Ase Ef Severity, or the severity of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) as assessed by the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE), is a crucial indicator of heart health and overall cardiovascular risk. It plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing various heart conditions, influencing treatment strategies and predicting patient outcomes. Understanding how ASE EF severity is determined and what it signifies is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
What is ASE EF Severity and Why Does it Matter?
ASE EF severity categorizes the LVEF, a measurement of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction, into different levels of dysfunction. This categorization, based on ASE guidelines, helps standardize the assessment of heart function across different healthcare settings. Why is this so important? Because a weakened heart, indicated by a low LVEF, can lead to a cascade of health problems, including heart failure, shortness of breath, fatigue, and even sudden cardiac death. Knowing the severity of LVEF dysfunction allows doctors to tailor treatment plans and improve patient prognosis.
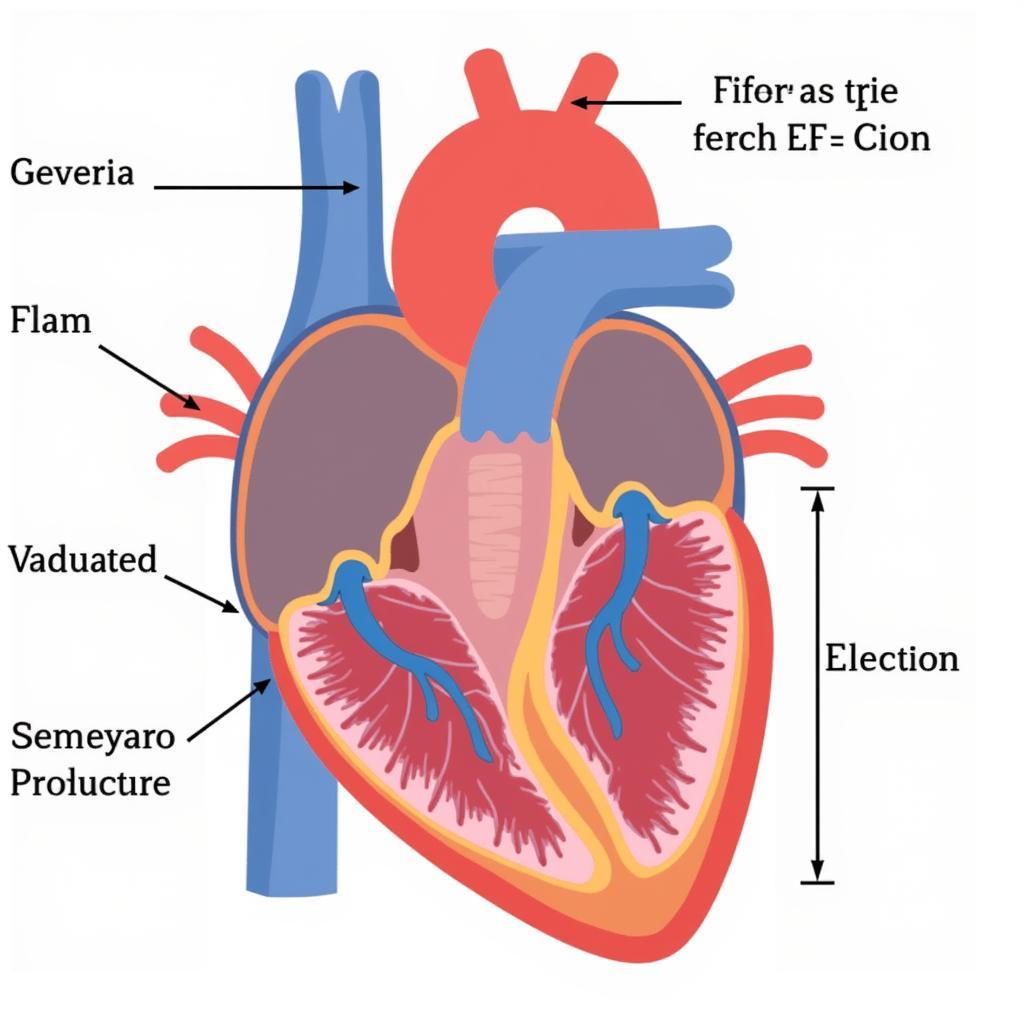 ASE EF Severity and Heart Diagram
ASE EF Severity and Heart Diagram
How is ASE EF Severity Determined?
The ASE has established clear guidelines for assessing LVEF. These guidelines incorporate various echocardiographic techniques, including the biplane method of disks (MOD), which utilizes measurements of the left ventricle’s dimensions during systole and diastole to calculate the EF. The calculated EF is then categorized into different severity levels: normal, mildly reduced, moderately reduced, and severely reduced. Each category corresponds to a specific EF range, allowing for a standardized and consistent evaluation of cardiac function. For further information on valvular stenosis, you can refer to the ase guidelines native valvular stenosis.
Interpreting ASE EF Severity Categories
Understanding what each ASE EF severity category signifies is crucial for effective patient management. A normal EF typically indicates healthy heart function. Mildly reduced EF might suggest early stages of heart dysfunction, warranting close monitoring and lifestyle modifications. Moderately reduced EF often signifies more significant heart damage and necessitates medical intervention. Severely reduced EF indicates significant impairment of heart function, requiring aggressive treatment strategies. It’s important to remember that while these categories provide valuable information, they should be interpreted in conjunction with the patient’s overall clinical picture. You can also find helpful resources on diastolic function at ase guidelines diastolic function 2016 ppt.
The Impact of ASE EF Severity on Treatment Decisions
ASE EF severity plays a critical role in guiding treatment decisions for patients with heart conditions. The severity level influences the choice of medications, the need for implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators, and the consideration of advanced therapies like heart transplantation. A comprehensive summary of ASE valvular values can be found at ase valvular values summary.
Living with Different Levels of ASE EF Severity
Living with reduced EF can present various challenges depending on the severity level. Patients with mildly reduced EF may experience minimal symptoms and can often manage their condition with lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring. However, as the severity increases, symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles become more prominent, requiring more intensive medical management. Understanding the implications of each severity level empowers patients to actively participate in their care and make informed decisions about their health. Information on mitral stenosis is available at ase mitral stenosis.
“Understanding the patient’s ASE EF severity is like having a roadmap. It helps us navigate the complexities of heart disease and tailor treatment strategies for optimal outcomes,” says Dr. Amelia Carter, a leading cardiologist at the Southeast Asia Heart Institute.
 ASE EF Severity and Lifestyle Changes
ASE EF Severity and Lifestyle Changes
In conclusion, ASE EF severity provides a standardized and valuable framework for assessing and managing heart function. Understanding its implications empowers both healthcare professionals and patients to make informed decisions and improve cardiovascular health outcomes. For more information about hypertrophic cardiomyopathy guidelines, visit ase hypertrophic cardiomyopathy guidelines. This understanding is vital for navigating the complexities of heart disease and achieving better patient outcomes.
FAQ
- What is a normal EF range?
- What causes a reduced EF?
- Can EF improve over time?
- What are the long-term implications of reduced EF?
- What lifestyle changes can improve EF?
- How often should I get my EF checked?
- What should I do if my EF is low?
Need support? Contact us 24/7 at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] or visit our address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.

