APEC, ASEAN, and NAFTA are acronyms often encountered in discussions about international trade and economic cooperation. These three represent significant trade blocs that have shaped the global economic landscape in profound ways. While each organization has its unique characteristics and objectives, they all share the common goal of fostering economic growth and cooperation among member nations. This article delves into the history, purpose, and impact of APEC, ASEAN, and NAFTA, shedding light on their relevance in today’s interconnected world.
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
Established in 1989, APEC is a regional economic forum comprising 21 economies around the Pacific Rim. Unlike traditional trade blocs that establish legally binding agreements, APEC operates based on consensus and open dialogue. Its primary goal is to promote free trade and investment, facilitate business, and encourage economic cooperation across the Asia-Pacific region.
Key Features of APEC
- Focus on Regional Economic Integration: APEC emphasizes reducing trade barriers, harmonizing regulations, and promoting economic and technical cooperation among member economies.
- Diverse Membership: APEC’s membership spans four continents and includes economies of varying sizes and stages of development, reflecting the region’s economic diversity.
- Non-Binding Commitments: APEC agreements are non-binding, allowing member economies flexibility in implementation and encouraging a cooperative approach to economic integration.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Founded in 1967, ASEAN is a political and economic union of 10 Southeast Asian countries. It aims to accelerate economic growth, social progress, and cultural development among its members while promoting regional peace and stability. ASEAN plays a crucial role in fostering economic integration and cooperation within Southeast Asia.
Key Pillars of ASEAN
- ASEAN Economic Community: This pillar focuses on creating a single market and production base, enhancing competitiveness, and promoting equitable economic development within ASEAN.
- ASEAN Security Community: This pillar aims to address traditional and non-traditional security challenges through dialogue and cooperation, contributing to regional peace and stability.
- ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community: This pillar emphasizes the development of human resources, social protection, environmental sustainability, and the promotion of ASEAN identity and cultural diversity.
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
NAFTA, established in 1994, was a trilateral trade agreement between Canada, Mexico, and the United States. It aimed to eliminate trade barriers and facilitate the cross-border movement of goods, services, and investments among the three North American nations.
Impact and Evolution of NAFTA
NAFTA significantly impacted the economies of its member countries, leading to increased trade, investment, and economic interdependence. However, it also sparked debates about job displacement and the impact on certain industries. In 2020, NAFTA was replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which retained many of NAFTA’s provisions while introducing updated rules on digital trade, labor, and environmental standards.
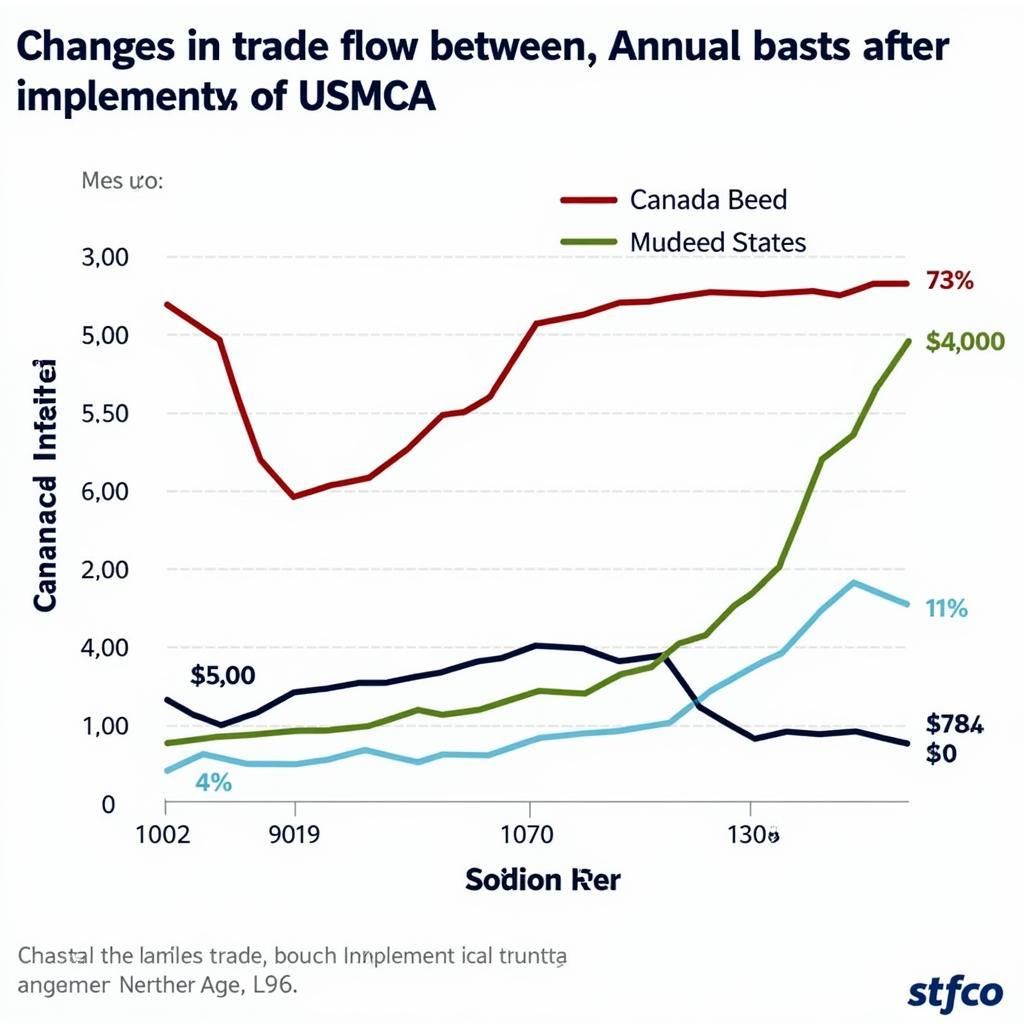 Trade Flow under NAFTA and USMCA
Trade Flow under NAFTA and USMCA
Comparing APEC, ASEAN, and NAFTA
While APEC, ASEAN, and NAFTA share the common goal of promoting economic cooperation, they differ in geographical scope, membership, and the nature of their agreements.
- Geographical Focus: APEC covers the Asia-Pacific region, ASEAN focuses on Southeast Asia, and NAFTA/USMCA involves North America.
- Legal Binding: NAFTA/USMCA is a legally binding agreement with established dispute settlement mechanisms. In contrast, APEC relies on voluntary commitments and consensus-building. ASEAN’s agreements are becoming increasingly legally binding as the organization deepens its integration.
- Scope: APEC focuses primarily on economic cooperation and trade liberalization. ASEAN has a broader mandate, encompassing political, security, and socio-cultural cooperation. NAFTA/USMCA primarily addresses trade and investment issues.
The Future of Trade Blocs
In an increasingly interconnected world, trade blocs like APEC, ASEAN, and NAFTA/USMCA will continue to play a vital role in shaping the global economic landscape. As countries seek to deepen economic ties, address shared challenges, and navigate the complexities of international trade, these organizations provide platforms for dialogue, cooperation, and rule-setting. The future of these trade blocs will be shaped by evolving geopolitical dynamics, technological advancements, and the ongoing efforts to create a more inclusive and sustainable global economy.
 Network of Global Trade Blocs
Network of Global Trade Blocs
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between APEC and ASEAN?
APEC is a regional economic forum spanning the Asia-Pacific region, while ASEAN is a political and economic union of Southeast Asian countries. APEC focuses primarily on trade and investment liberalization, while ASEAN has a broader mandate that includes political, security, and socio-cultural cooperation. -
How did NAFTA impact its member countries?
NAFTA led to increased trade, investment, and economic interdependence between Canada, Mexico, and the United States. It also sparked debates about job displacement and its impact on certain industries. -
What is the significance of trade blocs in the global economy?
Trade blocs promote economic cooperation, reduce trade barriers, and foster regional integration. They can boost trade, attract investment, and contribute to economic growth in member countries. -
What are some of the challenges faced by trade blocs?
Trade blocs can face challenges such as managing economic disparities between member countries, addressing non-tariff barriers to trade, and adapting to evolving global trade patterns. -
What is the future outlook for trade blocs like APEC, ASEAN, and USMCA?
These trade blocs are expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping regional and global trade rules, fostering economic cooperation, and addressing shared challenges in an interconnected world.
For any inquiries or assistance, please reach out to us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you. You can also explore our other informative articles on APEC, ASEAN and NAFTA, ASEAN Canada Free Trade Agreement and APEC and ASEAN comparison for further insights.