The Ase Db Poscar File is a crucial component for anyone working with atomic simulations, especially using the Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE) and the Vienna Ab initio Simulation Package (VASP). It essentially bridges the gap between these two powerful tools, allowing researchers to define and manipulate atomic structures efficiently. Let’s dive deeper into understanding this important file format.
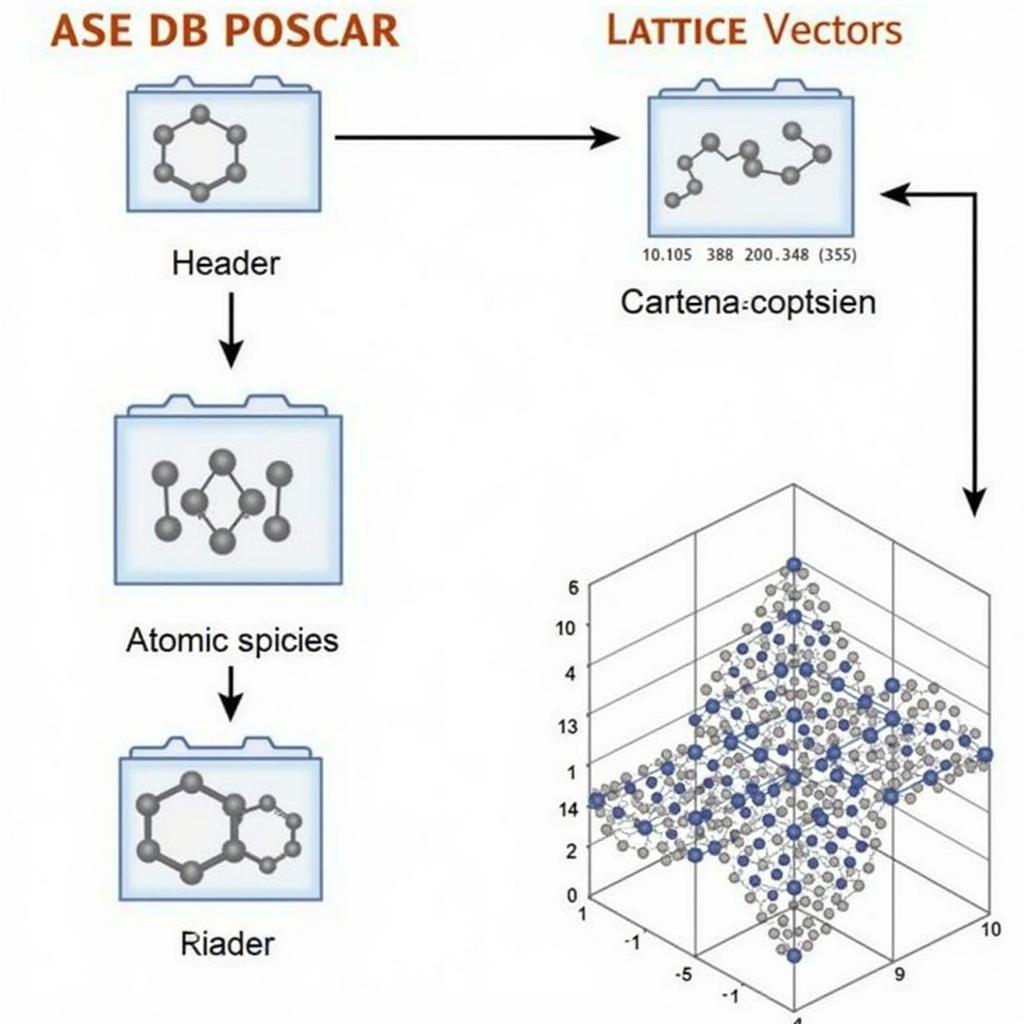 ASE DB POSCAR File Structure
ASE DB POSCAR File Structure
What is an ASE DB POSCAR File?
An ASE DB POSCAR file is a text file that describes the crystal structure of a material. It’s based on the POSCAR file format used by VASP, a popular software package for performing ab initio quantum mechanical calculations. ASE, a Python library for working with atoms, extends this functionality by allowing the storage and retrieval of POSCAR data within a database. This combination simplifies workflows and promotes reproducibility in computational materials science. This integration provides a powerful way to manage and analyze simulation data, making complex tasks more manageable.
 ASE VASP Workflow with POSCAR
ASE VASP Workflow with POSCAR
Decoding the Structure of an ASE DB POSCAR File
A typical ASE DB POSCAR file contains several key sections:
- Header: A comment line describing the system.
- Scale Factor: A single number that scales the lattice vectors.
- Lattice Vectors: Three lines defining the unit cell vectors.
- Atomic Species: A list of the elements present in the system.
- Number of Atoms: The number of atoms for each species.
- Cartesian or Direct Coordinates: The positions of each atom, either in Cartesian coordinates or fractional coordinates (direct coordinates).
Imagine building with LEGOs. The ASE DB POSCAR file is like the instruction manual, telling you which bricks (atoms) to use and how to arrange them (coordinates) to create the final structure. The lattice vectors define the size and shape of your LEGO baseplate.
Why Use ASE DB POSCAR Files?
The use of ASE DB POSCAR files offers several advantages:
- Seamless Integration with ASE and VASP: Streamlines the process of setting up and running calculations.
- Database Management: Facilitates efficient storage, retrieval, and manipulation of structural data.
- Reproducibility: Enables consistent and reliable simulations.
- Flexibility: Supports various atomic configurations and allows for easy modification of structural parameters.
“ASE’s ability to handle POSCAR files within a database is a game-changer for high-throughput calculations,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a computational materials scientist at the National University of Singapore. “It drastically reduces the overhead in managing large datasets.”
Practical Applications of ASE DB POSCAR Files
ASE DB POSCAR files are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Materials Design and Discovery: Exploring new materials with desired properties.
- Catalysis Research: Studying the interactions between molecules and surfaces.
- Surface Science: Investigating surface reconstructions and adsorption phenomena.
- Nanotechnology: Modeling and simulating nanoscale devices.
Working with ASE DB POSCAR Files
ASE provides a comprehensive set of tools for working with POSCAR files:
- Reading and Writing POSCAR Files: Easily import and export structural data.
- Manipulating Atomic Structures: Modifying coordinates, adding or removing atoms, and creating supercells.
- Visualizing Structures: Generating graphical representations of atomic arrangements.
- Performing Calculations: Setting up and running VASP calculations directly from ASE.
“The ability to manipulate POSCAR files programmatically using ASE is incredibly powerful,” adds Dr. Sharma. “It opens up new possibilities for automated workflows and complex simulations.”
Conclusion
The ASE DB POSCAR file is an essential tool for anyone working with atomic simulations using ASE and VASP. It provides a standardized and efficient way to define, manipulate, and store atomic structures, ultimately facilitating research and discovery in various fields. Understanding its structure and functionality is key to unlocking the full potential of these powerful computational tools. Utilizing ASE DB POSCAR files significantly enhances the efficiency and reproducibility of computational materials science research.
FAQ
- What is the difference between a standard POSCAR file and an ASE DB POSCAR file?
- How can I convert a CIF file to a POSCAR file using ASE?
- What are the common errors encountered when working with POSCAR files?
- How can I visualize an ASE DB POSCAR file?
- What are some best practices for managing POSCAR files in a database?
- How can I modify the lattice vectors in a POSCAR file using ASE?
- How can I access specific atomic coordinates within an ASE DB POSCAR file?
Need help?
Contact us for 24/7 support:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.

