Understanding the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines for stenotic valves is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of heart valve disease. These guidelines provide a standardized framework for evaluating valve stenosis, utilizing echocardiography to assess severity and guide treatment decisions.
What are the ASE Guidelines for Stenotic Valves?
The Ase Guidelines For Stenotic Valves offer a comprehensive approach to evaluating the severity of stenosis in various heart valves, including the aortic, mitral, pulmonic, and tricuspid valves. They incorporate various echocardiographic parameters, such as mean pressure gradients, peak velocities, valve area, and other supporting findings. These guidelines are regularly updated to reflect advancements in echocardiographic techniques and clinical understanding of valvular heart disease. Following these guidelines ensures consistent and accurate assessment of stenotic valves, contributing to improved patient outcomes. ase guidelines valve stenosis
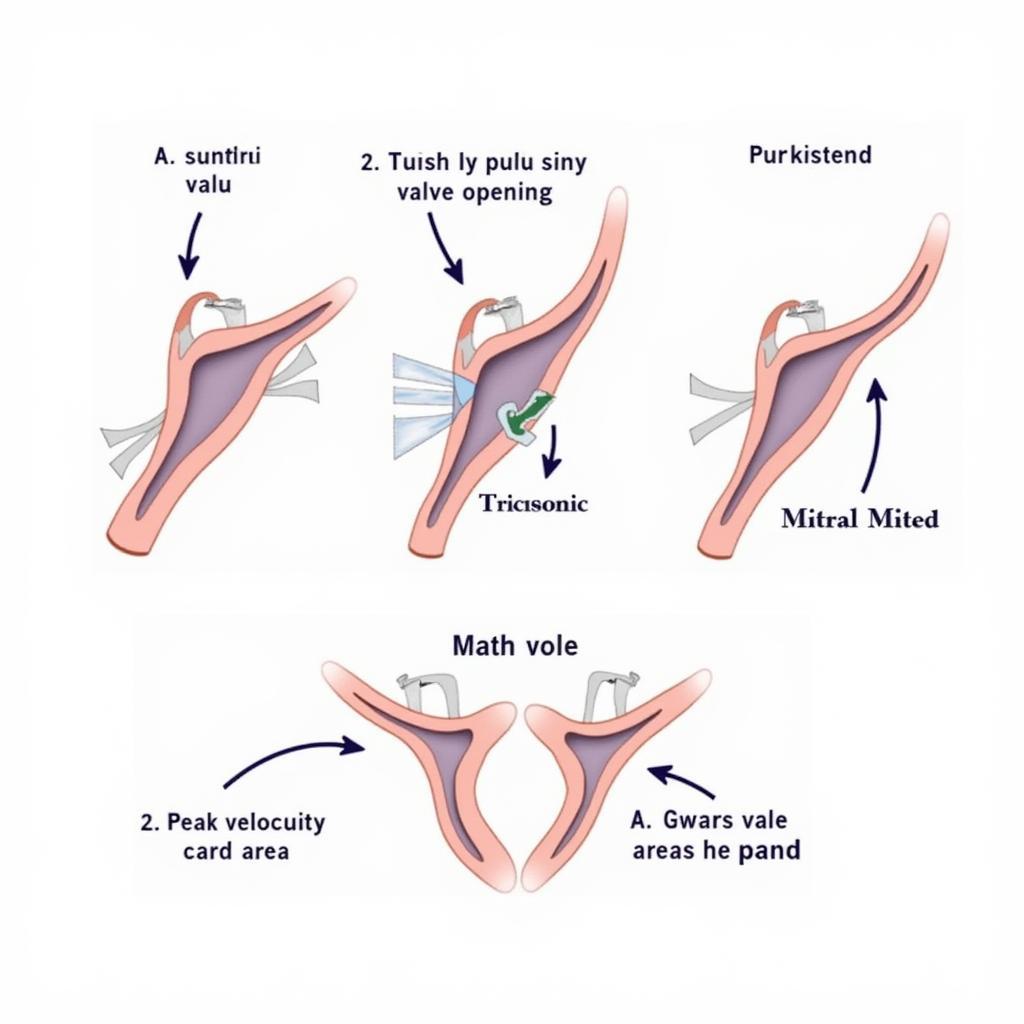 Diagram illustrating stenotic heart valves and key parameters for assessment
Diagram illustrating stenotic heart valves and key parameters for assessment
Key Parameters in ASE Guidelines for Stenotic Valves
The ASE guidelines utilize several key echocardiographic parameters to assess valve stenosis. These include:
- Peak Velocity: The highest velocity of blood flow across the stenotic valve.
- Mean Pressure Gradient: The average pressure difference across the stenotic valve.
- Valve Area: The effective opening area of the stenotic valve.
- Valve Morphology: Assessment of the valve structure and leaflets, including thickening, calcification, and mobility.
These parameters are integrated to provide a comprehensive evaluation of stenosis severity, guiding clinical decision-making regarding the need for intervention. ase valvular stenosis guidelines
Why are the ASE Guidelines Important?
The ASE guidelines are crucial for several reasons:
- Standardization: They ensure consistent evaluation of valve stenosis across different healthcare settings.
- Accuracy: The guidelines promote accurate diagnosis and assessment of stenosis severity.
- Treatment Guidance: They provide a framework for determining appropriate treatment strategies, including medical therapy, percutaneous interventions, or surgical valve replacement.
- Improved Outcomes: Adherence to the guidelines contributes to improved patient outcomes by ensuring timely and appropriate management of valve stenosis.
How are the ASE Guidelines Applied in Practice?
Echocardiographers use the ASE guidelines during echocardiographic examinations to evaluate suspected valve stenosis. Measurements are obtained according to the guidelines, and the severity of stenosis is classified based on specific criteria. This information is then communicated to the patient’s healthcare team to guide treatment decisions.
What are the Different Levels of Stenosis Severity?
The ASE guidelines typically classify stenosis severity into mild, moderate, and severe categories based on the echocardiographic parameters. Each category has specific criteria based on the combination of peak velocity, mean pressure gradient, and valve area.
“Accurate assessment of stenosis severity is paramount for appropriate management. The ASE guidelines provide a crucial framework for achieving this.” – Dr. Amelia Tan, Cardiologist
Mild Stenosis
Mild stenosis often requires monitoring and medical management.
Moderate Stenosis
Moderate stenosis may necessitate more frequent monitoring and potential intervention.
Severe Stenosis
Severe stenosis typically requires intervention, either percutaneous or surgical, to alleviate the obstruction.
“Following the ASE guidelines ensures we’re speaking the same language when evaluating valve stenosis, facilitating effective communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals.” – Dr. Wei Ming Lee, Echocardiographer
Conclusion
The ASE guidelines for stenotic valves are essential for standardized, accurate, and effective evaluation and management of valvular heart disease. Adhering to these guidelines allows for consistent assessment of stenosis severity, informing treatment decisions and ultimately improving patient outcomes. Understanding these guidelines is paramount for anyone involved in the care of patients with valvular heart disease.
FAQs
- What is valve stenosis?
- How is valve stenosis diagnosed?
- What are the symptoms of valve stenosis?
- What are the treatment options for valve stenosis?
- What are the long-term implications of valve stenosis?
- How often should I have an echocardiogram if I have valve stenosis?
- What are the risks associated with valve replacement surgery?
If you need further assistance, please contact us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com
Address: Ngoc Lien Village, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.
Our customer service team is available 24/7.
