Southeast Asia, a vibrant and dynamic region, is home to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic alliance of 10 Countries Of Asean. These nations, diverse in their cultures, languages, and histories, are united by a common goal of promoting regional cooperation and development. From bustling metropolises to tranquil rice paddies, the countries of ASEAN offer a captivating blend of tradition and modernity.
Unveiling the 10 Countries of ASEAN
The ASEAN community encompasses a rich tapestry of nations, each with its unique charm and character. These countries, geographically clustered in Southeast Asia, are: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. They represent a fascinating spectrum of cultural influences, from ancient empires to colonial legacies, shaping their present identities.
What are the countries of ASEAN and what makes them unique? Let’s delve into the individual characteristics of these nations, exploring their historical backgrounds, economic landscapes, and cultural nuances.
Brunei, a tiny but wealthy nation on the island of Borneo, is known for its opulent royal family and vast oil reserves. Cambodia, a land steeped in history, boasts the magnificent Angkor Wat temple complex, a testament to the Khmer Empire’s grandeur. Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago, is a melting pot of cultures and languages, with breathtaking natural beauty from Bali’s beaches to Sumatra’s rainforests.
what are the countries of asean
Laos, a landlocked nation known as the “Land of a Million Elephants,” offers a tranquil escape with its serene landscapes and Buddhist temples. Malaysia, a multicultural country with a blend of Malay, Chinese, and Indian influences, is a dynamic hub of commerce and tourism. Myanmar, also known as Burma, is emerging from decades of isolation, revealing its rich cultural heritage and stunning pagodas.
The Philippines, an archipelago of over 7,000 islands, is renowned for its warm hospitality, vibrant festivals, and stunning beaches. Singapore, a city-state known for its efficiency and modernity, is a global financial center and a testament to urban planning. Thailand, the “Land of Smiles,” captivates visitors with its ancient temples, bustling markets, and idyllic beaches. Vietnam, a country shaped by its resilient spirit and rich history, is experiencing rapid economic growth and development.
ASEAN Integration: A Catalyst for Growth
The formation of ASEAN has been instrumental in fostering economic cooperation and regional integration among its member states. Through initiatives like the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), the countries of ASEAN have significantly reduced trade barriers, promoting intra-regional trade and investment.
What are the benefits of ASEAN integration? The reduction of tariffs and non-tariff barriers has facilitated the flow of goods and services within the region, creating a larger market for businesses and consumers. This has led to increased competition, lower prices, and greater consumer choice.
Cultural Exchange within ASEAN
Beyond economic cooperation, ASEAN also plays a vital role in promoting cultural exchange and understanding among its member countries. Through various programs and initiatives, ASEAN fosters dialogue and interaction between different cultures, strengthening the bonds of friendship and cooperation.
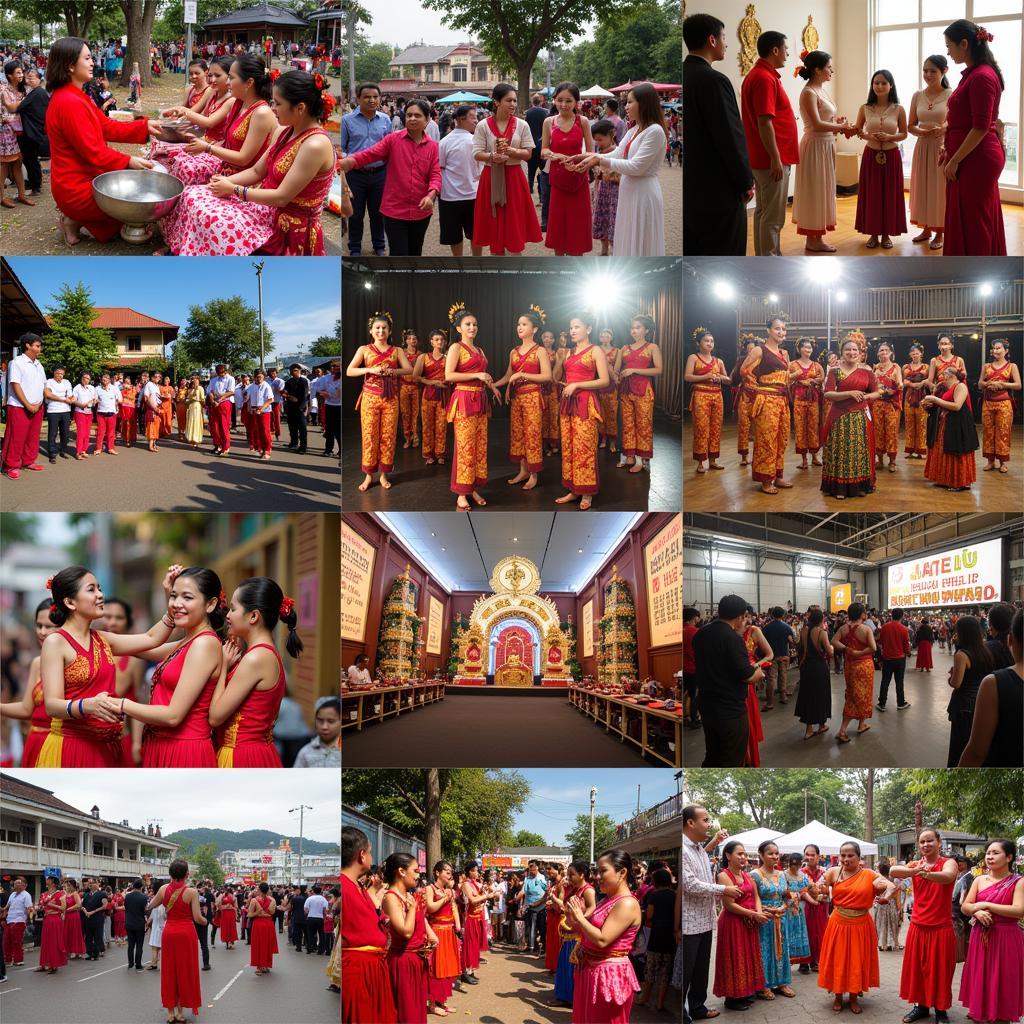 ASEAN Cultural Exchange
ASEAN Cultural Exchange
“ASEAN’s strength lies in its diversity,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a prominent Southeast Asian anthropologist. “By embracing their cultural differences, these nations create a vibrant tapestry that enriches the region as a whole.”
ASEAN’s Role on the Global Stage
As a collective entity, ASEAN wields considerable influence on the global stage. The organization actively participates in international forums, advocating for the interests of its member states and promoting regional stability and security. Through its diplomatic efforts, ASEAN plays a crucial role in shaping the political and economic landscape of Southeast Asia.
“ASEAN’s collective voice amplifies the concerns and aspirations of Southeast Asian nations on the global stage,” notes Professor Kenji Tanaka, a leading expert on international relations. “By working together, these countries can effectively address shared challenges and advance their collective interests.”
10 member countries of asean integration
The Future of ASEAN: A Region of Promise
The countries of ASEAN, with their dynamic economies and rich cultural heritage, hold immense potential for future growth and development. As the region continues to integrate and embrace globalization, the ASEAN community is poised to become a major force in the 21st century.
In conclusion, the countries of ASEAN represent a dynamic and diverse region, united by their shared commitment to regional cooperation and development. From Brunei to Vietnam, each nation contributes its unique strengths and characteristics to the ASEAN community, creating a vibrant tapestry of cultures and economies. The future of ASEAN is bright, promising a region of continued growth, prosperity, and cultural exchange.
FAQ:
- What is ASEAN?
- How many countries are in ASEAN?
- What are the benefits of ASEAN membership?
- How does ASEAN promote regional cooperation?
- What is the role of ASEAN in the global economy?
- How does ASEAN promote cultural exchange?
- What are the future prospects for ASEAN?
For further information and support regarding ASEAN, please contact us at Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit our office at Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.