The term “Ase Biology Definition” often leads to searches about enzymes. Enzymes, crucial for life, are biological catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions. These proteins, often ending in “-ase,” play a vital role in various biological processes, from digestion to DNA replication. Let’s explore the world of enzymes and delve deeper into the meaning behind the “-ase” suffix in biology.
What exactly does “ase” signify in a biological context? The suffix “-ase” is used to denote enzymes. It’s a powerful tool in the scientific community, providing a clear and concise way to identify these essential biomolecules. Understanding the “-ase” suffix is fundamental to grasping the complexities of biological systems. For example, lactase breaks down lactose, and polymerase synthesizes polymers. This consistent naming convention helps researchers quickly understand the function of a particular enzyme. This article will provide a comprehensive understanding of the “-ase” suffix and its significance in biology. You can learn more about word formation with the ase suffix and prefix.
Exploring the “-ase” Suffix: A Key to Enzyme Identification
The “-ase” suffix is derived from the Greek word “diastase,” the first enzyme discovered. This historical root highlights the significance of “-ase” in the evolution of biological understanding. Since then, the convention has become a standard practice, simplifying the classification and identification of countless enzymes.
Why is a standardized naming system important? In the vast landscape of biological molecules, a clear naming convention is crucial for effective communication and research. The “-ase” suffix provides a simple yet effective way to distinguish enzymes from other proteins and molecules. This clarity is paramount for scientific progress, especially in fields like medicine and biotechnology.
How Enzymes Work: A Closer Look at Biological Catalysts
Enzymes achieve their catalytic prowess by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. Think of it like a shortcut on a mountain path – the enzyme provides an easier route for the reaction to take place, speeding up the process without being consumed itself. They achieve this by binding to specific substrates, forming an enzyme-substrate complex, which then facilitates the reaction. After the reaction, the enzyme remains unchanged and is ready to catalyze another reaction.
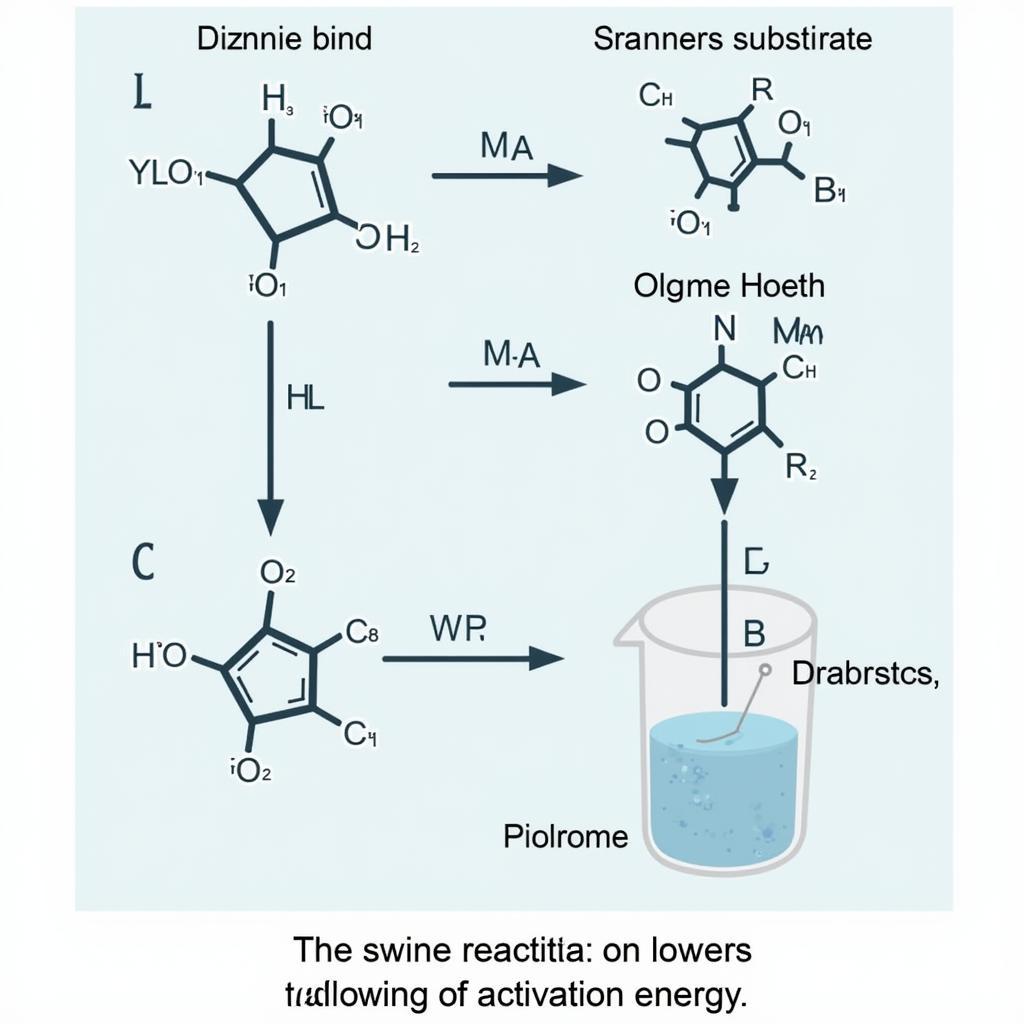 Enzyme Catalysis Process: A Visual Explanation
Enzyme Catalysis Process: A Visual Explanation
The specificity of enzymes is another crucial characteristic. Each enzyme is designed to work with a specific substrate, much like a lock and key. This specificity ensures that the correct reactions occur at the right time and place within the complex machinery of a cell.
Examples of Common Enzymes and Their Functions
Numerous enzymes contribute to the intricate web of life. Here are a few examples:
- Amylase: Breaks down starch into simpler sugars. This process is crucial for digestion in humans and animals.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats and lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. This is essential for energy metabolism and nutrient absorption.
- Protease: Breaks down proteins into amino acids. This is crucial for building and repairing tissues.
These are just a few examples of the thousands of enzymes that contribute to the proper functioning of living organisms. If you’re curious about other five-letter words ending in “ase,” check out 5 letter word ase at the end.
The Importance of Enzymes in Biological Systems
Enzymes are indispensable for life. They regulate countless biological processes, ensuring that reactions occur efficiently and at the appropriate pace. From DNA replication to metabolism and cellular signaling, enzymes are the silent workhorses that keep life’s intricate machinery running smoothly. Without enzymes, many essential biological reactions would occur too slowly to sustain life.
Enzyme Dysfunction and Its Implications
When enzymes malfunction, it can lead to a variety of health issues. Enzyme deficiencies can disrupt metabolic pathways, causing a range of symptoms and diseases. Understanding enzyme function is crucial for diagnosing and treating these conditions. For a more detailed explanation on the “-ase” suffix, see ase suffix definition.
 Enzyme Dysfunction and its Impact on Human Health
Enzyme Dysfunction and its Impact on Human Health
Conclusion: The “-ase” Suffix – A Small Suffix with a Big Role
The “ase biology definition” essentially revolves around the understanding of enzymes and their vital role in biological systems. The “-ase” suffix is a powerful tool for identifying these essential biomolecules, simplifying communication and research in the life sciences. From digestion to DNA replication, enzymes are the driving force behind countless biological processes, highlighting the importance of this seemingly small suffix in the grand scheme of life. For further exploration on five-letter words with “ase” in the middle, refer to 5 letter word with ase in the middle.
FAQ
- What does the suffix “-ase” indicate?
- Why is the “-ase” suffix important in biology?
- How do enzymes function as catalysts?
- What are some common examples of enzymes?
- What happens when enzymes malfunction?
- Can you provide more information regarding words ending in “ase”? Consider exploring 5 letter word ening in ase for further details.
- What is the origin of the “-ase” suffix?
For any support, please contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected], or visit our address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. Our customer support team is available 24/7.

