Abk Asing, an Indonesian term short for Anak Buah Kapal Asing, translates to “foreign ship crew”. However, in the broader Southeast Asian context, it often refers to foreign workers in general. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of foreign labor in the ASEAN region, exploring the challenges, opportunities, and cultural impacts.
The Growing Significance of ABK Asing in ASEAN Economies
Southeast Asia’s dynamic economies rely heavily on foreign labor. From construction and manufacturing to domestic work and the maritime sector, ABK asing contribute significantly to the region’s growth. Countries like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand depend on foreign workers to fill labor shortages and maintain competitiveness in various industries. This dependence creates a complex interplay of economic benefits and social challenges.
One key aspect of understanding the role of ABK asing is recognizing the diversity of their origins. Workers come from countries like Indonesia, the Philippines, Myanmar, Vietnam, and even further afield. This influx of different cultures enriches the ASEAN tapestry but also necessitates careful management to ensure fair labor practices and social integration.
The Legal Framework Surrounding ABK Asing
Each ASEAN member state has its own set of regulations governing foreign labor. These laws address issues such as work permits, visa requirements, minimum wage, and worker protections. Navigating this legal landscape can be complex for both employers and foreign workers. Understanding the specific requirements of each country is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting the rights of all parties involved.
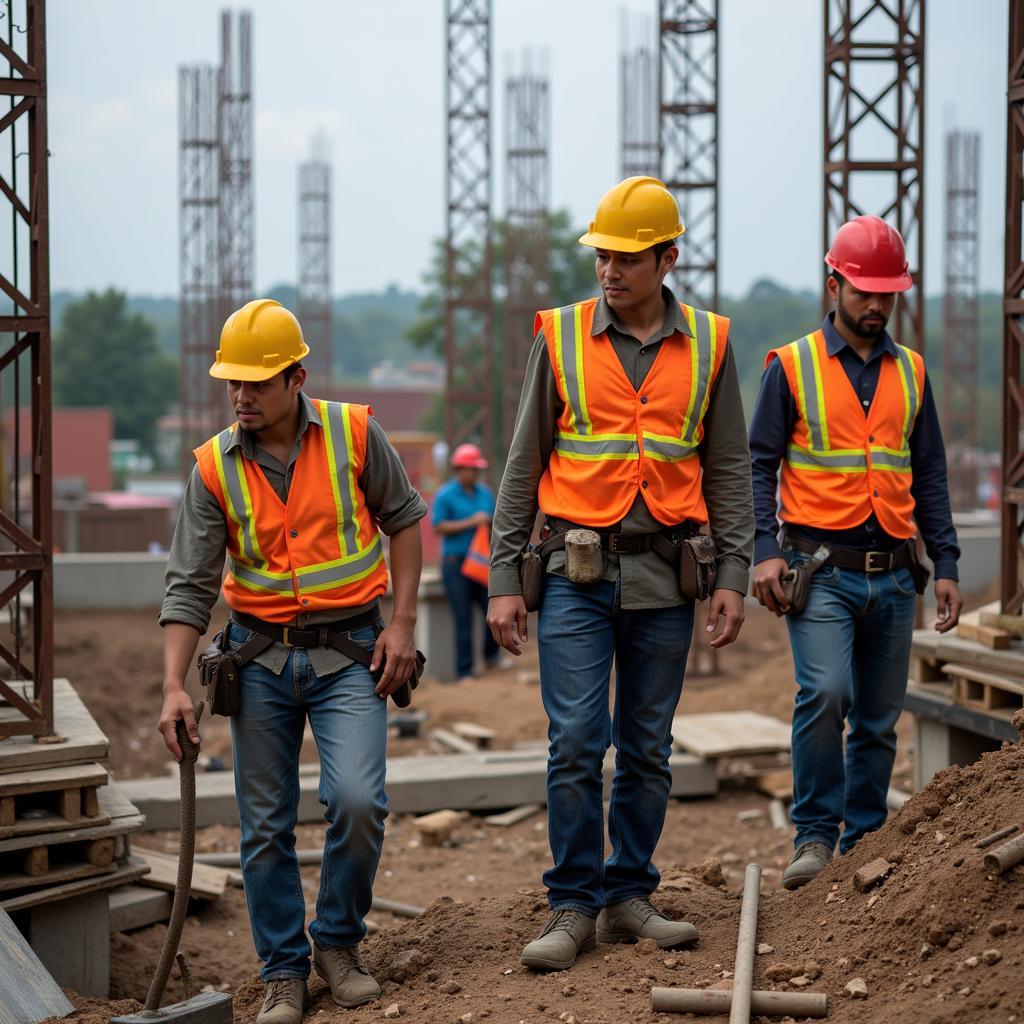 Foreign workers on a construction site in Southeast Asia
Foreign workers on a construction site in Southeast Asia
Challenges Faced by ABK Asing
Foreign workers in Southeast Asia often face a range of challenges. These can include language barriers, cultural differences, exploitation by unscrupulous employers, and difficulties accessing healthcare and other essential services. Moreover, they can be vulnerable to discrimination and social isolation. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring ethical and sustainable labor practices.
Opportunities for ABK Asing and ASEAN Countries
Despite the challenges, working abroad provides significant opportunities for ABK asing. It allows them to earn higher wages, gain new skills, and support their families back home. For ASEAN countries, foreign labor contributes to economic growth, fills critical labor shortages, and fosters regional connectivity. Harnessing the full potential of foreign labor requires a commitment to fair labor practices and creating inclusive work environments.
Cultural Exchange and Integration
The presence of ABK asing in ASEAN countries fosters cultural exchange. Food, music, traditions, and languages intermingle, creating a vibrant and diverse cultural landscape. While integration can be challenging, it also offers opportunities for mutual understanding and enriching experiences for both foreign workers and host communities.
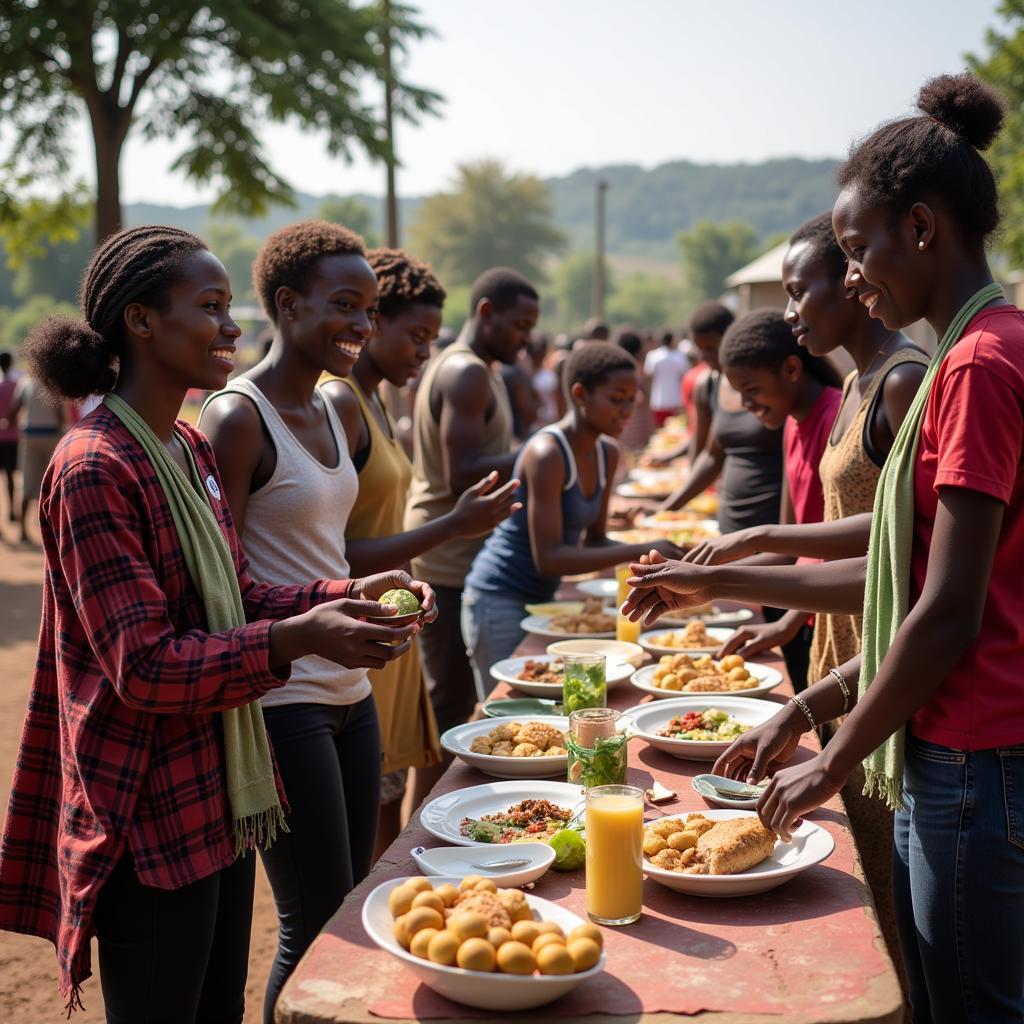 Cultural exchange between foreign workers and the local community in Southeast Asia
Cultural exchange between foreign workers and the local community in Southeast Asia
The Future of ABK Asing in ASEAN
The flow of foreign labor in Southeast Asia is expected to continue. As the region’s economies grow and develop, the demand for skilled and unskilled labor will likely increase. Managing this flow effectively and ensuring the well-being of ABK asing will be crucial for sustainable development and regional stability.
Conclusion: ABK Asing and the Future of ASEAN
ABK asing play a vital role in the economic and social fabric of Southeast Asia. Addressing the challenges and maximizing the opportunities associated with foreign labor is crucial for the region’s continued growth and prosperity. By fostering fair labor practices, promoting integration, and ensuring the well-being of all workers, ASEAN can further strengthen its position as a dynamic and interconnected region.
 ASEAN flags symbolizing unity and diversity in the context of foreign labor
ASEAN flags symbolizing unity and diversity in the context of foreign labor
FAQ
- What does ABK Asing stand for? ABK Asing is an Indonesian abbreviation for Anak Buah Kapal Asing, meaning foreign ship crew. It is often used more broadly to refer to foreign workers.
- Which ASEAN countries rely most on foreign labor? Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand are among the ASEAN countries that heavily rely on foreign labor.
- What are some of the challenges faced by ABK Asing? Common challenges include language barriers, cultural differences, exploitation, and difficulties accessing essential services.
- How does foreign labor benefit ASEAN economies? Foreign labor contributes to economic growth, fills labor shortages, and fosters regional connectivity.
- What is the future of ABK Asing in ASEAN? The demand for foreign labor in ASEAN is expected to continue to grow as the region develops.
Common Scenarios and Questions
Scenario: A foreign worker is unsure about their rights and obligations.
Question: Where can I find information about my rights as a foreign worker in [Country]?
Scenario: An employer is looking to hire foreign workers.
Question: What are the legal procedures for hiring foreign workers in [Country]?
Further Resources
Explore more related articles on our website about specific regulations for foreign workers in each ASEAN country.
For any assistance, please contact us: Phone: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.