The ACFTA agreement, spearheaded by the ASEAN Secretariat, stands as a testament to the region’s commitment to economic integration and shared prosperity. This comprehensive free trade pact significantly impacts businesses and economies across Southeast Asia, fostering a dynamic environment for growth and development. But what exactly does the ACFTA entail, and how does it work in practice?
Demystifying the ACFTA: Key Features and Objectives
The ACFTA, short for ASEAN-China Free Trade Area, is a trade agreement between the ten member states of ASEAN and China. Established in 2010, it represents the world’s largest free trade area in terms of population, encompassing a market of over 2 billion people.
The agreement’s primary objective is to boost economic cooperation and eliminate barriers to trade between ASEAN and China. This is achieved through:
- Tariff reductions and eliminations: ACFTA progressively reduces and eliminates tariffs on a wide range of goods traded between participating countries.
- Trade facilitation measures: The agreement simplifies customs procedures, streamlines regulations, and promotes transparency to make cross-border trade smoother and more efficient.
- Investment liberalization: ACFTA encourages greater investment flows between ASEAN and China by providing a more predictable and open investment environment.
Delving Deeper: The Impact and Benefits of the ACFTA Agreement
The ACFTA agreement has had a profound impact on the economic landscape of Southeast Asia. Let’s explore some of its key benefits:
1. Increased Trade and Investment Flows
By lowering trade barriers, the ACFTA has significantly boosted trade between ASEAN and China. This increased trade volume translates to economic growth and job creation in both regions.
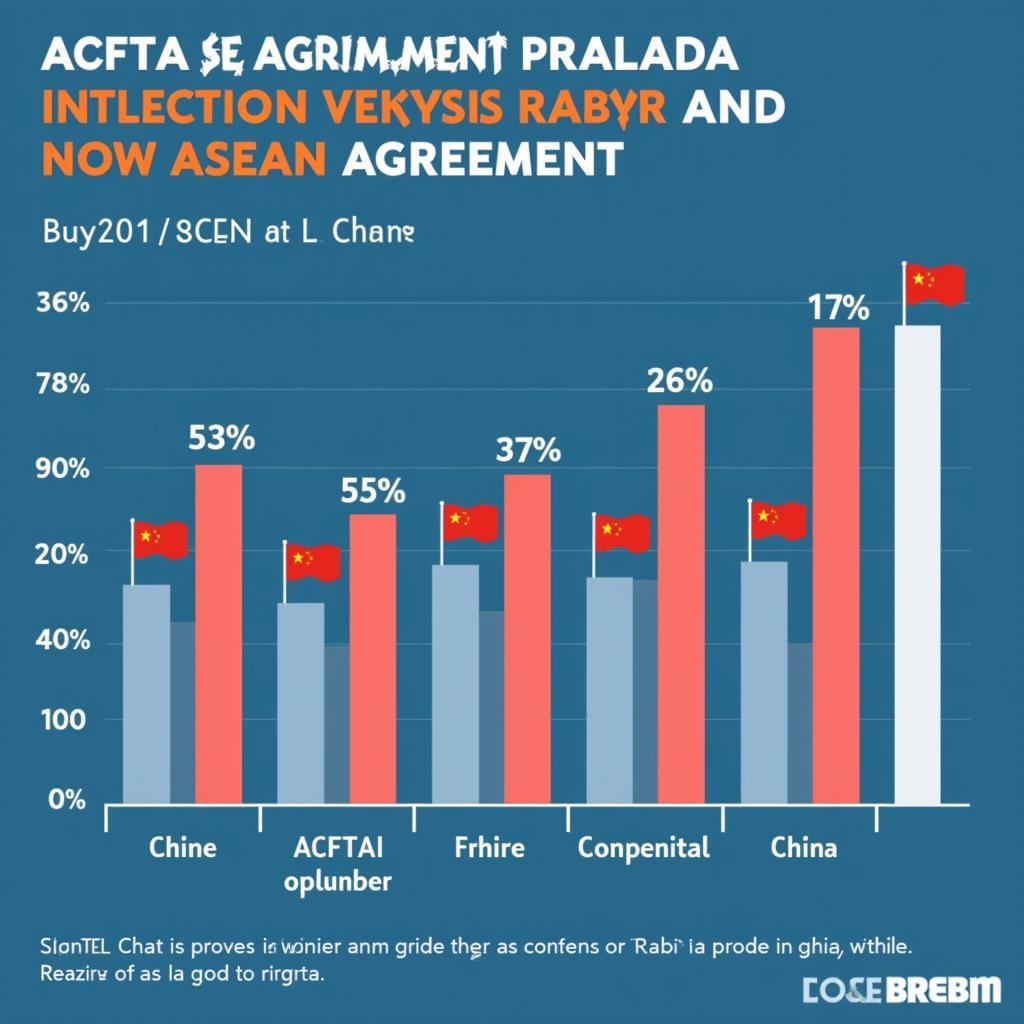 ASEAN-China Trade Growth Chart
ASEAN-China Trade Growth Chart
2. Enhanced Competitiveness
The ACFTA fosters a competitive business environment that drives innovation and efficiency. Businesses in ASEAN benefit from access to a larger market and lower-cost inputs from China, while Chinese companies gain access to ASEAN’s diverse consumer base and resources.
3. Regional Integration and Cooperation
Beyond its economic impact, the ACFTA strengthens political and cultural ties between ASEAN and China. The agreement provides a platform for dialogue, collaboration, and the peaceful resolution of trade-related issues.
Navigating the ACFTA: Rules of Origin and Implementation
To benefit from the preferential tariff rates under the ACFTA, businesses must comply with the agreement’s rules of origin. These rules determine the nationality of a product and ensure that only goods originating from ASEAN or China receive preferential treatment.
 ACFTA Rules of Origin Guide
ACFTA Rules of Origin Guide
The ASEAN Secretariat plays a crucial role in overseeing the implementation of the ACFTA. It provides technical assistance to member states, monitors compliance with the agreement, and facilitates dialogue on trade-related issues.
Conclusion: ACFTA – A Catalyst for Shared Prosperity
The ACFTA agreement, facilitated by the ASEAN Secretariat, stands as a cornerstone of economic integration in Southeast Asia. It has successfully fostered trade, investment, and regional cooperation, paving the way for a more prosperous and interconnected ASEAN. As the agreement continues to evolve, its impact on the region’s economic landscape is expected to grow even further.
FAQs about the ACFTA Agreement:
-
What are the main product categories covered under the ACFTA?
The ACFTA covers a wide range of products, including manufactured goods, agricultural products, and processed food products. -
How can businesses determine if their products qualify for preferential tariffs under the ACFTA?
Businesses should consult their local customs authorities or refer to the ASEAN Secretariat’s guidelines on rules of origin. -
What are the dispute settlement mechanisms available under the ACFTA?
The agreement includes provisions for consultations and dispute settlement mechanisms to address trade-related disagreements between participating countries.