The ASEAN Board of Governors (ABOG) plays a pivotal role in advancing ASEAN integration and cooperation. This group of high-ranking officials from each member state provides strategic guidance and oversight for various ASEAN initiatives, ensuring their alignment with the overall goals of the organization.
The Role and Importance of the ASEAN Board of Governors
The ABOG’s primary function is to oversee the implementation of the ASEAN Charter and its various agreements. They review progress, identify challenges, and make recommendations to the ASEAN Summit and other relevant bodies. This ensures that ASEAN remains on track towards achieving its shared goals of economic prosperity, political security, and socio-cultural cooperation.
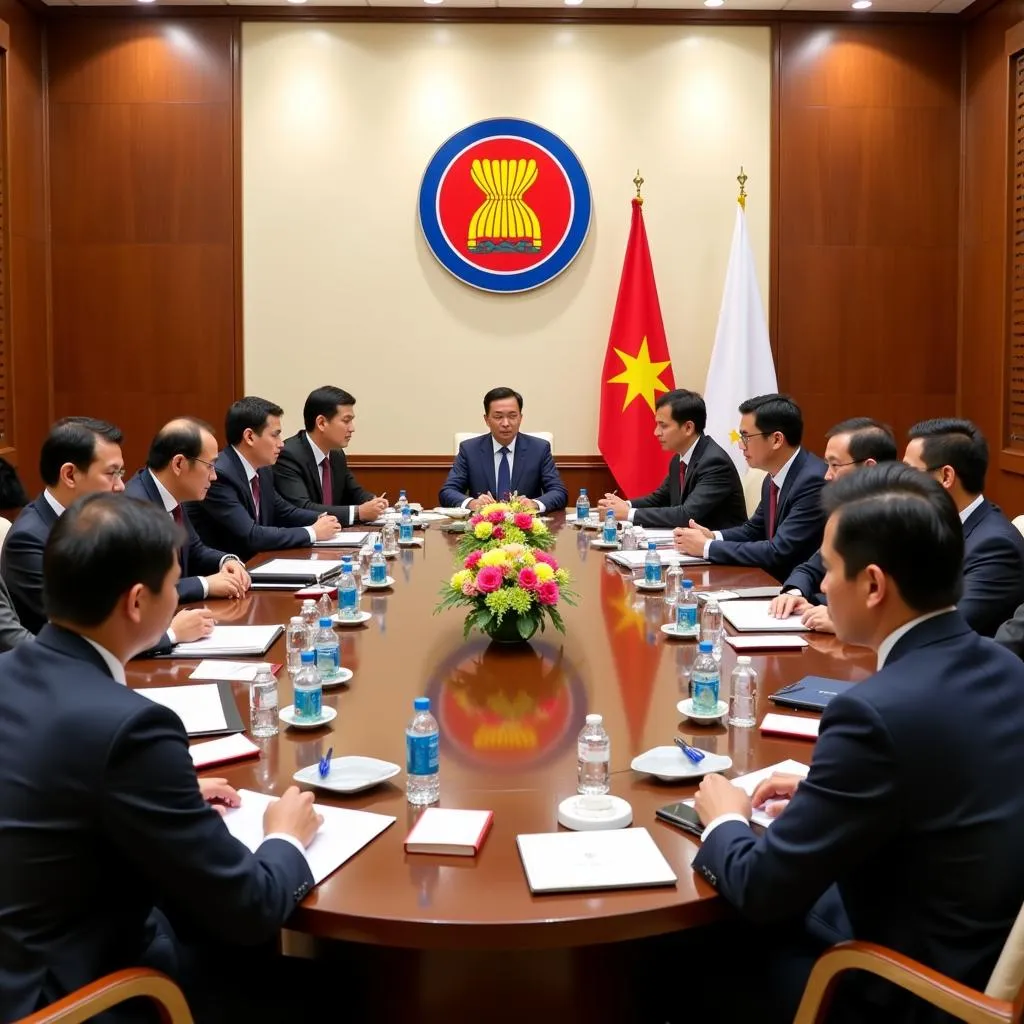 ASEAN Board of Governors Meeting
ASEAN Board of Governors Meeting
Key Responsibilities of the ABOG
The ABOG’s responsibilities are multifaceted and crucial for the effective functioning of ASEAN. These include:
- Strategic Planning: ABOG develops and monitors the implementation of strategic plans for various ASEAN sectors, ensuring they align with the ASEAN Community Vision 2025 and beyond.
- Policy Coordination: ABOG fosters policy coherence across different ASEAN sectors and facilitates cooperation among member states on critical issues.
- Resource Mobilization: ABOG explores avenues for securing financial and technical resources to support ASEAN initiatives and programs.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: ABOG monitors the progress of ASEAN initiatives, assesses their impact, and recommends adjustments to improve effectiveness.
Composition and Structure of the ABOG
The ABOG typically comprises senior officials from each ASEAN member state, usually at the Permanent Secretary or equivalent level. The board operates on a rotating chairmanship basis, with each country taking turns to lead for a specific term.
 ASEAN Board of Governors Structure
ASEAN Board of Governors Structure
Challenges and Opportunities for the ABOG
The ABOG faces numerous challenges in today’s complex geopolitical landscape. These include:
- Navigating Geopolitical Tensions: Balancing national interests with regional priorities in a rapidly evolving geopolitical environment.
- Addressing Development Gaps: Bridging the development gap among ASEAN member states to ensure inclusive and equitable growth.
- Enhancing ASEAN’s Global Role: Strengthening ASEAN’s position as a significant player in the global arena.
Despite these challenges, the ABOG has significant opportunities to further enhance ASEAN’s regional and global standing:
- Deepening Regional Integration: Leveraging digital technology and innovation to accelerate economic integration and connectivity.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: Prioritizing environmental protection and climate action in all ASEAN initiatives.
- Strengthening People-to-People Connectivity: Fostering closer ties among the peoples of ASEAN through cultural exchanges and educational programs.
Conclusion
The ASEAN Board of Governors plays a critical role in steering ASEAN towards a future of shared prosperity, peace, and unity. By providing strategic guidance, ensuring effective implementation of ASEAN initiatives, and navigating complex regional and global challenges, the ABOG significantly contributes to realizing the full potential of ASEAN.