The Afta Asean Free Trade Agreement is a cornerstone of Southeast Asian economic integration. Established in 1992, it aims to boost intra-ASEAN trade by reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers. This article delves into the intricacies of AFTA, exploring its impact, benefits, and challenges.
What is the AFTA ASEAN Free Trade Agreement?
AFTA’s primary goal is to create a single market and production base within ASEAN, making the region more competitive globally. It does this by reducing or eliminating tariffs on most goods traded within the region. This encourages businesses to invest and operate across borders, stimulating economic growth and creating job opportunities. The asean free trade area agreement is a key driver of prosperity in Southeast Asia.
Key Features of AFTA
AFTA operates on several key principles, including:
- Tariff Reduction: Most tariffs on goods traded within ASEAN have been reduced to 0-5%. This has made ASEAN goods more affordable and competitive.
- Non-Tariff Barrier Reduction: AFTA also addresses non-tariff barriers, such as customs procedures and technical regulations, to facilitate smoother trade.
- Trade Facilitation: Measures like simplified customs procedures and harmonized standards help expedite the movement of goods across borders.
- Rules of Origin: These rules ensure that only goods originating from ASEAN countries benefit from AFTA preferences.
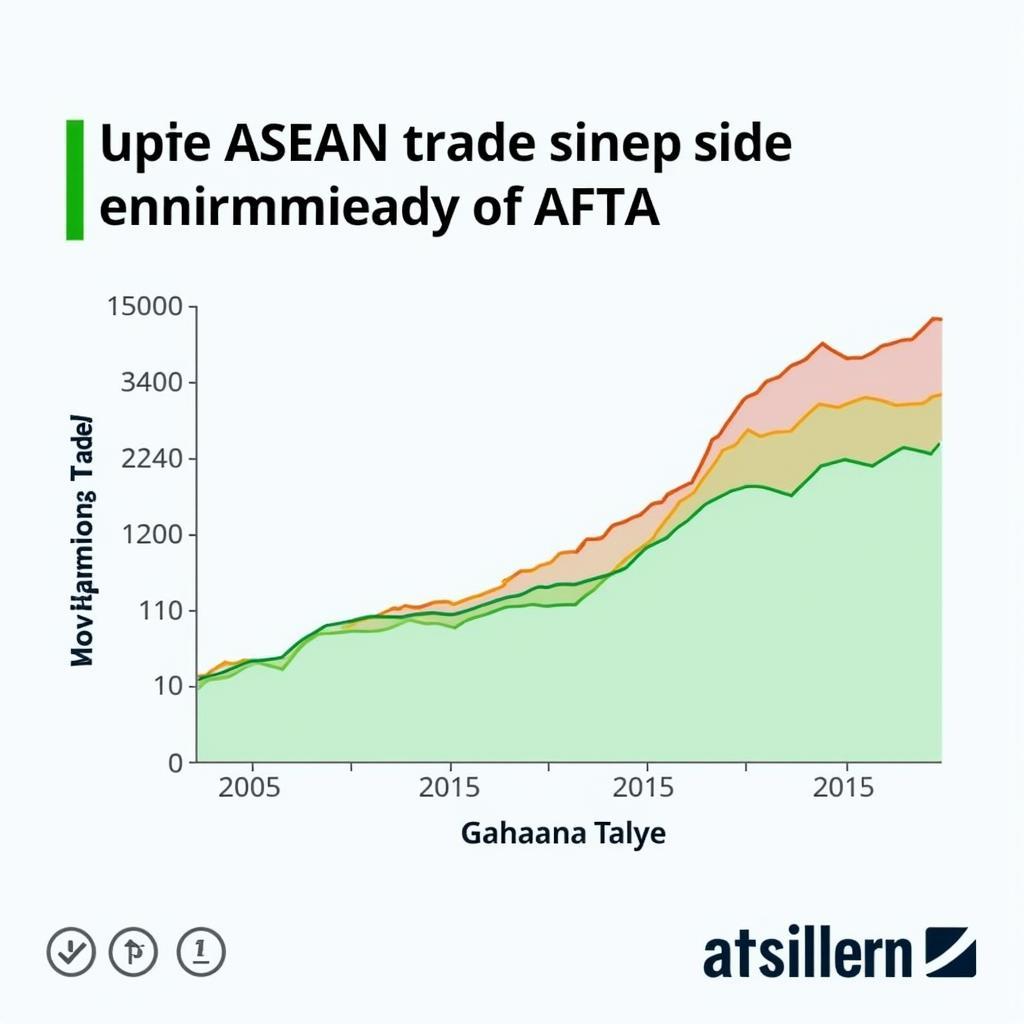 The Impact of AFTA on ASEAN Economies
The Impact of AFTA on ASEAN Economies
Benefits of AFTA
The advantage of asean free trade area are numerous, including increased trade, foreign investment, and economic growth. Businesses have access to a larger market, consumers enjoy lower prices, and the region has become more attractive to foreign investors.
How does AFTA benefit consumers?
AFTA directly benefits consumers by offering them a wider selection of products at competitive prices. This can lead to improved living standards and greater consumer choice.
Challenges and Future of AFTA
While AFTA has achieved significant success, it faces challenges, including non-tariff barriers, varying levels of development among member states, and external competition.
What are the remaining challenges for AFTA?
Despite its successes, AFTA still faces challenges such as persistent non-tariff barriers and the need to further harmonize regulations and standards across member states. The asean main objective is to continually improve and strengthen the agreement.
“AFTA has been instrumental in transforming Southeast Asia into a dynamic economic region,” says Dr. Maria Santos, a leading economist specializing in ASEAN trade. “Its impact on regional integration and prosperity is undeniable.”
Conclusion
The AFTA ASEAN Free Trade Agreement has played a crucial role in promoting regional economic integration and driving growth in Southeast Asia. While challenges remain, its continued evolution is essential for the region’s future prosperity. The apa itu intra asean question is central to understanding the importance of AFTA.
FAQ
- What is the main purpose of AFTA? To increase trade within ASEAN by reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
- When was AFTA established? 1992
- How does AFTA benefit businesses? It provides access to a larger market and reduces trade costs.
- What are some of the challenges facing AFTA? Non-tariff barriers and varying levels of development among member states.
- How does AFTA impact consumers? Lower prices and greater product variety.
- What is the future of AFTA? Continued efforts to further reduce barriers and enhance regional integration.
- Where can I find more information on AFTA’s rules and regulations? ase q and a provides valuable insights.*
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7 at Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, or visit us at Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam.