The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), often referred to as the ASEAN EF (Economic Framework), represents a significant step towards regional integration in Southeast Asia. This initiative aims to create a single market and production base, allowing for the free flow of goods, services, investments, skilled labor, and freer flow of capital. This article will delve into the key aspects of the ASEAN EF, exploring its benefits, challenges, and its impact on the region.
What is the ASEAN EF and its Objectives?
The ASEAN EF, established in 2015, envisions a highly competitive, integrated, and dynamic economic region. Its core objectives include reducing poverty and socioeconomic disparities, enhancing competitiveness, and promoting equitable economic development. The framework focuses on creating a rules-based, transparent, and predictable business environment, attracting foreign investment and boosting intra-ASEAN trade. A key component is the facilitation of skilled labor movement, allowing professionals to work across borders more easily.
One crucial element of the ASEAN EF is the focus on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These businesses are considered the backbone of many ASEAN economies. The framework aims to provide support and resources to empower SMEs, enabling them to participate actively in the integrated market. This includes initiatives to improve access to finance, technology, and market information.
The Pillars of the ASEAN EF
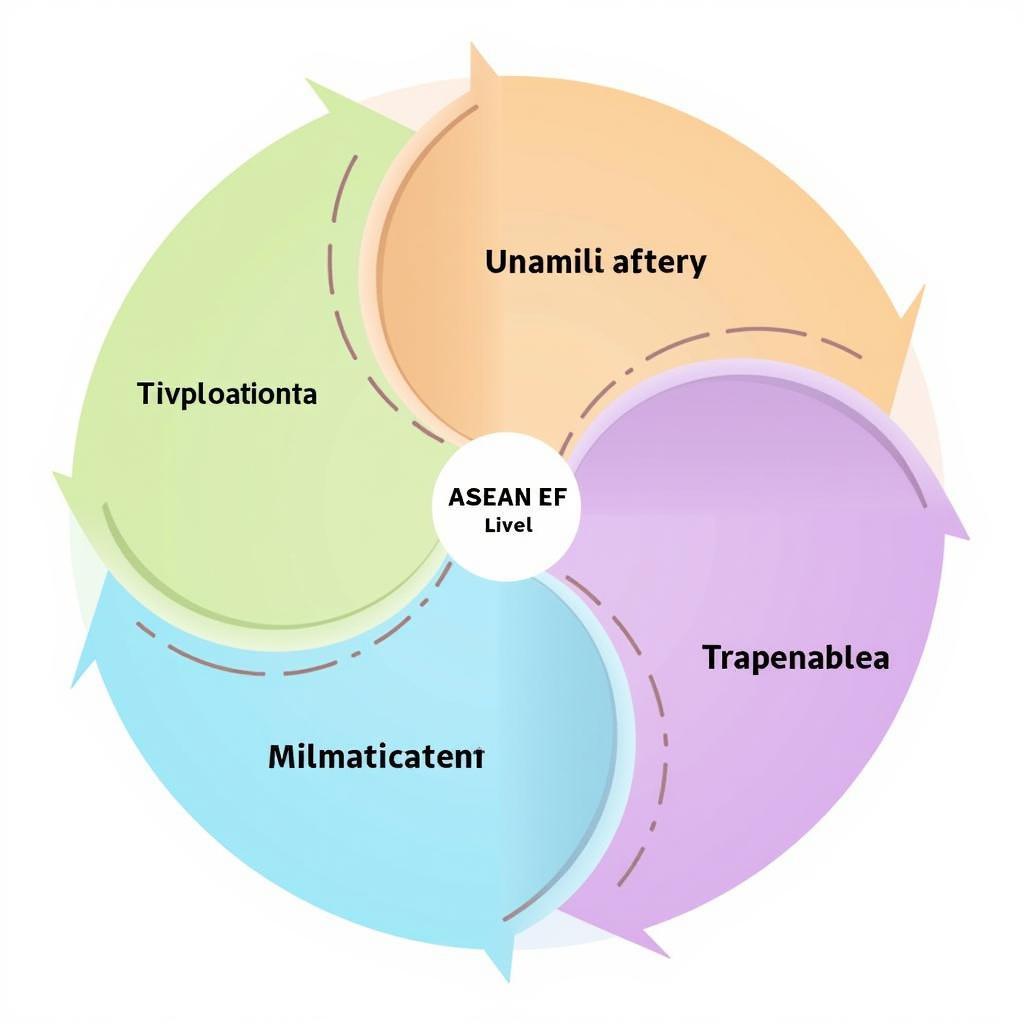
The ASEAN EF is built upon four key pillars that drive its integration efforts:
- Single Market and Production Base: This pillar promotes the free flow of goods, services, investment, and capital, fostering a more interconnected and efficient regional economy.
- Competitive Economic Region: This focuses on enhancing the competitiveness of ASEAN member states by promoting innovation, productivity, and entrepreneurship. It also emphasizes the development of infrastructure and connectivity.
- Equitable Economic Development: This pillar aims to reduce development gaps and ensure that all member states benefit from economic integration. It prioritizes initiatives to develop less developed economies and promote inclusive growth.
- Integration into the Global Economy: This pillar seeks to enhance ASEAN’s engagement with the global economy through free trade agreements and other forms of international cooperation. It aims to position ASEAN as a key player in global trade and investment.
 ASEAN EF Pillars Explained
ASEAN EF Pillars Explained
“The ASEAN EF is not just about economic growth, but about shared prosperity,” states Dr. Maria Lourdes Sereno, a prominent Southeast Asian economist. “It’s about ensuring that the benefits of integration reach all segments of society, particularly the most vulnerable.”
Challenges and Opportunities of the ASEAN EF
While the ASEAN EF presents numerous opportunities, it also faces challenges:
- Non-Tariff Barriers: Despite progress in reducing tariffs, non-tariff barriers, such as varying regulations and standards, continue to hinder trade and investment.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate infrastructure in some member states limits connectivity and hampers the efficient movement of goods and people.
- Skills Development: Developing a skilled workforce capable of competing in the integrated market is crucial. Addressing skills gaps and promoting lifelong learning are key priorities.
- Digital Divide: Bridging the digital divide within ASEAN is essential for ensuring equitable access to the benefits of the digital economy.
“Navigating the complexities of regional integration requires a collaborative approach,” notes Mr. Tran Van Tho, an expert in ASEAN affairs. “Addressing the challenges collectively will unlock the full potential of the ASEAN EF.”
Conclusion: The Future of the ASEAN EF
The ASEAN EF represents a bold vision for regional economic integration. While challenges remain, the framework holds immense potential for promoting sustainable and inclusive growth in Southeast Asia. By addressing these challenges and fostering collaboration, the ASEAN EF can continue to drive economic progress and prosperity for all ASEAN member states. The ASEAN EF is a crucial framework for ensuring the region’s continued economic growth.
FAQ
- What does ASEAN EF stand for? It stands for ASEAN Economic Framework.
- When was the ASEAN EF established? It was established in 2015.
- What are the key pillars of the ASEAN EF? The four pillars are the Single Market and Production Base, Competitive Economic Region, Equitable Economic Development, and Integration into the Global Economy.
- What are some challenges faced by the ASEAN EF? Challenges include non-tariff barriers, infrastructure gaps, skills development, and the digital divide.
- How does the ASEAN EF benefit SMEs? It aims to provide SMEs with access to finance, technology, and market information, empowering them to participate in the integrated market.
- What is the role of the AEC in the ASEAN EF? The AEC is the core component of the ASEAN EF, focusing on creating a single market and production base.
- How can I learn more about the ASEAN EF? Visit the official ASEAN website and reputable research institutions for comprehensive information.
a los cuantos dias ase efecto la inyeccion de penicilina
ase effective regurgitant orifice area
When you need support, please contact Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com Or visit the address: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer care team.
