A growing ASEAN concern is the economic ascendancy of China, and its implications for the region’s economic and political landscape. This rapid growth has fostered both opportunities and anxieties among ASEAN member states. From trade and investment to infrastructure development and geopolitical influence, China’s presence in Southeast Asia has become increasingly significant. This article will delve into the complexities of this relationship, examining the various dimensions of China’s economic rise and its impact on ASEAN nations.
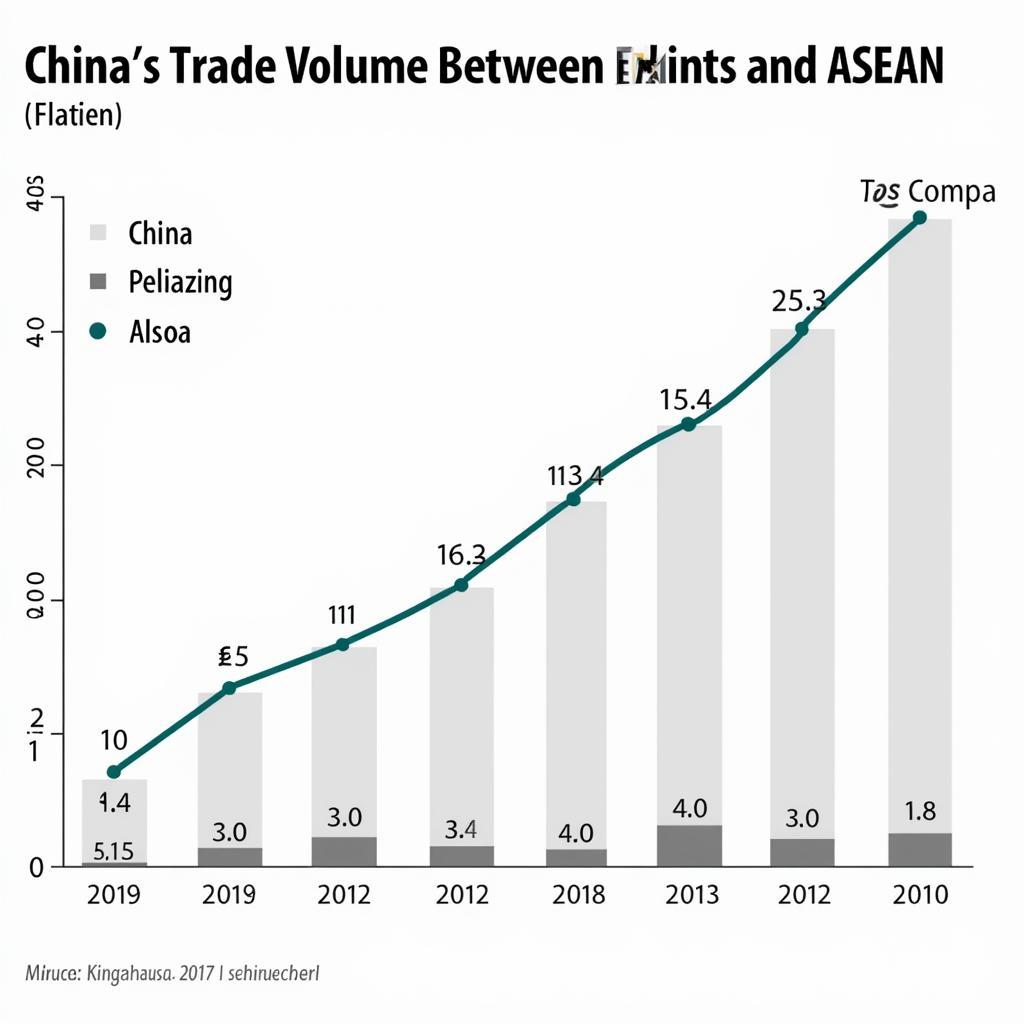 China's Economic Influence on ASEAN Trade
China's Economic Influence on ASEAN Trade
China’s Growing Economic Footprint in ASEAN
China’s economic influence within ASEAN is multifaceted. Trade between China and asc asean has grown exponentially in recent years, with China becoming the region’s largest trading partner. Chinese investments have also poured into various sectors, ranging from manufacturing and infrastructure to technology and tourism. This influx of capital has contributed to economic growth in many ASEAN countries, but has also raised concerns about over-reliance and potential debt traps. Furthermore, China’s Belt and Road Initiative (asean belt and road) has further cemented its economic presence in the region, with large-scale infrastructure projects connecting Southeast Asia to China and beyond.
Navigating the Opportunities and Challenges
While the economic ascendancy of China presents undeniable opportunities for ASEAN, navigating the associated challenges is crucial. ASEAN member states must strive to balance economic cooperation with safeguarding their own national interests. This requires fostering a strong, unified ASEAN voice in negotiations with China, as well as promoting regional economic integration to reduce dependence on any single partner.
- Strengthening intra-ASEAN trade and investment.
- Diversifying economic partnerships beyond China.
- Investing in human capital and technological innovation.
- Promoting sustainable development and environmental protection.
What are the potential risks of China’s economic dominance in ASEAN?
One potential risk is the exacerbation of existing economic disparities within ASEAN. While some countries have benefited significantly from Chinese investments, others have lagged behind, creating a widening gap between the more developed and less developed nations in the region. Another concern is the potential for China to use its economic leverage to exert political influence, undermining ASEAN’s centrality and regional autonomy.
 China-ASEAN Economic Cooperation: Addressing the Challenges
China-ASEAN Economic Cooperation: Addressing the Challenges
How Can ASEAN Mitigate the Negative Impacts?
Dr. Anisha Rahman, a leading economist specializing in Southeast Asian affairs, notes, “ASEAN must prioritize regional economic integration and diversification to mitigate the potential negative impacts of China’s economic dominance.” This involves strengthening internal trade ties, fostering partnerships with other major economies, and investing in human capital development.
Another expert, Professor Wei Li, emphasizes the importance of fostering a rules-based order in the region. “A strong and cohesive ASEAN is crucial to ensure that China’s economic activities in the region adhere to international norms and standards,” he argues.
Conclusion
A growing ASEAN concern is the economic ascendancy of China, presenting both opportunities and challenges. By proactively addressing these challenges and fostering a strong, unified regional approach, ASEAN can harness the benefits of China’s economic growth while safeguarding its own interests and promoting sustainable development for all its member states. It is essential for ASEAN to leverage its collective strength and strategic partnerships to navigate this evolving landscape effectively.
FAQ
- What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
- How has China’s investment impacted ASEAN economies?
- What are the main concerns regarding China’s growing influence?
- How can ASEAN promote regional economic integration?
- What role do other major economies play in ASEAN’s development?
Common Scenarios and Questions
- Scenario: A small business in Vietnam struggles to compete with cheaper Chinese imports. Question: What support mechanisms are available for local businesses facing competition from Chinese imports?
- Scenario: A Cambodian community is displaced due to a Chinese-funded infrastructure project. Question: What are the social and environmental safeguards in place for such projects?
Further Exploration
Explore other articles on our website related to ASEAN-China relations, economic development, and regional integration.
Need Help?
For any assistance or further information, please contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our customer service team is available 24/7.