Constrictive pericarditis, a condition where the pericardium (the sac surrounding the heart) becomes thickened and scarred, limiting the heart’s ability to fill properly, requires careful diagnosis and management. The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines for constrictive pericarditis provide valuable recommendations for healthcare professionals utilizing echocardiography in evaluating this often complex cardiac condition. This article explores the key aspects of these guidelines, offering insights into their importance and practical application.
Echocardiography’s Role in Diagnosing Constrictive Pericarditis According to ASE Guidelines
Echocardiography plays a crucial role in evaluating patients suspected of having constrictive pericarditis. The ASE guidelines outline specific echocardiographic findings that support the diagnosis, including abnormal diastolic function, respirophasic changes in mitral and tricuspid inflow velocities, and exaggerated septal motion. These guidelines emphasize the importance of integrating echocardiographic findings with clinical presentation and other diagnostic modalities for a comprehensive assessment.
Understanding the Key Echocardiographic Criteria in ASE Guidelines Constrictive Pericarditis
The ASE guidelines highlight specific echocardiographic criteria that are highly suggestive of constrictive pericarditis. These include:
- Increased pericardial thickness: While not always present, a thickened pericardium can be a significant finding.
- Abnormal septal motion: Exaggerated septal shift during respiration is a classic sign.
- Respirophasic variations in mitral and tricuspid inflow: Changes in blood flow across the mitral and tricuspid valves during breathing are characteristic of constrictive pericarditis.
- Hepatic vein flow reversal: This finding can indicate elevated right-sided heart pressures.
Differentiating Constrictive Pericarditis from Restrictive Cardiomyopathy using ASE Guidelines
One of the most challenging aspects of diagnosing constrictive pericarditis is differentiating it from restrictive cardiomyopathy, as both conditions can present with similar symptoms and hemodynamic findings. The ASE guidelines provide crucial guidance on using echocardiography to distinguish between these two entities. Specific parameters, such as the ratio of mitral inflow E velocity to mitral annular early diastolic velocity (E/e’), can help differentiate between the two. For example, a high E/e’ is more suggestive of restrictive cardiomyopathy.
The Significance of Tissue Doppler Imaging in ASE Guidelines
Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) plays a vital role in evaluating diastolic function and is particularly helpful in distinguishing constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy. TDI assesses the velocity of myocardial motion, providing valuable information about the early diastolic filling phase. The ASE guidelines recommend using TDI to assess mitral annular velocities, which can be markedly reduced in constrictive pericarditis.
The Importance of Integrating Echocardiography with Other Diagnostic Modalities
While echocardiography is a powerful tool, the ASE guidelines emphasize the importance of integrating echocardiographic findings with other diagnostic tests, including cardiac catheterization, cardiac MRI, and CT scans. Cardiac catheterization is often considered the gold standard for differentiating constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy.
ase guidelines pericardial disease
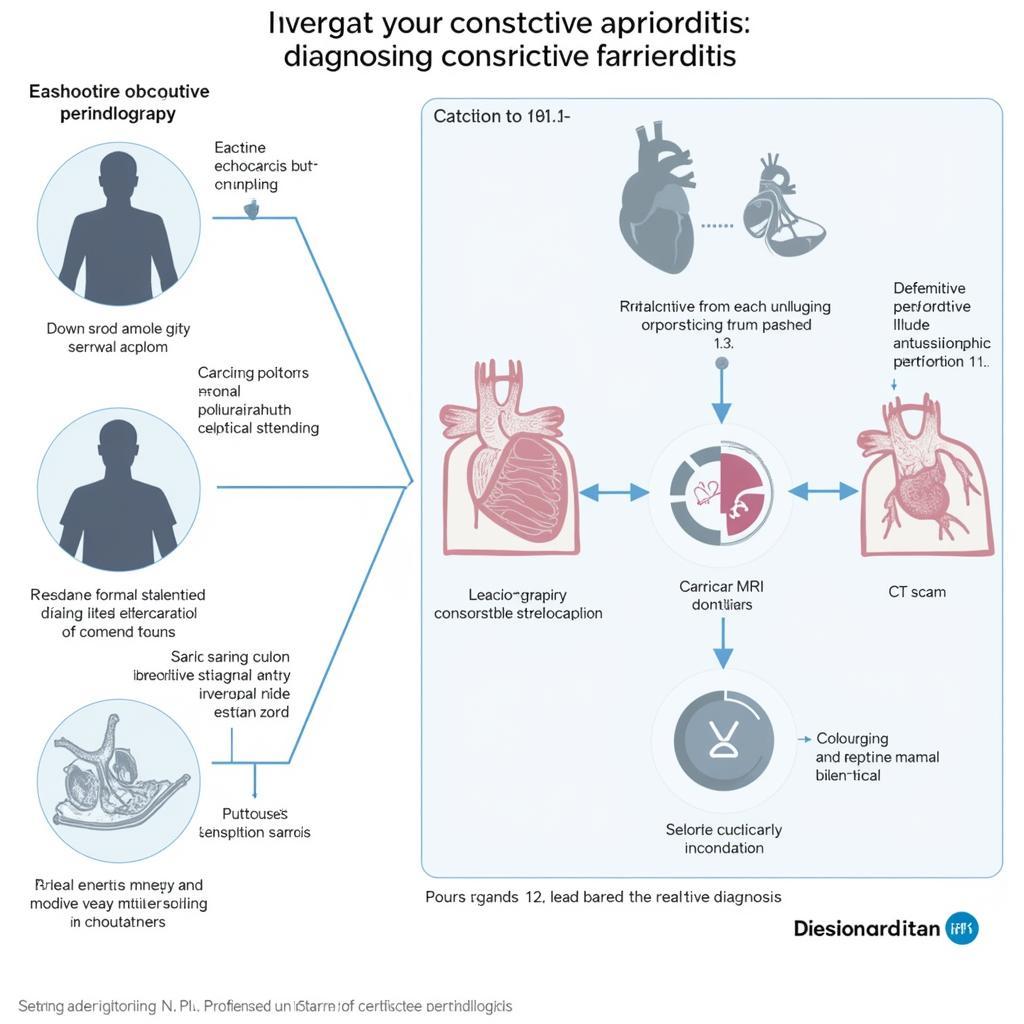 Integrated Approach to Diagnosing Constrictive Pericarditis
Integrated Approach to Diagnosing Constrictive Pericarditis
“Accurate diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis relies on a multidisciplinary approach,” says Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a renowned cardiologist at the National Heart Institute in Singapore. “The ASE guidelines provide a valuable framework for echocardiographers, but it’s crucial to consider the clinical context and other diagnostic information.”
“Echocardiography, when interpreted within the context of the ASE guidelines, empowers clinicians to make informed decisions regarding patient management,” adds Dr. Suresh Kumar, a leading cardiac imaging specialist at the Bangkok Heart Hospital. “This leads to improved outcomes for patients with this challenging condition.”
In conclusion, the ASE guidelines for constrictive pericarditis provide essential guidance for healthcare professionals utilizing echocardiography in the evaluation of this complex condition. By adhering to these guidelines and integrating echocardiographic findings with other diagnostic modalities, clinicians can ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
FAQs:
- What is constrictive pericarditis?
- What are the common symptoms of constrictive pericarditis?
- How is constrictive pericarditis diagnosed?
- What is the role of echocardiography in diagnosing constrictive pericarditis?
- How is constrictive pericarditis treated?
- What is the prognosis for constrictive pericarditis?
- What are the complications of constrictive pericarditis?
Need further assistance?
Contact us: Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.
