The Acs Ase Medical Student Core Curriculum Shock is a critical component of surgical education, equipping aspiring surgeons with the fundamental knowledge and skills to manage shock effectively. Understanding the various types of shock, their pathophysiology, and appropriate management strategies is crucial for positive patient outcomes. This article delves into the core aspects of shock management as outlined in the ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum, providing a comprehensive overview for medical students.
Understanding the Different Types of Shock
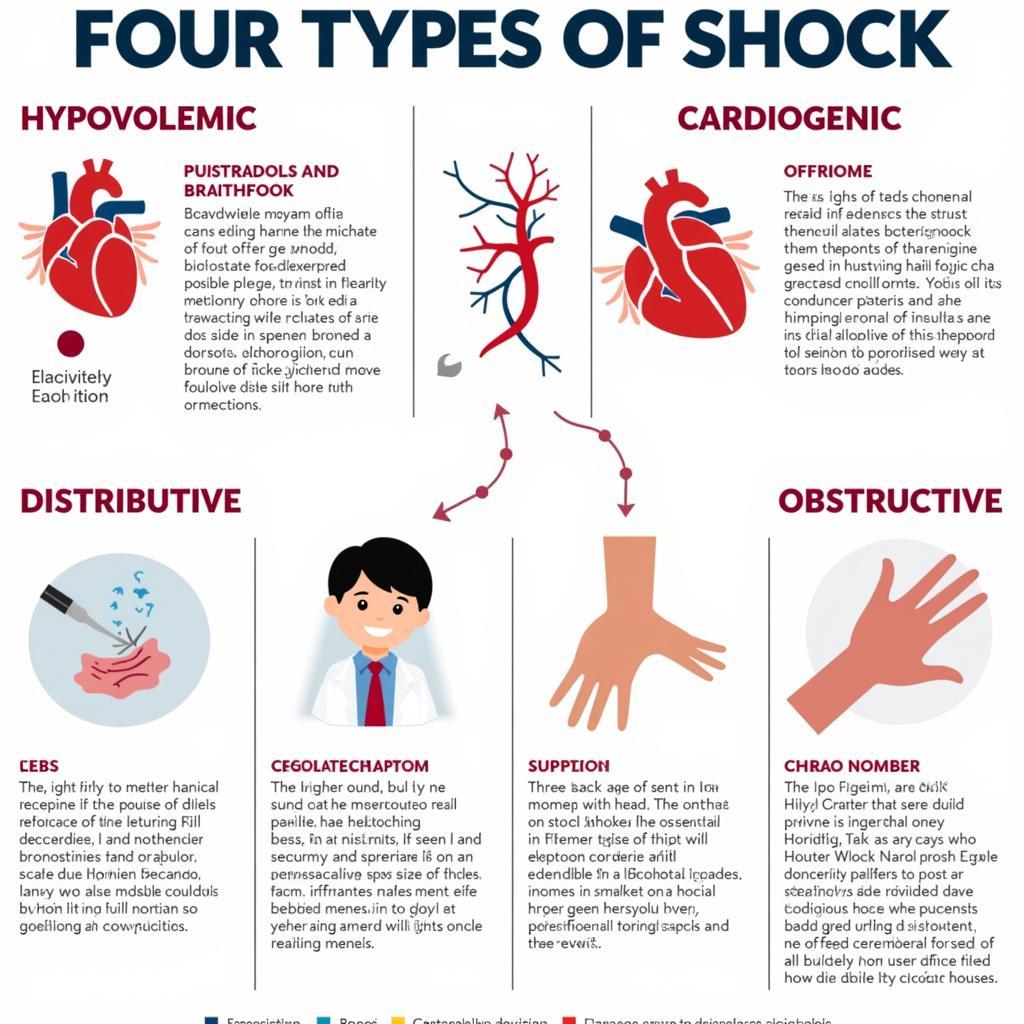
Shock is a life-threatening condition characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion, leading to cellular dysfunction and organ damage. The ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum emphasizes the importance of recognizing the different types of shock, which include:
- Hypovolemic shock: Caused by a significant decrease in blood volume, often due to hemorrhage or severe dehydration.
- Cardiogenic shock: Results from the heart’s inability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, commonly seen in conditions like myocardial infarction or heart failure.
- Distributive shock: Characterized by widespread vasodilation and increased capillary permeability, encompassing septic, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock.
- Obstructive shock: Occurs when blood flow is impeded by a physical obstruction, such as a tension pneumothorax or pulmonary embolism.
Recognizing the specific type of shock is crucial for tailoring appropriate treatment strategies.
 Different Types of Shock
Different Types of Shock
Key Principles of Shock Management according to ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum
The ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum emphasizes a systematic approach to shock management, focusing on rapid assessment and intervention. The core principles include:
- Airway management: Ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is paramount.
- Breathing support: Providing supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation as needed.
- Circulation restoration: Addressing the underlying cause of shock and restoring adequate blood volume and pressure. This often involves intravenous fluid resuscitation and vasopressor administration.
- Disability assessment: Evaluating neurological status and identifying any potential central nervous system compromise.
- Exposure and environmental control: Preventing hypothermia and maintaining normothermia.
These principles, often remembered by the acronym ABCDE, provide a framework for prioritizing interventions in a critical situation.
 ACS ASE Shock Management ABCDE Principles
ACS ASE Shock Management ABCDE Principles
Why is the ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum Shock Important?
The ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum on shock provides a foundational understanding of this critical condition. It equips medical students with the knowledge and skills necessary to recognize, assess, and manage shock effectively, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes. This curriculum emphasizes a systematic approach, ensuring that students develop a comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of various shock states.
How do I assess a patient in shock?
A quick assessment using the ABCDE approach is essential: Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure. This provides a systematic method to identify and address immediate life-threatening issues.
What are the common signs of shock?
Common signs include rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, pale or clammy skin, confusion, and decreased urine output.
Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a renowned trauma surgeon at the Singapore General Hospital, emphasizes the significance of early recognition and intervention. “Seconds can make a difference in shock management,” she states. “A prompt and systematic approach, as outlined in the ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum, is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.”
Conclusion
The ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum Shock provides essential knowledge and skills for aspiring surgeons. Understanding and applying the core principles outlined in this curriculum is crucial for effective shock management and ultimately improving patient outcomes. By mastering the principles of ABCDE and recognizing the various types of shock, medical students can contribute to timely and appropriate interventions in critical situations.
FAQ
- What is the most common type of shock? Hypovolemic shock, often caused by blood loss.
- What is the first step in managing shock? Securing the airway and ensuring adequate breathing.
- What is the role of fluids in shock management? Fluids are used to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion.
- What are vasopressors, and when are they used in shock? Vasopressors are medications that constrict blood vessels, increasing blood pressure. They are used when fluid resuscitation alone is insufficient.
- What is the importance of monitoring in shock management? Continuous monitoring of vital signs and other parameters is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of treatment and identifying any complications.
- How does the ACS ASE Medical Student Core Curriculum prepare students for managing shock? It provides a structured framework for understanding the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of various shock states.
- What are some long-term complications of shock? Organ damage, including kidney failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS).
Suggest other related articles
- Understanding Sepsis and its Management
- Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) Guidelines
- Critical Care Management in Surgical Patients
Contact Us
For any further assistance or inquiries, please contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our customer service team is available 24/7 to assist you.