Aortic regurgitation, a condition affecting the heart’s aortic valve, can significantly impact an individual’s health. This article delves into the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines for managing aortic regurgitation, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
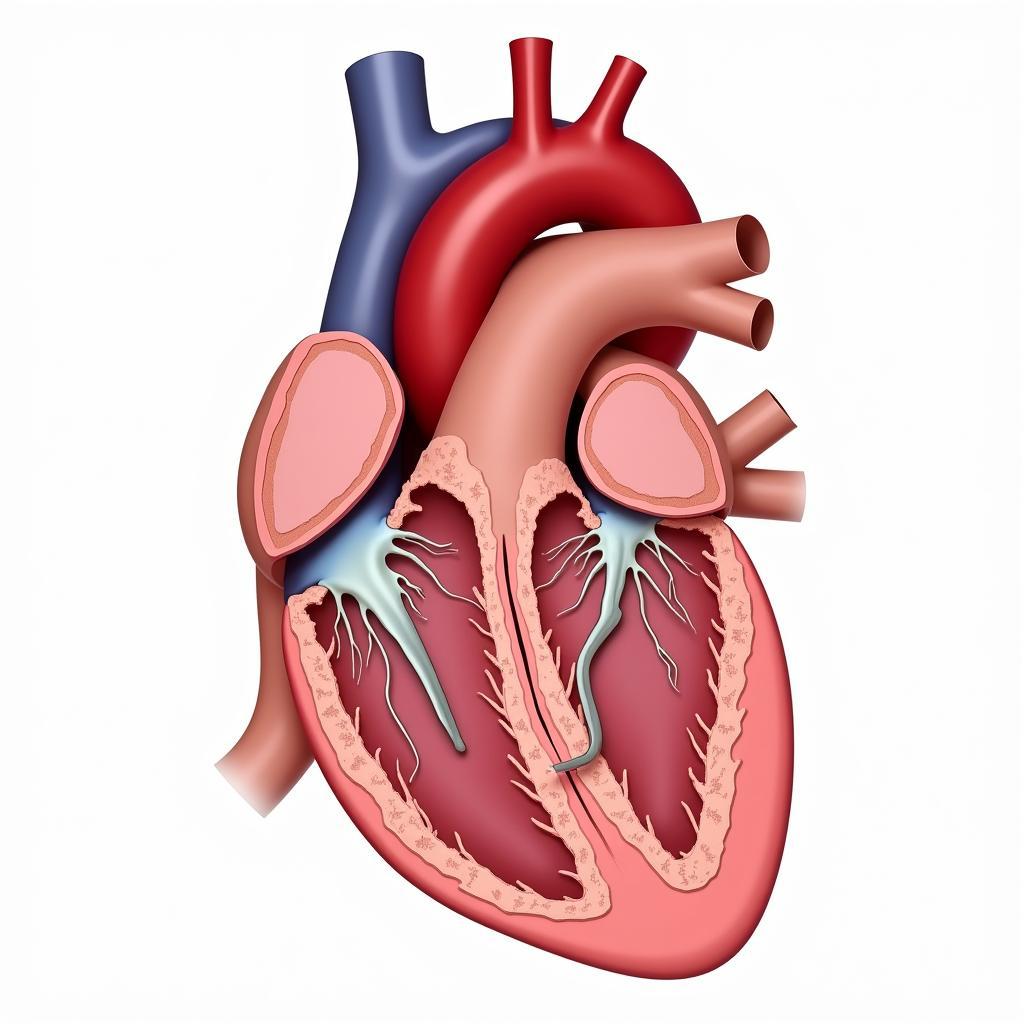 Aortic Regurgitation Illustration
Aortic Regurgitation Illustration
What is Aortic Regurgitation?
The aortic valve, situated between the heart’s left ventricle and the aorta, plays a crucial role in ensuring blood flows in one direction. Aortic regurgitation, also known as aortic insufficiency, occurs when this valve doesn’t close tightly, causing blood to leak back into the left ventricle.
This backflow forces the heart to work harder, potentially leading to heart enlargement and other complications. Understanding the severity and progression of aortic regurgitation is essential for effective management, which is where the ASE guidelines come into play.
The Importance of ASE Guidelines for Aortic Regurgitation
The ASE guidelines offer comprehensive recommendations for diagnosing and managing aortic regurgitation using echocardiography, a non-invasive ultrasound of the heart. These guidelines help healthcare providers:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Determine the presence and severity of aortic regurgitation.
- Risk Stratification: Identify individuals at risk of complications.
- Treatment Decisions: Guide decisions on the timing of surgery or other interventions.
- Follow-up Care: Monitor disease progression and treatment effectiveness.
Key Aspects of the ASE Guidelines
The ASE guidelines cover a wide range of aspects related to aortic regurgitation, including:
1. Echocardiographic Assessment
The guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive echocardiography in evaluating aortic regurgitation. This includes assessing:
- Regurgitant Jet: Size and shape of the blood flow leaking back into the ventricle.
- Left Ventricle Size and Function: Impact of the backflow on the heart’s main pumping chamber.
- Aortic Root Dimensions: Assessing the size of the aorta, as dilation can be a concern.
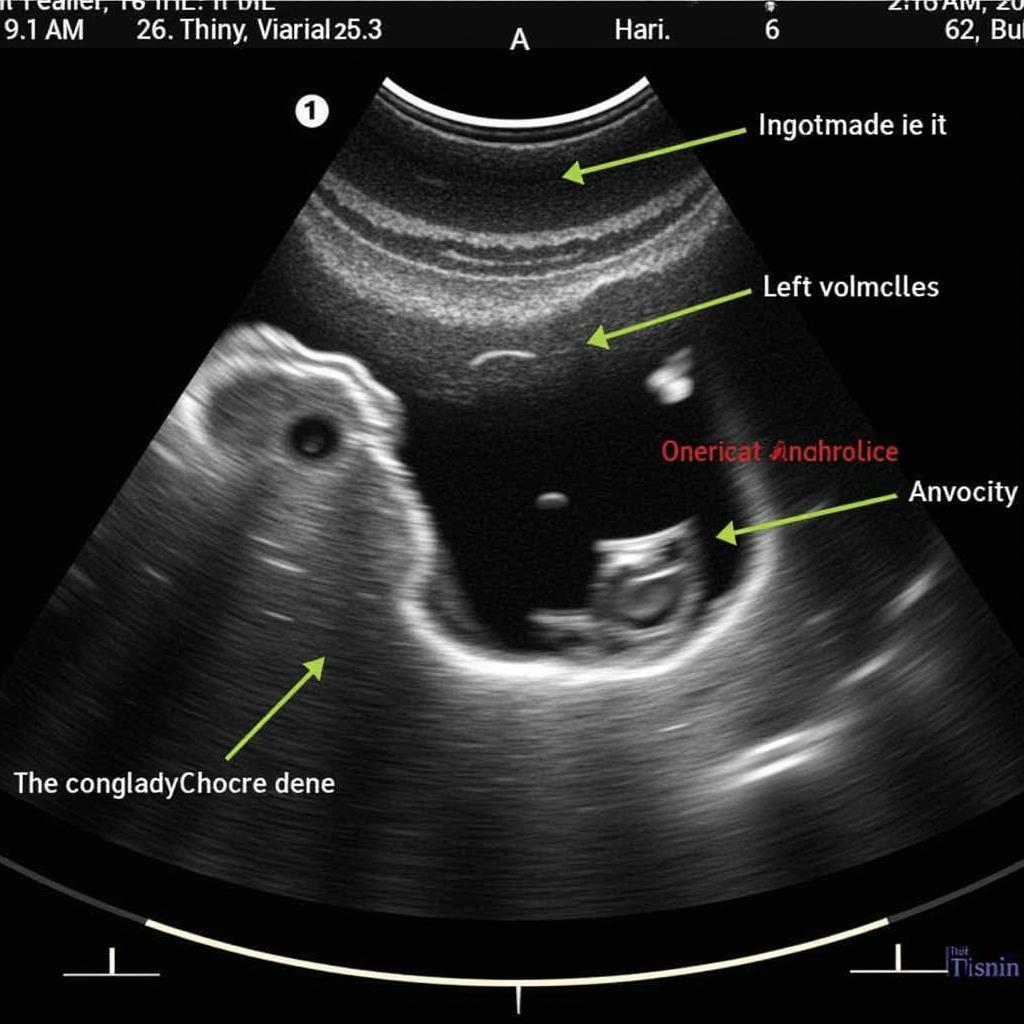 Echocardiography of Aortic Regurgitation
Echocardiography of Aortic Regurgitation
2. Severity Assessment
Determining the severity of aortic regurgitation is crucial for treatment decisions. The ASE guidelines provide specific criteria based on echocardiographic findings, including:
- Mild Aortic Regurgitation: Often managed conservatively with regular monitoring.
- Moderate Aortic Regurgitation: May require closer monitoring and potential intervention.
- Severe Aortic Regurgitation: Often necessitates surgical intervention to repair or replace the aortic valve.
3. Timing of Intervention
One of the most critical aspects of managing aortic regurgitation is determining the optimal timing for intervention. The ASE guidelines offer recommendations based on factors like:
- Severity of Regurgitation: More severe cases often require earlier intervention.
- Symptoms: Presence of symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Left Ventricle Function: Deterioration in left ventricle function may prompt intervention.
The Impact of the ASE Guidelines
The ASE guidelines have significantly improved the care of patients with aortic regurgitation by:
- Standardizing Diagnosis and Assessment: Ensuring consistency in evaluating the condition.
- Guiding Treatment Decisions: Providing evidence-based recommendations for intervention.
- Improving Patient Outcomes: Leading to better long-term outcomes for individuals with aortic regurgitation.
Living with Aortic Regurgitation
While aortic regurgitation can be a serious condition, many people live full and active lives with appropriate management. Following the ASE guidelines, healthcare providers can provide personalized treatment plans and ongoing monitoring to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
Aortic regurgitation requires careful evaluation and management to prevent complications. The ASE guidelines, leveraging the power of echocardiography, provide a roadmap for healthcare providers to accurately diagnose, assess severity, and determine the optimal timing for intervention. By adhering to these guidelines, medical professionals can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with aortic regurgitation.
ase guidelines native valvular regurgitation 2017
FAQs about Aortic Regurgitation
1. What causes aortic regurgitation?
Aortic regurgitation can be caused by various factors, including congenital heart defects, rheumatic fever, infections, and age-related valve degeneration.
2. Can aortic regurgitation be cured?
While lifestyle changes and medications can manage symptoms, the only definitive cure for severe aortic regurgitation is often surgery to repair or replace the valve.
3. What are the risks of not treating aortic regurgitation?
Untreated aortic regurgitation can lead to heart failure, heart rhythm abnormalities, and other serious complications.
4. What is the long-term outlook for someone with aortic regurgitation?
With proper management, including medication and potential surgery, many individuals with aortic regurgitation can live long and healthy lives.
5. How often do I need echocardiograms if I have aortic regurgitation?
The frequency of echocardiograms depends on the severity of your condition. Your doctor will personalize a monitoring plan based on your individual needs.
 Healthy Heart Lifestyle
Healthy Heart Lifestyle
Need support? Contact us 24/7 at Phone: +84369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com or visit us at Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Viet Nam.