APEC and ASEAN are both prominent organizations in the Asia-Pacific region, but they have distinct focuses and memberships. Understanding the Apec Asean Difference is crucial for anyone interested in regional economics, politics, and international relations. This article delves into the core distinctions between these two influential bodies, exploring their origins, objectives, and impacts on the region and beyond.
What is the Difference Between APEC and ASEAN?
A key difference lies in their primary goals. ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, prioritizes regional economic and socio-cultural cooperation among its Southeast Asian member states. APEC, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, focuses on promoting free trade and economic growth across a broader trans-Pacific membership, including major economies like the US, China, and Japan. This broader scope is a defining characteristic in the APEC ASEAN difference. Another important distinction is their approach to integration. ASEAN pursues deeper integration among its members, moving towards a single market and production base, while APEC emphasizes open regionalism, encouraging cooperation without requiring binding commitments.
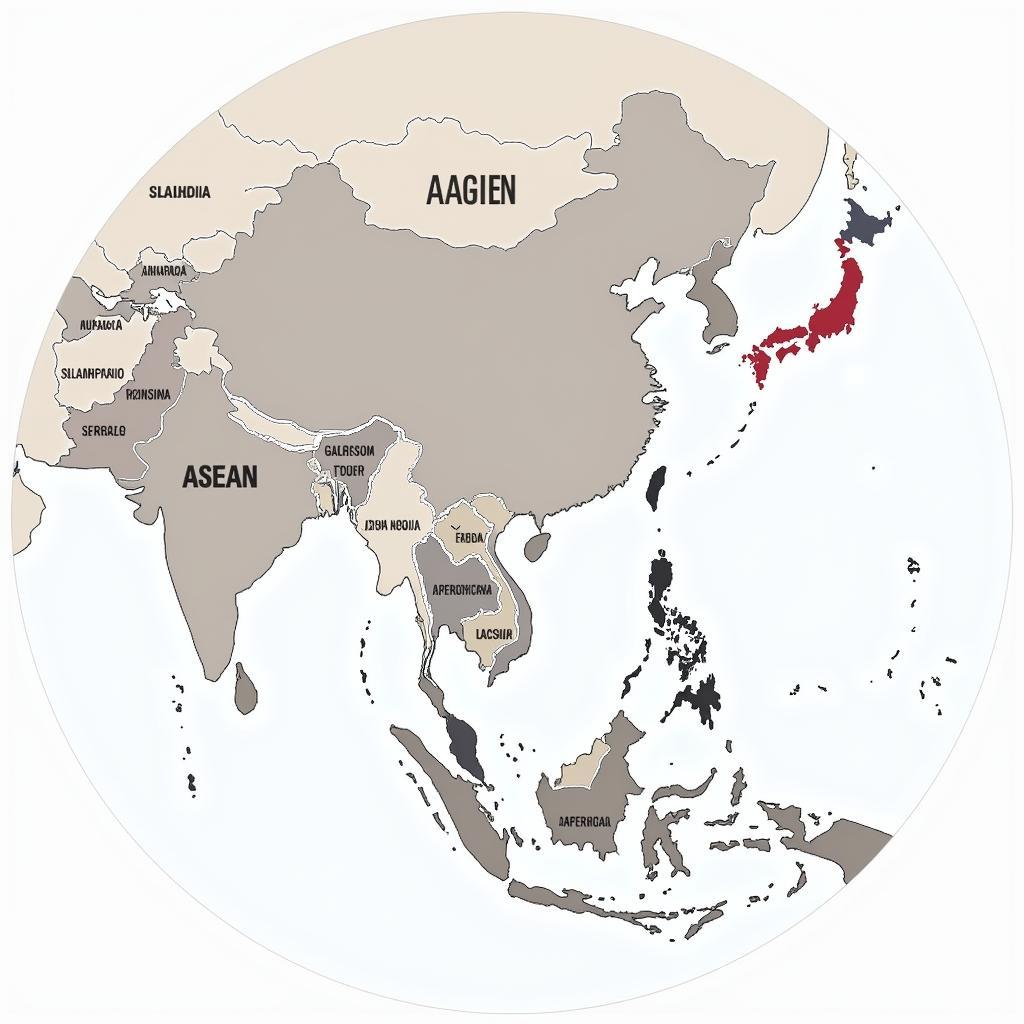 APEC and ASEAN Member States Map Comparison
APEC and ASEAN Member States Map Comparison
Further differentiating APEC and ASEAN is their organizational structure. ASEAN operates on a consensus-based decision-making process, emphasizing equality among its members. APEC, on the other hand, functions through voluntary cooperation and non-binding commitments. This difference reflects the diverse economic and political landscape of its broader membership. Thinking about the “apec asean difference” also necessitates examining their history. ASEAN, established in 1967, predates APEC, which was formed in 1989. This historical context reveals the evolving dynamics of regional cooperation in the Asia-Pacific.
Key Differences in Membership, Focus, and Approach
The difference between APEC and ASEAN is readily apparent in their membership composition. ASEAN comprises ten Southeast Asian nations, while APEC includes 21 economies spanning the Pacific Rim. This geographical distinction underscores their differing scopes and objectives. ASEAN prioritizes regional stability, political dialogue, and socio-cultural exchange, while APEC concentrates on trade liberalization, business facilitation, and economic technical cooperation. Understanding this core distinction is essential for grasping the nuances of the “apec asean difference.”
Another crucial aspect of the “apec asean difference” is their approach to decision-making. ASEAN emphasizes consensus and equality among its member states. In contrast, APEC’s approach is based on voluntary cooperation and non-binding commitments. This flexibility accommodates the diverse economic and political systems of its members.
How Does AFTA Relate to ASEAN and APEC?
AFTA, the ASEAN Free Trade Area, is a key initiative of ASEAN aimed at reducing tariffs and promoting intra-regional trade. While not directly related to APEC, AFTA exemplifies ASEAN’s commitment to economic integration within Southeast Asia. Understanding the relationship between AFTA, ASEAN, and APEC provides a comprehensive view of the complex web of regional economic cooperation in the Asia-Pacific. It’s an important facet when exploring the broader context of the “apec asean difference.” AFTA’s existence showcases how ASEAN pursues deeper economic ties within its own bloc, while APEC works towards broader, albeit less integrated, trans-Pacific economic cooperation.
Comparing ASEAN, APEC, and G20
Expanding the scope beyond the “apec asean difference”, it’s useful to compare both organizations with the G20. The G20, a group of the world’s largest economies, has a global focus on international economic cooperation. Both APEC and ASEAN have overlapping membership with the G20, indicating the interconnectedness of these forums in addressing global economic challenges. While ASEAN concentrates on Southeast Asia and APEC on the Pacific Rim, the G20’s scope is global, highlighting the varying geographical and political reach of these organizations.
 APEC, ASEAN, and G20 Global Influence Comparison
APEC, ASEAN, and G20 Global Influence Comparison
Conclusion
Understanding the APEC ASEAN difference is essential for navigating the complexities of regional and global economic cooperation. While both organizations contribute to promoting economic growth and stability in the Asia-Pacific, their distinct memberships, focuses, and approaches reflect the diverse political and economic landscape of the region. By recognizing these key distinctions, we can better appreciate the unique roles played by APEC and ASEAN in shaping the future of the Asia-Pacific and beyond.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between APEC and ASEAN? ASEAN focuses on regional cooperation within Southeast Asia, while APEC promotes free trade across the broader Asia-Pacific region.
- What does AFTA stand for? AFTA stands for ASEAN Free Trade Area.
- Is the US a member of ASEAN? No, the US is a member of APEC, not ASEAN.
- Which organization is older, APEC or ASEAN? ASEAN, established in 1967, is older than APEC, which was founded in 1989.
- Do APEC and ASEAN have overlapping members? Yes, several countries are members of both APEC and ASEAN.
- What is the primary focus of APEC? APEC’s primary focus is promoting free trade and economic growth across the Asia-Pacific region.
- How does ASEAN make decisions? ASEAN operates on a consensus-based decision-making process.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.