Cardiac tamponade, a serious medical condition, arises when fluid accumulates within the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart. This pressure impedes the heart’s ability to fill properly, compromising its function and potentially leading to life-threatening consequences. Understanding the role of advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) and echocardiography, especially as highlighted by the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE), is crucial in diagnosing and managing cardiac tamponade.
ASE guidelines play a significant role in identifying and managing cardiac tamponade. The society emphasizes the importance of echocardiography in rapid diagnosis, guiding clinicians towards prompt intervention. Recognizing the specific echocardiographic signs of tamponade, such as right atrial and ventricular diastolic collapse, is key for accurate assessment. Furthermore, understanding the hemodynamic compromise associated with tamponade is vital for effective management.
The Role of ASE in Cardiac Tamponade Management
The ASE has been instrumental in developing and disseminating best practices for cardiac tamponade management. Their guidelines provide a framework for utilizing echocardiography in the emergency setting, ensuring rapid and accurate diagnosis. These recommendations are particularly valuable in resource-limited settings, where access to advanced imaging modalities may be restricted. ase guidelines pericardial effusion provide valuable insights into the nuances of pericardial effusion assessment.
Key Echocardiographic Findings in ASE Cardiac Tamponade
Echocardiography offers a real-time visualization of the heart and pericardium, allowing for the identification of key features indicative of tamponade. These include:
- Right atrial collapse during diastole
- Right ventricular collapse during diastole
- Swinging heart motion
- Dilated inferior vena cava with absent inspiratory collapse
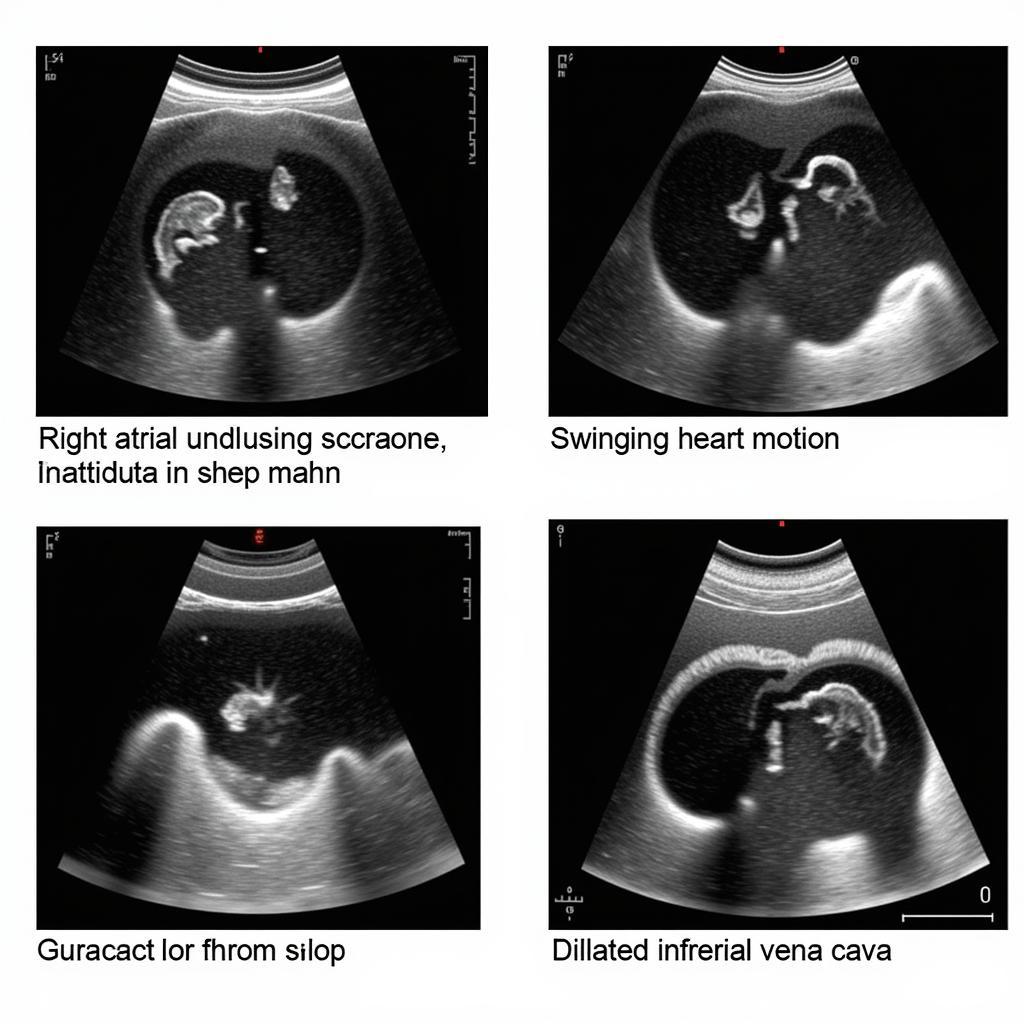 Echocardiographic Signs of Cardiac Tamponade
Echocardiographic Signs of Cardiac Tamponade
These findings, when considered in conjunction with the patient’s clinical presentation, allow for a confident diagnosis of cardiac tamponade. ase critical care echocardiography further expands upon the utilization of echocardiography in critical care settings, including the assessment of cardiac tamponade.
Treatment Strategies Based on ASE Recommendations
Once cardiac tamponade is diagnosed, prompt intervention is crucial. Pericardiocentesis, a procedure involving needle insertion into the pericardial sac to drain the accumulated fluid, is the definitive treatment. ASE guidelines provide recommendations for performing pericardiocentesis safely and effectively, minimizing potential complications. ase pericardial tamponade ppt offers a concise overview of this critical intervention.
What are the immediate steps in managing ASE cardiac tamponade?
The immediate steps involve stabilizing the patient hemodynamically with intravenous fluids and inotropic support, followed by urgent pericardiocentesis.
How does ASE guide pericardial effusion size assessment?
ase pericardial effusion size outlines specific criteria for categorizing pericardial effusion size, aiding in risk stratification and treatment decisions.
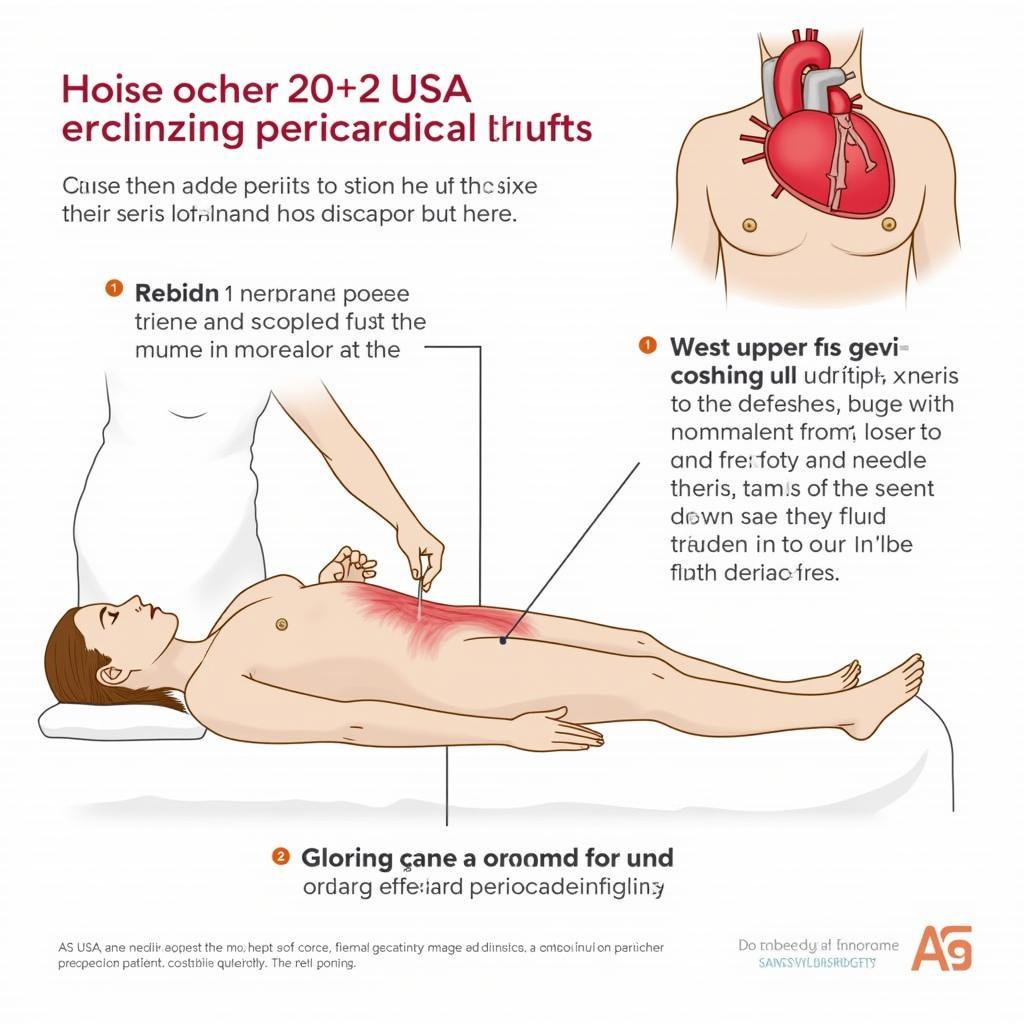 Pericardiocentesis Procedure for Cardiac Tamponade
Pericardiocentesis Procedure for Cardiac Tamponade
“Rapid diagnosis and intervention are paramount in managing cardiac tamponade. Echocardiography, as emphasized by the ASE, plays a critical role in facilitating this process,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading cardiologist specializing in critical care echocardiography.
In conclusion, Ase Cardiac Tamponade guidelines are crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Utilizing echocardiography as recommended enables prompt identification of key features and guides timely intervention, ultimately improving patient outcomes. ase pericardial effusion offers a comprehensive understanding of pericardial effusion and its management.
FAQ
- What is the most common cause of cardiac tamponade? Trauma is a frequent cause.
- What are the symptoms of cardiac tamponade? Symptoms can include shortness of breath, chest pain, and lightheadedness.
- How is cardiac tamponade diagnosed? Echocardiography is the primary diagnostic tool.
- What is the treatment for cardiac tamponade? Pericardiocentesis is the definitive treatment.
- What are the complications of cardiac tamponade? Untreated tamponade can lead to cardiac arrest.
- What is the prognosis of cardiac tamponade? With prompt treatment, the prognosis is generally good.
- What is the role of ASE in cardiac tamponade management? ASE provides crucial guidelines for diagnosis and treatment.
“Following ASE guidelines in cardiac tamponade management is essential for optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring the best possible care,” adds Dr. Ben Lee, a renowned expert in echocardiography and critical care medicine.
For further information on related topics, you might find these articles helpful: ASE Guidelines for Pericardial Effusion and ASE Critical Care Echocardiography.
When you need assistance, please contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.
We have a 24/7 customer service team.

