Navigating the complexities of intellectual property (IP) management in the dynamic ASEAN region requires a strategic and informed approach. With its diverse cultures, evolving regulations, and booming economic landscape, ASEAN presents unique opportunities and challenges for businesses looking to protect and leverage their intellectual property.
This guide provides valuable insights into ASEAN management IP, covering essential aspects from understanding different types of IP rights to navigating the registration process and enforcement mechanisms within the region.
Understanding IP and its Importance in ASEAN
Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, and symbols, names, and images used in commerce. It’s a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes, providing a competitive edge and fostering innovation and growth.
In the context of ASEAN, effective IP management is crucial for several reasons:
- Economic Growth: ASEAN is one of the fastest-growing economic regions globally, making it a hub for innovation and creativity. Strong IP protection encourages investment, attracts foreign direct investment, and promotes economic development.
- Foreign Investment: Investors are more likely to invest in countries with robust IP protection frameworks, as it provides a sense of security and confidence in the legal system.
- Brand Building: Protecting trademarks and other forms of IP helps businesses establish strong brand identities and differentiate themselves in the marketplace.
 ASEAN brand protection image
ASEAN brand protection image
Types of Intellectual Property Rights in ASEAN
ASEAN recognizes several types of intellectual property rights, each with its own set of laws and regulations:
- Patents: Granted for new inventions, including products and processes. In ASEAN, patents generally have a maximum term of 20 years from the filing date.
- Trademarks: Distinctive signs that identify goods or services of a particular enterprise. They can be words, logos, symbols, or a combination of these elements. Trademark protection in ASEAN typically lasts for ten years and is renewable indefinitely.
- Copyrights: Legal protection granted to creators of original literary and artistic works, including books, music, films, and software. Copyright protection in ASEAN generally lasts for the lifetime of the author plus 50 years.
- Industrial Designs: Protect the aesthetic aspects of a product, such as its shape, configuration, or pattern. Design protection in ASEAN typically lasts for five years and can be renewed for up to a total of 15 years.
- Geographical Indications: Signs used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation due to that origin.
Navigating the IP Registration Process in ASEAN
While ASEAN has made significant strides towards IP harmonization, the registration process for different IP rights varies across member states. However, some general steps apply:
- IP Search: Before filing for IP protection, it’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive search to ensure no conflicting marks or inventions exist.
- Filing an Application: Applications are typically filed with the respective national IP office of the ASEAN member state where protection is sought.
- Examination Process: The IP office examines the application to determine if it meets the requirements for registration.
- Publication and Opposition: If the application meets the criteria, it is published, allowing third parties to oppose the registration.
- Registration and Maintenance: Once the opposition period expires, and any oppositions are resolved, the IP right is registered, and the applicant must pay renewal fees to maintain the protection.
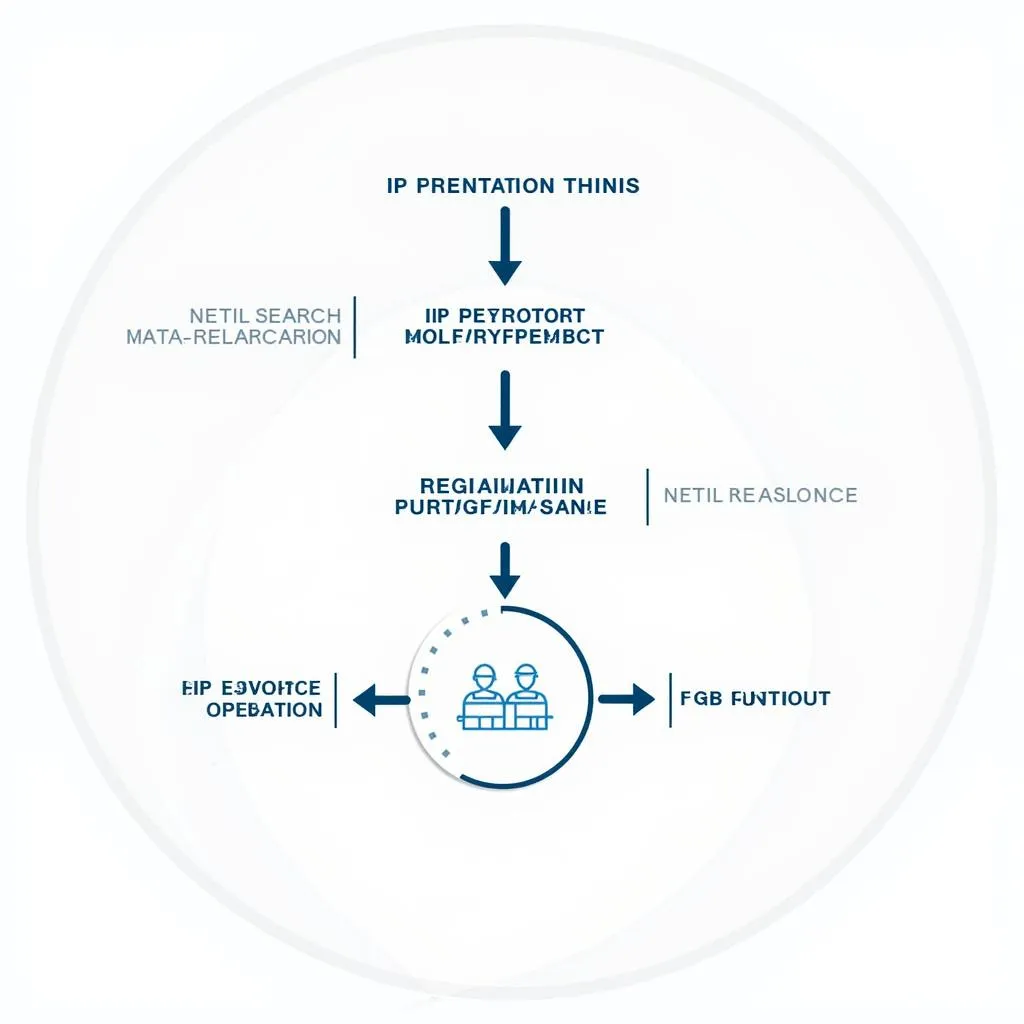 ASEAN IP registration process flowchart
ASEAN IP registration process flowchart
Enforcing Intellectual Property Rights in ASEAN
Enforcing IP rights in ASEAN involves various legal avenues and mechanisms. Businesses that believe their IP rights have been infringed upon can take the following actions:
- Civil Litigation: Filing a lawsuit in the relevant national court is a common approach to seek remedies such as injunctions, damages, and the destruction of infringing goods.
- Criminal Prosecution: In some cases, particularly for trademark counterfeiting and copyright piracy, criminal prosecution is possible, leading to fines and imprisonment.
- Administrative Enforcement: Certain ASEAN member states have administrative enforcement mechanisms, allowing authorities to seize counterfeit goods and impose fines.
Tips for Effective ASEAN Management IP
- Develop a Comprehensive IP Strategy: Businesses should develop a clear IP strategy aligned with their overall business objectives.
- Conduct Due Diligence: Thorough due diligence is crucial when entering new markets within ASEAN, understanding the specific IP laws and regulations of each country.
- Engage with Local Expertise: Seeking guidance from local IP lawyers and consultants can prove invaluable in navigating the nuances of ASEAN’s diverse legal landscape.
- Monitor the Market: Regularly monitoring the market for potential infringements and taking swift action is vital for protecting IP rights.
 ASEAN IP enforcement measures
ASEAN IP enforcement measures
Conclusion
Effective ASEAN management IP is paramount for businesses looking to thrive in this dynamic region. By understanding the intricacies of IP rights, navigating the registration process strategically, and implementing robust enforcement mechanisms, businesses can safeguard their innovations, build strong brands, and foster a culture of respect for intellectual property within ASEAN. For any assistance or guidance regarding IP matters in Southeast Asia, do not hesitate to reach out to us. Contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com Or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.