ASEAN, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a regional organization that has been instrumental in promoting economic cooperation and development in Southeast Asia. The organization has been instrumental in fostering economic growth and prosperity in the region, making it a leading economic powerhouse in the world. This article will delve into the different facets of ASEAN’s economic strength, and how its members are working together to create a prosperous future for the region.
The History of ASEAN’s Economic Integration
ASEAN was established in 1967 by five Southeast Asian nations: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. The organization’s primary goal was to promote regional stability and economic growth. It aimed to achieve this through the promotion of free trade, investment, and tourism among member states.
The establishment of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) in 1992 marked a significant step towards regional economic integration. AFTA aimed to eliminate tariffs on most goods traded among member states, thereby promoting intra-regional trade and economic growth. The implementation of AFTA has significantly contributed to ASEAN’s economic success.
ASEAN’s Economic Achievements
ASEAN has made significant economic progress over the years, achieving impressive growth rates and becoming a leading economic player in the global market. The organization has a combined GDP of over US$3 trillion, making it the sixth-largest economy in the world.
Here are some key economic achievements of ASEAN:
- Rapid Economic Growth: ASEAN has experienced consistent economic growth in recent decades, averaging over 5% annually. This growth has been driven by factors such as strong domestic demand, increasing foreign investment, and trade liberalization.
- Trade and Investment Growth: ASEAN’s trade and investment flows have surged significantly in recent years, driven by the region’s growing economic integration and the expansion of its global trade networks.
- Infrastructure Development: ASEAN has invested heavily in infrastructure development, including roads, railways, airports, and ports. This has improved connectivity within the region, facilitating trade and investment flows.
- Human Capital Development: ASEAN has recognized the importance of human capital development, investing in education, healthcare, and skills training. This has helped to create a skilled workforce that can support the region’s economic growth.
ASEAN’s Future Economic Prospects
ASEAN’s economic prospects remain strong, driven by several key factors:
- Growing Middle Class: ASEAN’s rapidly growing middle class is creating a significant increase in domestic demand for goods and services, boosting economic growth.
- Rising Foreign Investment: ASEAN is attracting substantial foreign investment due to its strategic location, growing economies, and skilled workforce.
- Regional Economic Integration: ASEAN’s commitment to further regional economic integration, including through the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), is creating a more attractive business environment.
- Digital Economy Growth: The digital economy is booming in ASEAN, with increasing use of e-commerce, online services, and fintech. This is creating new opportunities for businesses and job creation.
Challenges for ASEAN’s Economic Growth
While ASEAN’s economic prospects remain positive, the region faces several challenges:
- Income Inequality: Income inequality remains a challenge in several ASEAN countries, with some populations facing poverty and limited access to opportunities.
- Environmental Sustainability: ASEAN needs to address environmental sustainability concerns, including climate change, deforestation, and pollution.
- Political and Social Stability: Political and social instability in some member states can hinder economic growth and investment.
“The economic integration of ASEAN is a testament to the power of collaboration and shared vision,” says Dr. [Insert expert name], a renowned economist specializing in Southeast Asian economies. “Despite the challenges, the region’s commitment to economic cooperation is strong, and its future prospects remain bright.”
FAQ
What are the benefits of ASEAN’s economic integration?
ASEAN’s economic integration has brought significant benefits, including increased trade and investment, economic growth, improved infrastructure, and a more skilled workforce.
What are the key drivers of ASEAN’s economic growth?
Key drivers of ASEAN’s economic growth include a growing middle class, increasing foreign investment, regional economic integration, and the growth of the digital economy.
What are some challenges faced by ASEAN’s economic growth?
Challenges include income inequality, environmental sustainability concerns, and political and social instability in some member states.
How is ASEAN addressing the challenges to its economic growth?
ASEAN is addressing these challenges through various initiatives, including poverty reduction programs, environmental protection policies, and efforts to promote political and social stability.
What is the future outlook for ASEAN’s economy?
ASEAN’s economic prospects remain strong, driven by its growing middle class, increasing foreign investment, regional economic integration, and the digital economy. However, the region needs to address challenges such as income inequality and environmental sustainability to ensure continued growth and prosperity.
ase style review questions answers chapter 20
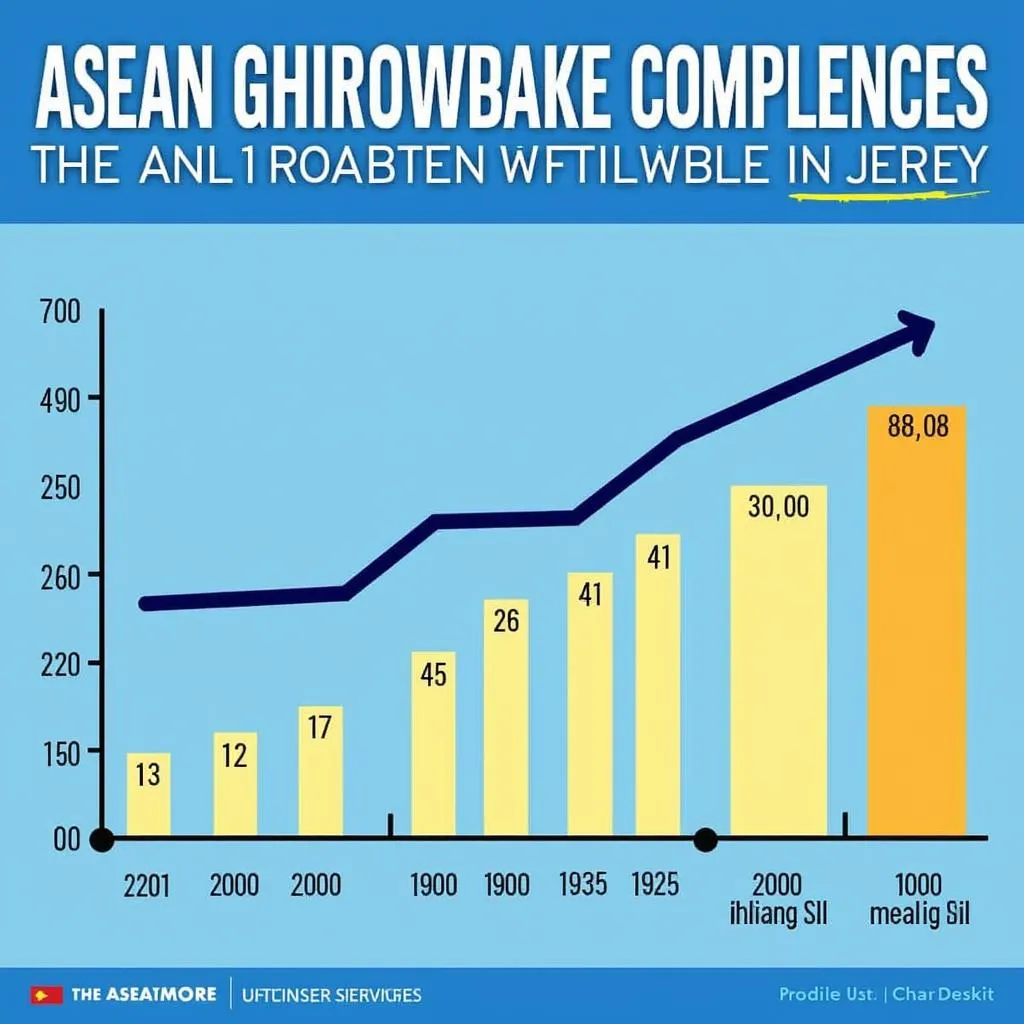 ASEAN's Economic Growth Over Time
ASEAN's Economic Growth Over Time
ASEAN’s economic integration is a journey that requires continuous efforts and collaboration. By addressing challenges, leveraging opportunities, and working together, ASEAN can continue its path towards a prosperous future for all its member states.