Ase Chemosensory Neurons are crucial components of the C. elegans nervous system, playing a vital role in the nematode’s ability to detect and respond to environmental cues. These specialized neurons allow the worm to navigate its surroundings, locate food sources, and avoid harmful stimuli. Understanding the function and development of these neurons provides valuable insights into the fundamental principles of sensory perception and behavior. ase c.elegans
The Role of ASE Chemosensory Neurons in C. elegans
ASE neurons are primarily located in the head of the C. elegans worm and are responsible for sensing various chemicals in the environment. This chemosensory information is then processed by the worm’s nervous system, ultimately leading to specific behavioral responses. For instance, ASE neurons can detect attractive cues, like food odors, causing the worm to move towards the source. Conversely, they can also sense repulsive cues, triggering avoidance behavior. The remarkable sensitivity and specificity of these neurons highlight their importance in the worm’s survival.
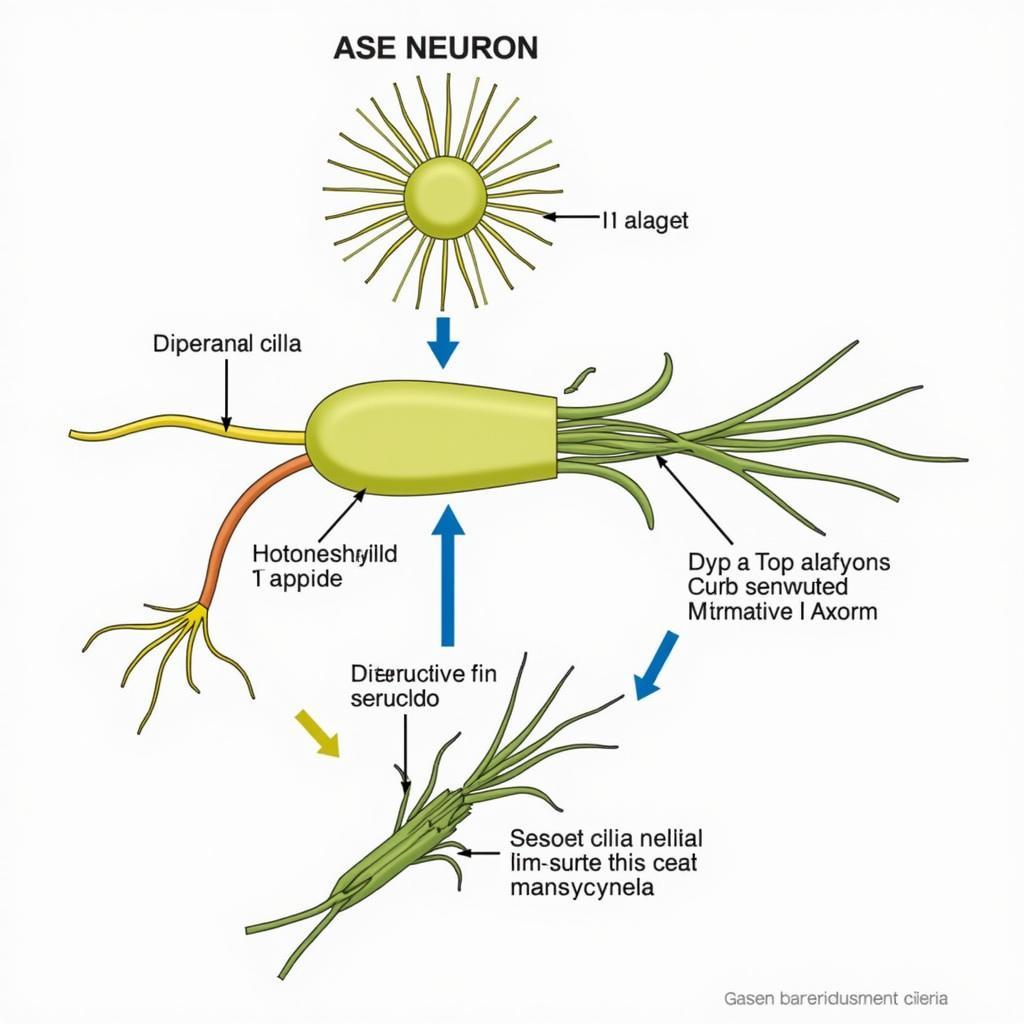 C. Elegans ASE Neuron Structure Diagram
C. Elegans ASE Neuron Structure Diagram
How ASE Neurons Detect Chemical Stimuli
The process of chemoreception in ASE neurons involves specialized receptor proteins located on the surface of the neuron’s sensory cilia. These receptors bind to specific chemicals in the environment, triggering a cascade of intracellular signaling events. This signaling ultimately leads to changes in the neuron’s activity, which are then transmitted to other neurons in the nervous system, ultimately resulting in a behavioral response. The intricate molecular mechanisms underlying chemoreception in ASE neurons are a subject of ongoing research.
“Understanding the precise mechanisms by which ASE neurons detect and process chemical signals is key to unraveling the complex interplay between sensory perception and behavior,” explains Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading neuroscientist at the National Institute of Biological Sciences.
Development and Differentiation of ASE Chemosensory Neurons
The development of ASE neurons is a tightly regulated process involving a complex network of genetic and molecular interactions. During embryonic development, specific genes are activated that determine the fate of precursor cells, directing them to differentiate into ASE neurons. ase chemosensory neurons killed This process involves precise control over cell division, migration, and differentiation, ensuring that the correct number of ASE neurons are generated and positioned correctly within the nervous system.
Genetic Regulation of ASE Neuron Development
Several genes have been identified that play critical roles in the development and differentiation of ASE neurons. For example, the lim-4 gene is essential for specifying the ASE cell fate, while the ceh-36 gene is involved in the differentiation of ASE neurons into distinct subtypes. ase chemosensory neurons ced-3“Mutations in these genes can disrupt ASE neuron development, leading to defects in chemosensory behavior,” adds Dr. Sharma. Further research into the genetic regulation of ASE neuron development will provide valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms that shape the nervous system.
The Importance of ASE Neurons in Understanding Sensory Biology
The study of ASE chemosensory neurons in C. elegans provides a powerful model system for understanding the fundamental principles of sensory biology. The worm’s simple nervous system and the availability of powerful genetic tools make it an ideal organism for investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying sensory perception, neural development, and behavior. asea for depression Findings from these studies can have broader implications for understanding sensory processing in more complex organisms, including humans.
 C. Elegans Chemosensory Behavior
C. Elegans Chemosensory Behavior
“The insights gained from studying ASE neurons in C. elegans can contribute to our understanding of human sensory disorders and the development of new therapeutic strategies,” says Dr. Ben Carter, a researcher at the University of California, San Francisco. ASE chemosensory neurons are a fascinating area of research with significant implications for understanding the complex world of sensory biology.
Conclusion
ASE chemosensory neurons are essential for C. elegans survival, allowing the worm to navigate its environment and respond to chemical cues. Understanding these neurons provides a valuable window into the intricate mechanisms of sensory perception and neural development. ase caen Further research on ASE chemosensory neurons promises to yield important discoveries with broader implications for understanding sensory biology in diverse organisms.
FAQ
- What are ASE neurons?
- How do ASE neurons detect chemicals?
- What genes are involved in ASE neuron development?
- Why is C. elegans a good model for studying sensory biology?
- What are the broader implications of studying ASE neurons?
- How do ASE neurons contribute to C. elegans behavior?
- What are the future directions of research on ASE neurons?
Need help? Contact us 24/7 at Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com Or visit us at: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.
