ASEAN as an intergovernmental organization plays a crucial role in Southeast Asia’s political, economic, and social landscape. Formed in 1967, ASEAN has grown from its initial five members to ten, representing a diverse tapestry of cultures, economies, and political systems. This article delves into the structure, functions, and impact of ASEAN as a key player in regional and global affairs.
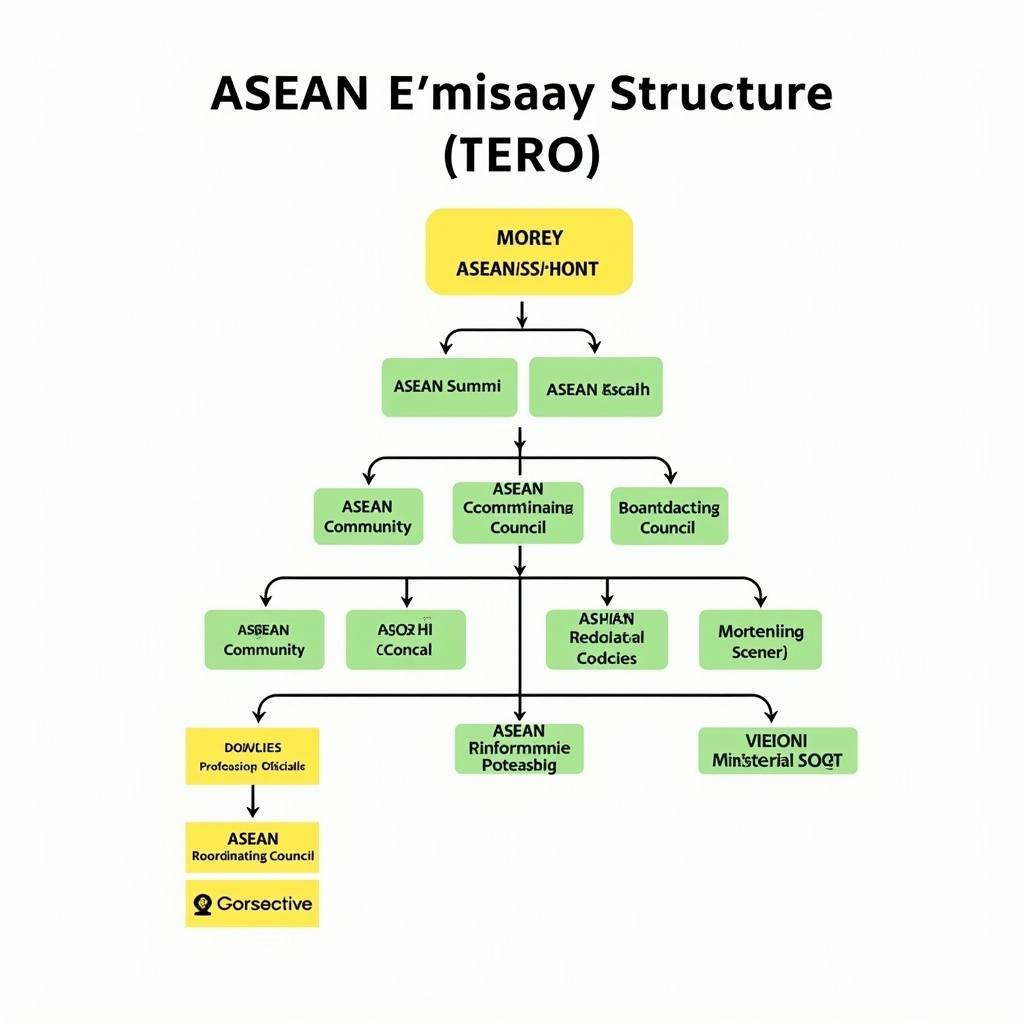 ASEAN Intergovernmental Organization Structure
ASEAN Intergovernmental Organization Structure
Understanding ASEAN’s Intergovernmental Structure
ASEAN’s framework as an intergovernmental organization is designed to facilitate cooperation and coordination among its member states. The abbreviation for asean stands for Association of Southeast Asian Nations. It operates on the principle of consensus-based decision-making, ensuring that all members have a voice and that decisions reflect the shared interests of the region. This structure allows for a balance of power and promotes a sense of ownership among the member states. But how does this work in practice? Different bodies within ASEAN perform specific roles, ranging from setting the overall direction to implementing specific initiatives.
The Role of the ASEAN Summit
The ASEAN Summit, comprising the heads of state or government of each member state, is the supreme decision-making body. It provides strategic guidance and sets the overall direction for ASEAN’s development. The Summit meets twice a year to discuss key issues and chart the course for regional cooperation. This regular interaction fosters a sense of community and helps to build trust among the leaders.
ASEAN’s Key Functions: Fostering Cooperation and Integration
As an intergovernmental organization, ASEAN plays a vital role in promoting peace, stability, and prosperity in the region. It achieves this through various functions, including political and security cooperation, economic integration, and socio-cultural development. For example, ASEAN has been instrumental in facilitating dialogue and resolving disputes among member states, contributing to a more peaceful and stable region. Through initiatives like the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), it has fostered economic integration, promoting trade and investment within the region.
Economic Integration: Driving Growth and Development
ASEAN’s economic integration efforts aim to create a single market and production base, enhancing competitiveness and attracting foreign investment. The asean and eu comparative analysis provides insights into different integration models. Initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) blueprint outline specific steps toward achieving this goal. These measures include reducing tariffs, harmonizing regulations, and facilitating the free flow of goods, services, and skilled labor.
Addressing Human Rights and Promoting Social Justice
While ASEAN’s primary focus is on economic and political cooperation, it also recognizes the importance of human rights and social justice. The aichr asean plays a significant role in promoting and protecting human rights in the region. While challenges remain, ASEAN has made strides in addressing these issues, including the establishment of the ASEAN Intergovernmental Commission on Human Rights (AICHR). The asean 2017 human rights report highlights the progress made and the ongoing efforts to strengthen human rights mechanisms in the region.
Conclusion: ASEAN’s Continuing Evolution as an Intergovernmental Organization
ASEAN as an intergovernmental organization continues to evolve, adapting to the changing dynamics of the region and the world. Its role in promoting regional cooperation, economic integration, and peaceful conflict resolution is undeniable. While challenges remain, ASEAN’s commitment to collaboration and its diverse membership position it as a vital force in shaping the future of Southeast Asia. What is the apa kepanjangan asean?
FAQ
- What are the main objectives of ASEAN?
- How does ASEAN promote economic cooperation?
- What is the role of the ASEAN Secretariat?
- How does ASEAN address regional security challenges?
- What are the future prospects for ASEAN integration?
- How does ASEAN engage with other international organizations?
- How can I get involved in ASEAN activities?
Please contact us for further support at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] Or visit us at: Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.