Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and its effect on diastolic function are significant concerns, impacting the heart’s ability to relax and fill with blood. This intricate relationship can lead to various symptoms and complications, requiring a thorough understanding for effective management.
The Interplay Between Atrial Fibrillation and Diastolic Function
Diastolic dysfunction refers to the heart’s impaired ability to relax and fill with blood between beats. This filling phase is crucial for proper cardiac output. Atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and often rapid heartbeats, further complicates this process. The absence of coordinated atrial contractions in AFib disrupts the normal filling pattern, contributing to or exacerbating pre-existing diastolic dysfunction.
How AFib Exacerbates Diastolic Dysfunction
The chaotic rhythm of AFib eliminates the atrial “kick,” the final boost of blood into the ventricles that normally occurs with coordinated atrial contraction. This loss contributes significantly to reduced ventricular filling, particularly in patients who already have underlying diastolic dysfunction. Furthermore, the rapid heart rate often associated with AFib shortens the diastolic filling time, further compromising ventricular filling.
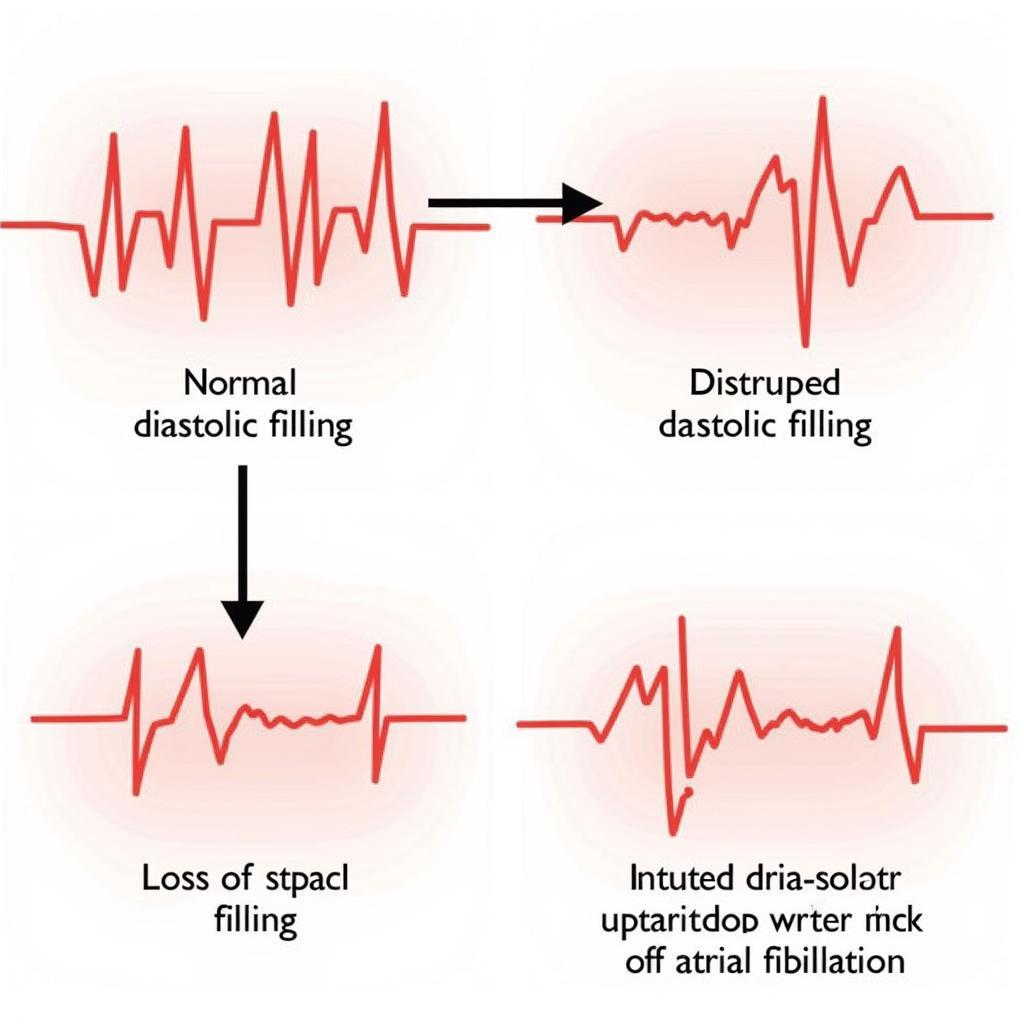 Impact of AFib on Diastolic Function
Impact of AFib on Diastolic Function
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Diastolic Dysfunction in AFib
Recognizing the symptoms of diastolic dysfunction in the context of AFib can be challenging, as they often overlap with symptoms of AFib itself, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. However, specific symptoms suggestive of worsening diastolic function include increased shortness of breath with exertion, orthopnea (shortness of breath when lying flat), and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (sudden shortness of breath at night). Echocardiography plays a crucial role in diagnosing and assessing the severity of diastolic dysfunction. This non-invasive test uses ultrasound to visualize the heart’s structure and function, providing detailed information about ventricular filling pressures and relaxation patterns.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Several diagnostic tools are used to evaluate diastolic function, including:
- Echocardiography: Assesses heart chamber size, valve function, and blood flow.
- Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function.
- Cardiac catheterization: Measures pressures within the heart chambers.
“Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management. A comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic testing, is essential,” says Dr. Amelia Carter, a leading cardiologist specializing in heart rhythm disorders.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Managing diastolic dysfunction in AFib requires a multi-faceted approach, addressing both the underlying heart rhythm disorder and the impaired diastolic function. Rate control and rhythm control strategies for AFib are employed to optimize heart rate and restore normal sinus rhythm when possible. Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly used to manage heart rate and rhythm. In addition, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and weight management, are essential for improving overall cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Changes and Their Benefits
Several lifestyle changes can significantly improve diastolic function:
- Regular exercise: Improves cardiovascular fitness and reduces stress on the heart.
- Healthy diet: Lowers cholesterol and blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Weight management: Reduces strain on the heart and improves overall health.
“Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing diastolic dysfunction and improving overall cardiovascular health,” adds Dr. David Miller, a renowned cardiac surgeon with extensive experience in treating heart failure.
 Lifestyle Modifications for Improved Heart Health
Lifestyle Modifications for Improved Heart Health
Conclusion
Atrial fibrillation and its impact on diastolic function represent a significant challenge in cardiovascular medicine. Understanding the interplay between these two conditions is vital for effective diagnosis and management. By addressing both the underlying heart rhythm disorder and the impaired diastolic function, healthcare professionals can help patients improve their symptoms, enhance their quality of life, and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing atrial fibrillation and diastolic dysfunction.
FAQ
- What is diastolic heart failure?
- How does atrial fibrillation affect diastolic filling?
- What are the common symptoms of diastolic dysfunction?
- How is diastolic dysfunction diagnosed?
- What are the treatment options for diastolic dysfunction in atrial fibrillation?
- Can lifestyle changes improve diastolic function?
- What is the long-term outlook for patients with diastolic dysfunction and AFib?
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, Address: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.