ASEAN as ESE, or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations as an Economic, Sociocultural, and Environmental entity, highlights the interconnectedness and shared destiny of the region. While often viewed through an economic lens, ASEAN’s true potential lies in embracing its multifaceted identity, acknowledging the intricate interplay between economic progress, social harmony, and environmental sustainability.
Beyond Economics: ASEAN as a Tapestry of Cultures and Values
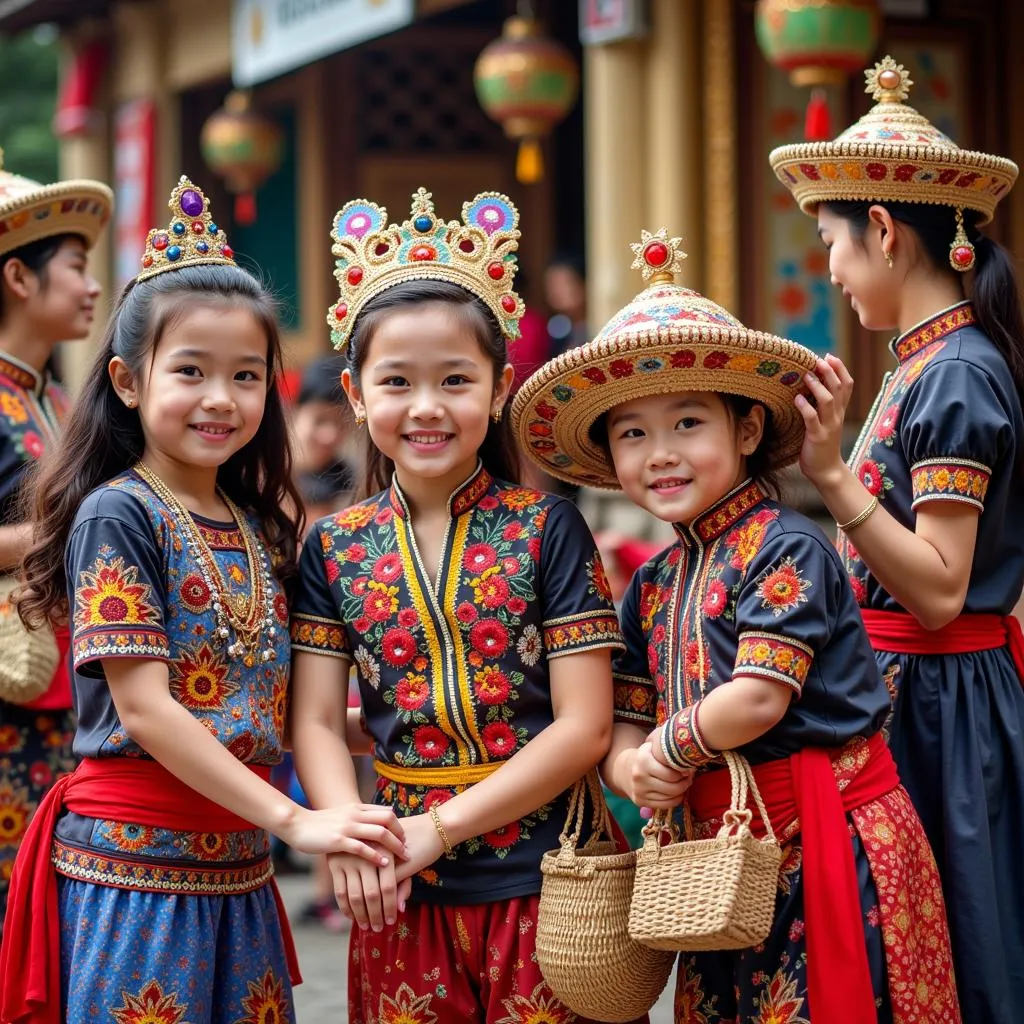 Cultural Diversity in ASEAN
Cultural Diversity in ASEAN
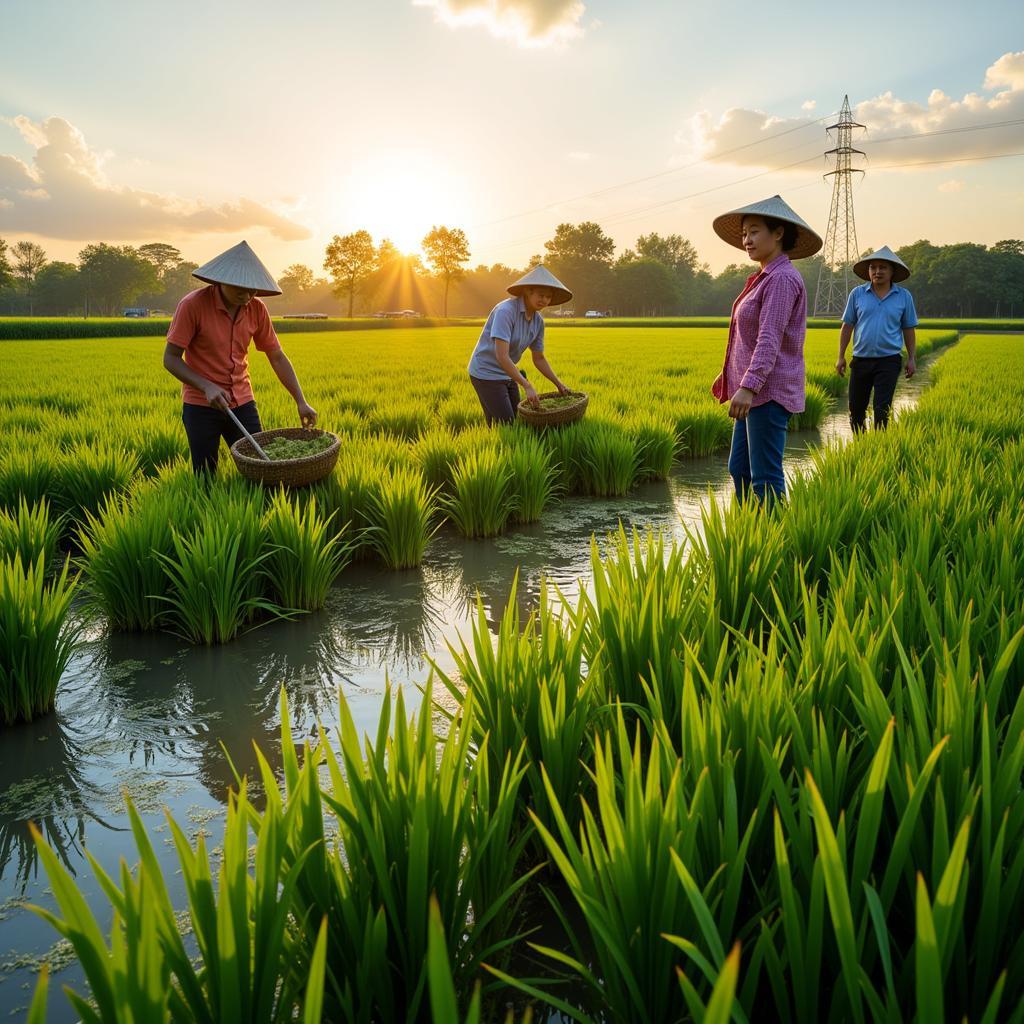
ASEAN is home to a mesmerizing array of cultures, languages, and religions. This diversity, far from being a point of division, is a source of strength and resilience. From the ancient temples of Angkor Wat to the bustling streets of Bangkok, from the serene rice paddies of Vietnam to the vibrant coral reefs of the Philippines, ASEAN is a region brimming with cultural treasures.
Recognizing and celebrating this cultural richness is essential for fostering a sense of shared identity and understanding. Through cultural exchanges, language programs, and collaborative projects, ASEAN can bridge cultural divides and nurture a greater appreciation for its diverse heritage.
A Shared Future: Addressing Socioeconomic Challenges Together
 Education and Healthcare in ASEAN
Education and Healthcare in ASEAN
Despite significant economic progress, ASEAN still grapples with socioeconomic challenges such as poverty, inequality, and access to education and healthcare. Addressing these issues requires a collective effort, one that prioritizes inclusive growth and social development.
ASEAN has made strides in promoting human development through initiatives like the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community Blueprint 2025. This blueprint outlines a vision for a resilient and inclusive ASEAN, focusing on areas such as education, health, social welfare, and disaster management. By working together, ASEAN member states can leverage their collective resources and expertise to create a brighter future for all.
Safeguarding Paradise: Environmental Sustainability in ASEAN
 Protecting ASEAN's Natural Environment
Protecting ASEAN's Natural Environment
From lush rainforests to pristine beaches, ASEAN is blessed with abundant natural resources. However, rapid development and climate change pose significant threats to the region’s fragile ecosystems.
ASEAN must prioritize environmental sustainability as a cornerstone of its development agenda. This involves transitioning to cleaner energy sources, promoting sustainable tourism practices, and implementing effective conservation measures. By safeguarding its natural heritage, ASEAN ensures a sustainable future for generations to come.
Conclusion: Embracing ASEAN as ESE for a Stronger, More Unified Region
Understanding ASEAN as ESE—an interconnected entity where economic, sociocultural, and environmental factors are intertwined—is crucial for unlocking its full potential. By embracing its multifaceted identity, fostering regional cooperation, and addressing shared challenges, ASEAN can truly thrive as a region of peace, prosperity, and sustainability.