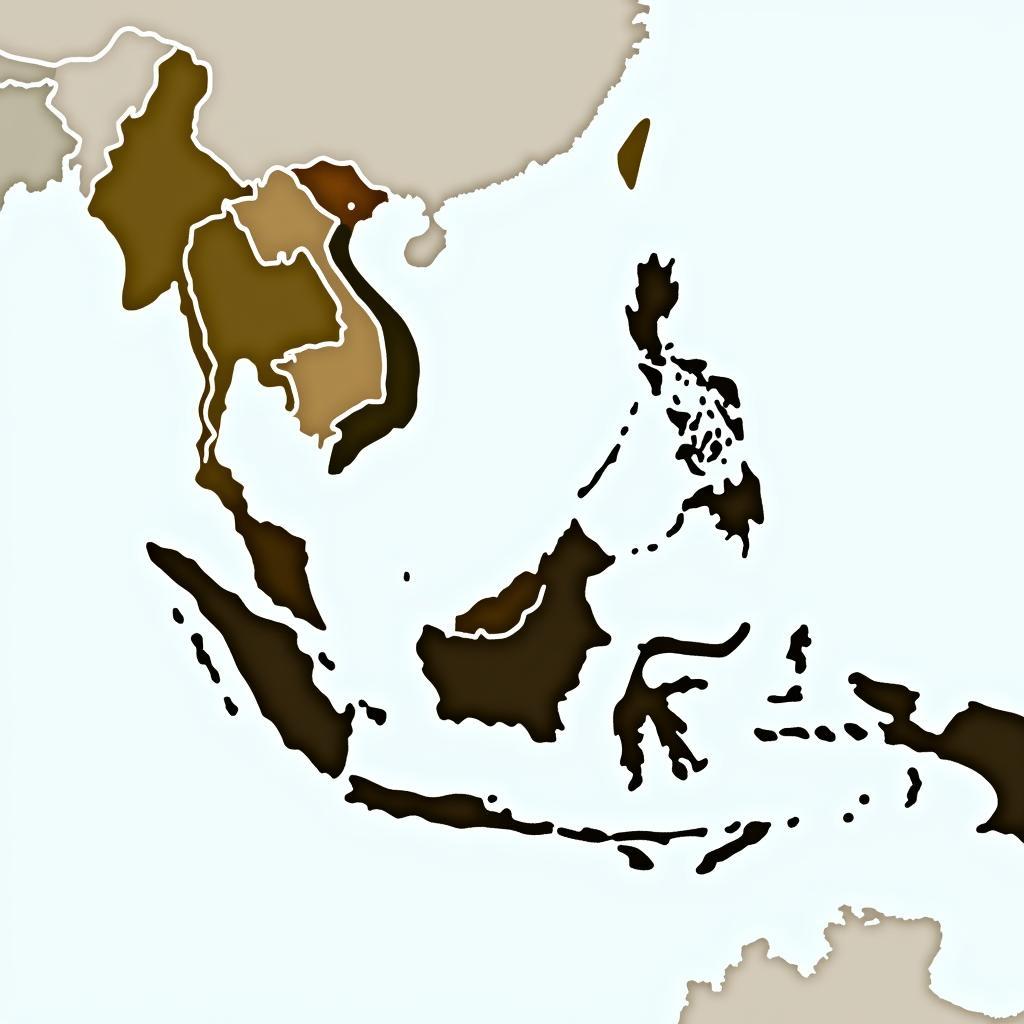 Map of ASEAN Member States
Map of ASEAN Member States
The formation of ASEAN was driven by a desire to create a stable and peaceful environment in the aftermath of post-colonial struggles and the escalating Cold War tensions. The Bangkok Declaration of 1967, which formally established ASEAN, laid the foundation for regional cooperation and mutual respect among member states.
The Significance of ASEAN’s Formation
The establishment of ASEAN marked a turning point in Southeast Asian history. By fostering dialogue and cooperation, ASEAN has helped prevent conflicts, manage disputes, and promote stability within the region. This has created a conducive environment for economic growth and development, attracting foreign investment and boosting intra-regional trade.
- Promotes regional peace and stability
- Facilitates economic cooperation and integration
- Enhances social and cultural exchange
- Strengthens regional identity and voice on the global stage
 ASEAN Economic Growth Chart
ASEAN Economic Growth Chart
Understanding what ASEAN stands for is not just about memorizing an acronym; it’s about recognizing the profound impact of this organization on Southeast Asia and the wider world.
How Does ASEAN Function?
ASEAN operates on the principles of consensus-building and non-interference in the internal affairs of member states. Decisions are made collectively, and member states work together to implement regional initiatives and programs.
ASEAN’s Organizational Structure
ASEAN has a structured framework that facilitates its operations. The ASEAN Summit, comprising the heads of state or government of member states, is the supreme policy-making body. The ASEAN Secretariat, based in Jakarta, Indonesia, provides administrative support and coordinates the implementation of ASEAN activities.
“ASEAN’s success lies in its ability to foster collaboration and build consensus among its diverse members,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading expert on Southeast Asian economics. “This collaborative spirit is crucial for navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of the region and achieving shared prosperity.”
ASEAN’s Impact on Southeast Asia and Beyond
ASEAN’s influence extends beyond its immediate region, playing a significant role in shaping the dynamics of Asia and the global community.
ASEAN’s Role in Global Affairs
ASEAN actively engages with international partners, promoting dialogue and cooperation on issues of mutual interest. The organization has free trade agreements with several countries and is a key player in regional security dialogues.
“ASEAN’s growing economic clout and strategic location make it a vital partner for countries around the world,” notes Dr. Michael Tan, a political analyst specializing in ASEAN affairs. “Its ability to bridge cultural and political divides further enhances its role as a key player in international diplomacy.”
 ASEAN International Partnerships
ASEAN International Partnerships
Conclusion: The Future of ASEAN
The ASEAN acronym represents more than just a regional organization; it symbolizes the hopes and aspirations of a dynamic and interconnected region. Understanding what ASEAN stands for provides valuable insights into the forces shaping Southeast Asia’s future. As ASEAN continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping the global landscape.
FAQ
- What are the 10 member states of ASEAN? Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- When was ASEAN established? ASEAN was established on August 8, 1967.
- Where is the ASEAN Secretariat located? Jakarta, Indonesia.
- What is the main objective of ASEAN? To promote regional peace, stability, and prosperity through cooperation and integration.
- How does ASEAN make decisions? Decisions are made through consensus among member states.
Need More Information?
For further inquiries regarding ASEAN, please contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our customer service team is available 24/7 to assist you.