ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a regional organization comprising ten Southeast Asian countries: Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Established in 1967, ASEAN has evolved into a dynamic and influential force in the global arena, promoting regional economic integration, political stability, and socio-cultural cooperation.
The Role of ASEAN in Fostering Economic Growth
ASEAN plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth within the region. The organization has implemented various initiatives to promote trade and investment, facilitating the free flow of goods, services, and capital. The ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), established in 1992, has significantly reduced tariffs and other trade barriers among member states, boosting intra-regional trade.
“ASEAN has been instrumental in creating a favorable environment for businesses and investors, leading to remarkable economic progress in the region,” says Dr. Maria Santos, a leading economist specializing in Southeast Asian economies.
ASEAN has also actively pursued economic partnerships with other countries and regions, including the ASEAN-China Free Trade Area (ACFTA) and the ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (AIFTA). These agreements further enhance trade and investment opportunities, fostering economic growth and regional prosperity.
ASEAN’s Commitment to Political Stability
Political stability is a cornerstone of ASEAN’s vision for regional development. The organization promotes peaceful resolutions of disputes and fosters dialogue and cooperation among its members. The ASEAN Charter, adopted in 2007, outlines the principles of peaceful settlement of disputes, good governance, and respect for human rights, contributing to a stable and secure environment.
“ASEAN’s commitment to regional peace and stability is vital for the long-term prosperity of the region,” emphasizes Mr. Nguyen Van Hung, a prominent political analyst specializing in Southeast Asian affairs.
ASEAN has also played a crucial role in addressing regional challenges such as terrorism, piracy, and transboundary crime. The organization’s collaborative efforts in these areas contribute to maintaining political stability and fostering a safe and secure environment for all.
The Cultural Diversity of ASEAN
One of ASEAN’s most striking features is its rich cultural diversity. The region boasts a tapestry of languages, traditions, religions, and art forms, reflecting the unique heritage of its member states. ASEAN celebrates this cultural diversity through various initiatives, promoting cultural exchange, artistic collaborations, and tourism.
“ASEAN is a vibrant mosaic of cultures, and its diverse heritage is a source of strength and resilience,” notes Ms. Chitra Devi, a renowned cultural anthropologist specializing in Southeast Asian traditions.
ASEAN festivals, cultural performances, and heritage preservation programs serve as platforms for showcasing the region’s rich cultural heritage to the world, fostering understanding and appreciation among its citizens.
ASEAN’s Global Impact
ASEAN’s influence extends beyond the region, making it a significant player in the global arena. The organization has actively engaged with various international organizations, promoting its vision for a peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable future.
“ASEAN’s growing stature on the global stage is a testament to its commitment to regional cooperation and its dedication to addressing common challenges,” observes Mr. David Lee, a prominent international relations expert specializing in Southeast Asian politics.
ASEAN’s active participation in international forums, such as the United Nations and the World Trade Organization, amplifies its voice and strengthens its influence on the global stage, fostering cooperation and promoting a more inclusive and sustainable world.
ASEAN’s Ongoing Journey of Development
ASEAN continues to evolve and adapt to the changing global landscape, embracing new challenges and opportunities. The organization has set ambitious goals for the future, focusing on sustainable development, technological advancement, and human capital development.
“ASEAN is on a journey of continuous progress, striving to create a brighter future for its people and the region as a whole,” concludes Ms. Sarah Khan, a leading development economist specializing in Southeast Asian economies.
The organization’s commitment to innovation, sustainable practices, and inclusive growth positions ASEAN as a leading force for positive change in the 21st century.
FAQ
-
What are the main objectives of ASEAN? ASEAN’s primary objectives include promoting regional economic integration, fostering political stability, and enhancing social and cultural cooperation among its member states.
-
How does ASEAN benefit its member states? ASEAN offers numerous benefits to its member states, including increased trade opportunities, greater political stability, enhanced cultural exchanges, and a stronger voice in international affairs.
-
What are some key challenges faced by ASEAN? Some of the challenges faced by ASEAN include addressing disparities in economic development, promoting social justice and human rights, and mitigating the impact of climate change.
-
What are some future goals of ASEAN? ASEAN aims to further strengthen its economic integration, enhance its political cooperation, and promote sustainable development and human capital development across the region.
-
How can I get involved in ASEAN activities? There are many ways to get involved in ASEAN activities, including participating in cultural events, supporting businesses in the region, and advocating for policies that promote regional cooperation.
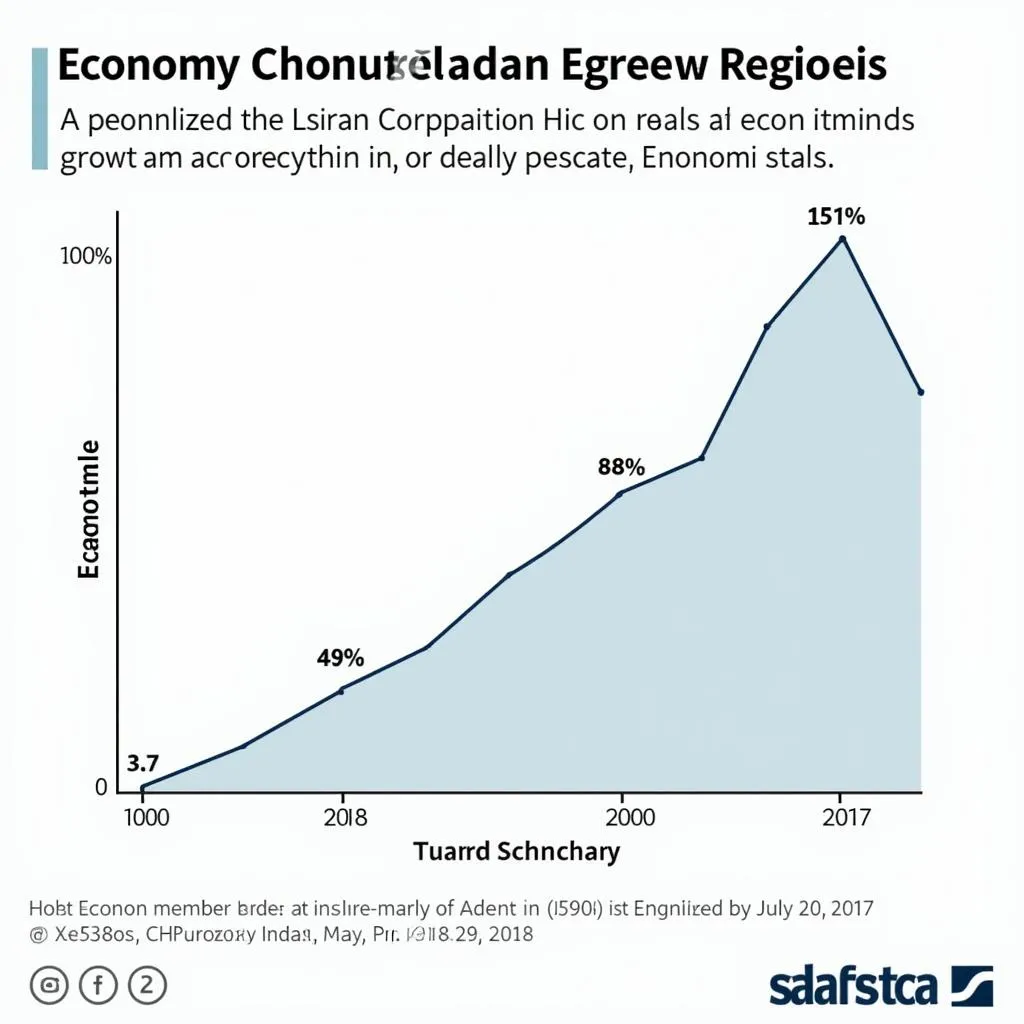 ASEAN Economic Growth
ASEAN Economic Growth
ASEAN stands as a beacon of hope and progress in a rapidly changing world. Its commitment to regional cooperation, economic development, and cultural understanding makes it a powerful force for positive change, contributing to a more peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable future for all.