The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional intergovernmental organization comprising ten Southeast Asian countries. Established on 8 August 1967, ASEAN promotes political, economic, and socio-cultural cooperation amongst its members. This article delves into the history, structure, objectives, and significance of What Is The AseAN, offering a thorough understanding of its role in shaping the future of Southeast Asia and its impact on the global stage.
 Flags of ASEAN Member Countries
Flags of ASEAN Member Countries
Understanding the Foundation: History and Formation of ASEAN
ASEAN’s genesis lies in the shared desire of its founding members to foster peace and stability in a region marred by conflict. The Bangkok Declaration, signed in 1967, laid the groundwork for this regional alliance. Initially comprised of five countries—Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand—ASEAN expanded over time to include Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia. This growth reflects the increasing recognition of the importance of regional cooperation. what is the asean
Key Objectives of ASEAN: Pillars of Cooperation
The core principles of ASEAN revolve around mutual respect for sovereignty, territorial integrity, non-interference in internal affairs, and the peaceful resolution of disputes. The organization works towards accelerating economic growth, social progress, and cultural development in the region. Moreover, ASEAN promotes regional peace and stability through adherence to the rule of law.
The ASEAN Community: Three Pillars of Integration
ASEAN’s vision is to create a single market and production base, a competitive economic region, a region of equitable economic development, and a region fully integrated into the global economy. This vision is realized through the ASEAN Community, based on three pillars: the Political-Security Community, the Economic Community, and the Socio-Cultural Community.
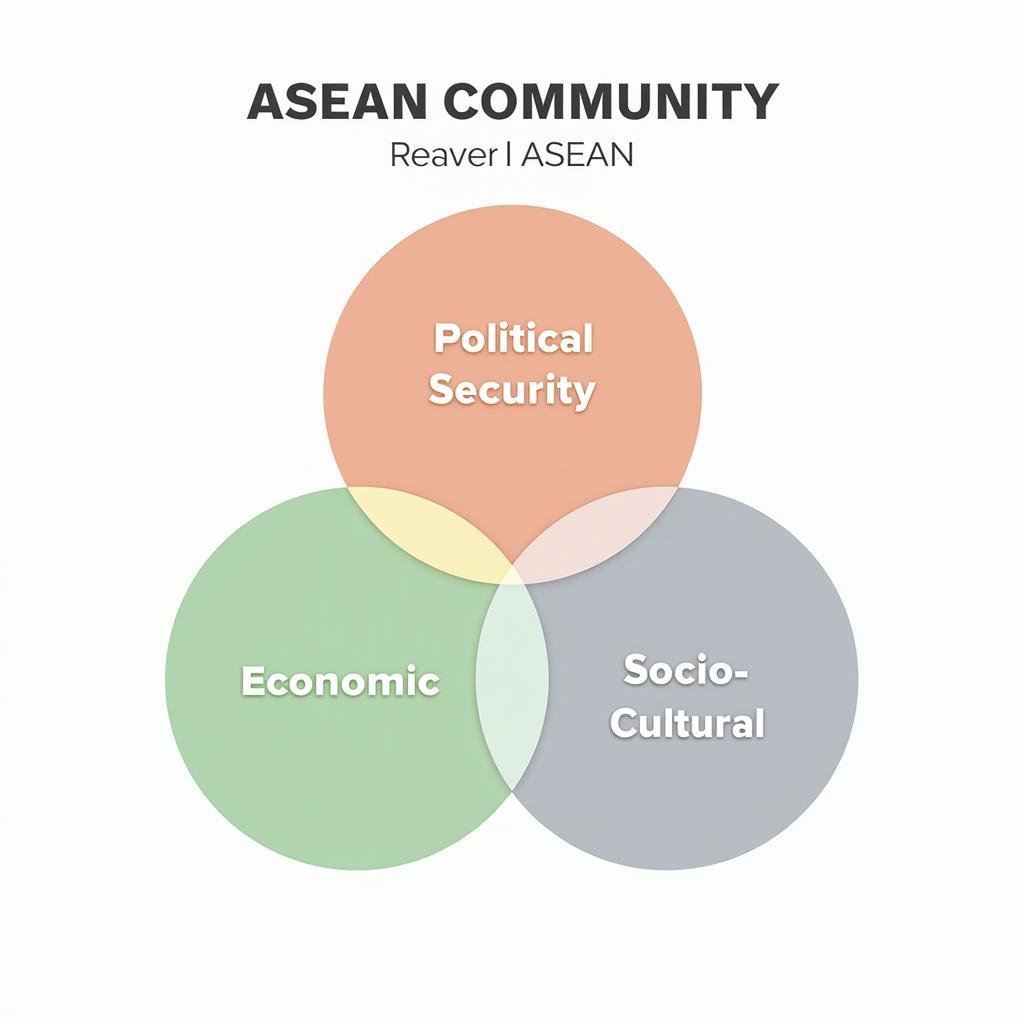 Three Pillars of ASEAN Community
Three Pillars of ASEAN Community
What is the ASEAN Economic Community?
The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) aims to create a single market and production base characterized by the free flow of goods, services, investment, skilled labor, and freer flow of capital. This integration boosts the region’s competitiveness and attracts foreign investment. ano ang asean economic community
Political-Security Cooperation: Maintaining Regional Stability
ASEAN plays a crucial role in maintaining regional peace and security. Through dialogue and cooperation, it addresses security challenges and promotes conflict resolution. The organization also fosters cooperation on transnational crime, terrorism, and other non-traditional security threats.
Socio-Cultural Cooperation: Fostering a Shared Identity
Recognizing the importance of people-to-people connectivity, ASEAN promotes socio-cultural cooperation among its members. This includes collaborations in education, health, culture, and sports, fostering a shared ASEAN identity and strengthening regional unity.
ASEAN and the World: A Key Player on the Global Stage
ASEAN actively engages with other countries and international organizations through various dialogues and partnerships. It plays a crucial role in promoting regional and global peace, stability, and prosperity. apa itu asean way, ano ang nilalaman ng asean summit
 ASEAN's Global Partnerships
ASEAN's Global Partnerships
What are some of the challenges faced by ASEAN?
Despite its achievements, ASEAN faces several challenges, including differing levels of economic development among member states, political instability in some countries, and territorial disputes. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing commitment and cooperation from all member states.
Conclusion: The Future of ASEAN
What is the ASEAN’s future? The organization continues to evolve and adapt to the changing regional and global landscape. Its commitment to regional cooperation and integration positions ASEAN to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of Southeast Asia and its engagement with the world.
FAQ
- How many members are there in ASEAN? ASEAN has ten member states.
- When was ASEAN established? ASEAN was founded on 8 August 1967.
- What are the three pillars of the ASEAN Community? The three pillars are the Political-Security Community, the Economic Community, and the Socio-Cultural Community.
- What is the main objective of ASEAN? The main objective is to promote regional cooperation and integration in Southeast Asia.
- How does ASEAN engage with the world? ASEAN engages with other countries and international organizations through dialogues and partnerships.
- What is the ASEAN Tourism Agreement? apa itu asean tourism agreement
- What are the benefits of ASEAN membership? Member states benefit from enhanced economic opportunities, increased regional security, and greater socio-cultural exchange.
Need More Information?
For any inquiries or assistance regarding ASEAN, please don’t hesitate to contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our customer service team is available 24/7 to assist you.

