The ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services (AFAS) is a key initiative of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to liberalize trade in services among its member states. It aims to create a more open, transparent, and predictable environment for service providers in the region.
What is AFAS?
AFAS was first established in 1995 with the goal of enhancing cooperation in the services sector among ASEAN member states. The agreement seeks to facilitate the progressive liberalization of trade in services through successive rounds of negotiations. These negotiations cover a wide range of service sectors, including financial services, telecommunications, tourism, and professional services.
 ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services Negotiations
ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services Negotiations
Objectives of AFAS
The primary objective of AFAS is to eliminate barriers and restrictions to trade in services between ASEAN member states. By creating a more liberalized environment, AFAS aims to:
- Boost economic growth: Enhanced trade in services is expected to contribute to economic growth and development in the ASEAN region.
- Increase competitiveness: By promoting competition and efficiency, AFAS aims to enhance the competitiveness of ASEAN service providers in the global market.
- Attract foreign investment: A more open and transparent services sector is likely to attract greater foreign direct investment into ASEAN economies.
- Create jobs: Liberalization of the services sector is expected to generate new employment opportunities, particularly in sectors like tourism, telecommunications, and finance.
Key Features of AFAS
The AFAS framework incorporates several key features:
- Most-Favored-Nation (MFN) Treatment: ASEAN member states are obligated to extend to each other treatment no less favorable than that accorded to any other country.
- National Treatment: Services and service providers from ASEAN member states should be treated no less favorably than domestic services and service providers.
- Transparency: ASEAN member states are required to ensure transparency in their laws, regulations, and procedures affecting trade in services.
- Progressive Liberalization: AFAS adopts a phased approach to liberalization, with commitments being gradually expanded over time through rounds of negotiations.
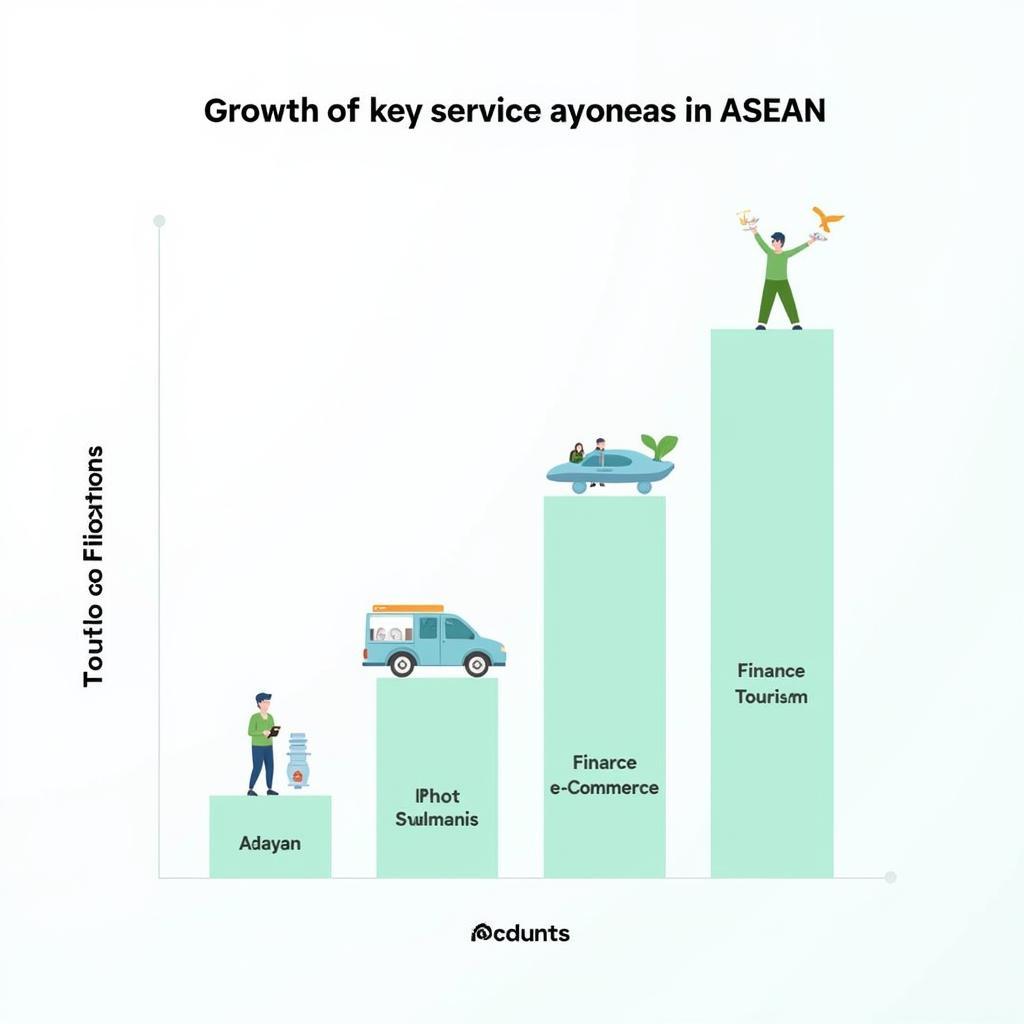 Growth of Service Sectors in ASEAN
Growth of Service Sectors in ASEAN
How Does AFAS Work?
AFAS operates through a series of agreements, packages of commitments, and negotiations. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Framework Agreement: This sets the overall principles and objectives for trade in services liberalization.
- Schedules of Commitments: Each member state submits a schedule outlining the specific service sectors where it is making market access commitments.
- Rounds of Negotiations: Regular negotiations are held to further liberalize trade in services and expand the scope of commitments.
Benefits of AFAS
AFAS offers several potential benefits:
- Increased market access: Service providers in ASEAN gain preferential access to larger markets within the region.
- Reduced costs: The elimination of barriers and restrictions can lead to lower costs for service providers.
- Greater competition: Increased competition encourages innovation and improves the quality of services.
- Job creation: The expansion of the services sector is expected to create new job opportunities.
 Future Outlook for AFAS
Future Outlook for AFAS
Challenges and Future Outlook
While AFAS has made significant strides in liberalizing trade in services, challenges remain:
- Non-tariff barriers: Regulations, licensing requirements, and other non-tariff barriers can still hinder trade in some sectors.
- Implementation gaps: There can be discrepancies between commitments made under AFAS and actual implementation at the national level.
Moving forward, ASEAN is focused on:
- Deepening integration: Further liberalizing trade in services and addressing remaining barriers.
- Strengthening implementation: Ensuring effective implementation of AFAS commitments across all member states.
- Harnessing digital trade: Adapting AFAS to the digital economy and promoting e-commerce in services.
Conclusion
The ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services (AFAS) is a testament to ASEAN’s commitment to economic integration and liberalization. By promoting greater openness and cooperation in the services sector, AFAS has the potential to unlock significant economic benefits for the region. As ASEAN continues to deepen integration and address remaining challenges, AFAS will play a pivotal role in shaping a more prosperous and interconnected Southeast Asia.
For those seeking more information on how to navigate the Asean Media landscape, resources like the AP style ASEAN guide and the ASE READ function offer valuable insights. Meanwhile, the ASE A5 study guide provides a comprehensive overview of important ASEAN agreements.
Do you have questions about specific ASEAN regulations or need help with media outreach in Southeast Asia? Contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit us at Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam. Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to assist you.

