The terms “Ark Ase Vs Asa” often appear when discussing Southeast Asian integration and cooperation. This article aims to clarify the distinctions between the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and its lesser-known predecessors, the Association of Southeast Asia (ASA) and the ill-fated Maphilindo (a portmanteau of Malaya, the Philippines, and Indonesia). We’ll explore their origins, objectives, and impact on the region’s development.
Delving into the History of Southeast Asian Cooperation
Post-colonial Southeast Asia was a complex landscape of emerging nations grappling with political instability and the specter of communism. The desire for regional cooperation, driven by shared economic and security concerns, led to the formation of ASA in 1961. Comprising Malaya (now Malaysia), the Philippines, and Thailand, ASA aimed to foster collaboration in areas like economic development, social progress, and cultural exchange. However, its limited membership and the exclusion of key regional players hampered its effectiveness. For instance, Indonesia, a significant force in Southeast Asia, was left out, contributing to ASA’s eventual decline.
The concept of Maphilindo emerged briefly in 1963, envisioned as a broader alliance encompassing Malaya, the Philippines, and Indonesia. It sought to address the Borneo dispute and promote closer ties among these Malay-speaking nations. However, Maphilindo proved short-lived, succumbing to internal disagreements and political tensions. Its fleeting existence, though unsuccessful, highlighted the ongoing need for a more inclusive and robust regional organization.
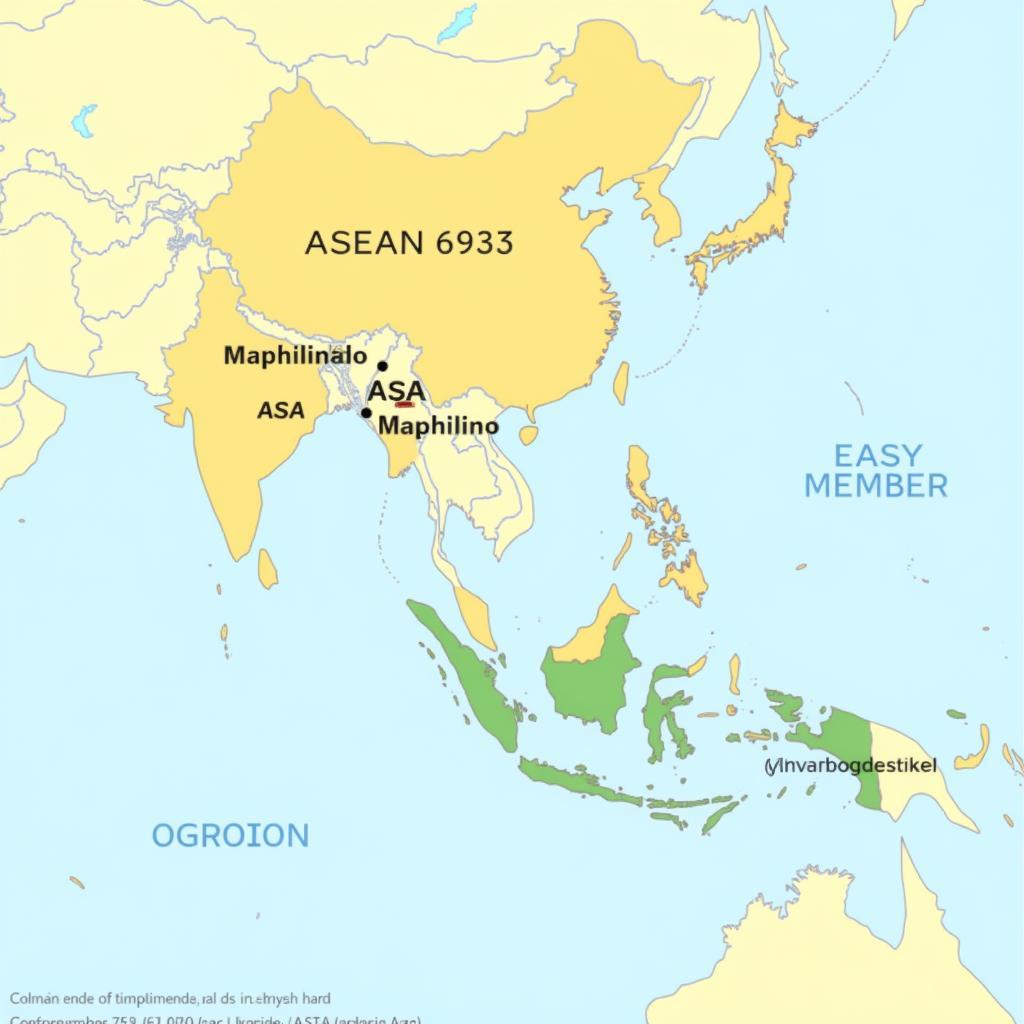 Map of ASA, Maphilindo, and ASEAN Member States
Map of ASA, Maphilindo, and ASEAN Member States
The Rise of ASEAN: A New Era of Cooperation
Learning from the limitations of ASA and Maphilindo, five Southeast Asian nations—Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand—came together in 1967 to establish ASEAN. ASEAN adopted a broader approach, focusing on accelerating economic growth, social progress, cultural development, regional peace, and collaboration. Unlike its predecessors, ASEAN embraced a policy of neutrality and non-interference in internal affairs, which proved crucial in navigating the region’s diverse political landscape.
What are the key differences between ASA and ASEAN?
ASEAN’s inclusivity and its commitment to peaceful conflict resolution set it apart. It also established mechanisms for dialogue and consultation, paving the way for greater cooperation on issues like trade, security, and environmental protection.
 Chart comparing the Economic Growth of ASEAN countries
Chart comparing the Economic Growth of ASEAN countries
How did ASEAN evolve from its predecessors?
ASEAN learned from the shortcomings of ASA and Maphilindo. ASA’s limited membership hindered its impact, while Maphilindo’s failure underscored the importance of a broader, more inclusive approach to regional cooperation. ASEAN adopted these lessons, fostering a platform for dialogue and collaboration among a wider range of Southeast Asian nations.
“ASEAN’s success lies in its ability to adapt to changing geopolitical realities and address the diverse needs of its member states,” notes Dr. Anya Sharma, a prominent Southeast Asian Studies scholar.
ASEAN’s Impact on Regional Development
ASEAN has played a pivotal role in promoting peace and stability in Southeast Asia. By facilitating dialogue and cooperation, it has helped manage regional disputes and prevent conflicts. Furthermore, ASEAN has become a key driver of economic integration, fostering trade and investment among its member states.
“The establishment of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) has significantly boosted intra-regional trade and contributed to the region’s economic dynamism,” adds Professor Chandra Wijaya, an expert in international trade.
Conclusion: Ark ASE vs ASA – A Journey of Regional Integration
Understanding the differences between ark ase, asa, and ASEAN provides valuable insights into the evolution of regional cooperation in Southeast Asia. While ASA and Maphilindo laid some groundwork, it was ASEAN’s inclusive approach, commitment to peaceful conflict resolution, and focus on economic integration that propelled the region forward. ASEAN continues to play a vital role in shaping the future of Southeast Asia.
FAQ
- What is the difference between ASA and ASEAN?
- What was Maphilindo’s role in Southeast Asian integration?
- How has ASEAN contributed to regional peace and stability?
- What are the key objectives of ASEAN?
- How does ASEAN promote economic cooperation among its members?
- What challenges does ASEAN face in the 21st century?
- How can ASEAN further enhance its role in regional development?
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.

