The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines for tricuspid valve assessment provide a crucial framework for evaluating this often-overlooked heart valve. Understanding the Ase Guidelines Tricuspid Valve recommendations is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of tricuspid valve disease.
What are the ASE Guidelines for Tricuspid Valve Assessment?
The ASE has developed comprehensive guidelines for evaluating the tricuspid valve using echocardiography. These guidelines address various aspects of tricuspid valve assessment, including:
- Quantifying Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR): The guidelines provide a detailed methodology for assessing the severity of TR, utilizing various parameters such as vena contracta width, proximal isovelocity surface area (PISA), and hepatic vein flow patterns. Understanding the different methods and their limitations is crucial for accurate TR quantification.
- Evaluating Tricuspid Stenosis (TS): While less common than TR, TS can also be effectively assessed using echocardiography. The guidelines outline the parameters for diagnosing and quantifying TS, including mean pressure gradient and valve area.
- Assessing Tricuspid Valve Morphology: Echocardiography allows visualization of the tricuspid valve leaflets and annulus, enabling assessment of morphological abnormalities such as prolapse, flail, or thickening. This information is essential for guiding treatment decisions.
Why are the ASE Guidelines Important?
The ASE guidelines for tricuspid valve play a vital role in standardizing echocardiographic assessment. This standardization ensures consistency and accuracy in diagnosis and facilitates communication among healthcare professionals. Adhering to the ASE guidelines allows for better patient care and improved outcomes. For example, accurately quantifying TR using the ASE guidelines helps determine appropriate timing for intervention, such as surgery or transcatheter procedures. The guidelines also aid in identifying patients who might benefit from medical therapies.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading cardiologist at the Heart Institute, emphasizes the importance of consistent assessment: “Following the ASE guidelines ensures that all clinicians are speaking the same language when it comes to tricuspid valve disease. This consistency is vital for making informed treatment decisions.”
Key Components of the ASE Guidelines
The ASE guidelines for tricuspid valve are quite detailed, covering a wide range of topics. However, some key components include:
- Two-Dimensional Echocardiography: 2D echo provides structural information about the valve and surrounding structures.
- Doppler Echocardiography: Doppler is crucial for assessing blood flow across the tricuspid valve, helping quantify TR and TS. Color Doppler helps visualize the regurgitant jet, while continuous-wave and pulsed-wave Doppler provide information about flow velocities and pressure gradients.
- Three-Dimensional Echocardiography: While not routinely used, 3D echo can provide additional insights into tricuspid valve morphology and function, particularly in complex cases.
ASE Guidelines in Practice
Implementing the ASE guidelines involves a systematic approach. The echocardiographer should acquire high-quality images and carefully measure the relevant parameters. The guidelines provide detailed instructions on image acquisition and measurement techniques.
Professor Robert Lee, a renowned echocardiography expert, shares his perspective: “Proper application of the ASE guidelines requires both technical expertise and clinical judgment. Understanding the nuances of the guidelines is crucial for accurate interpretation of echocardiographic findings.”
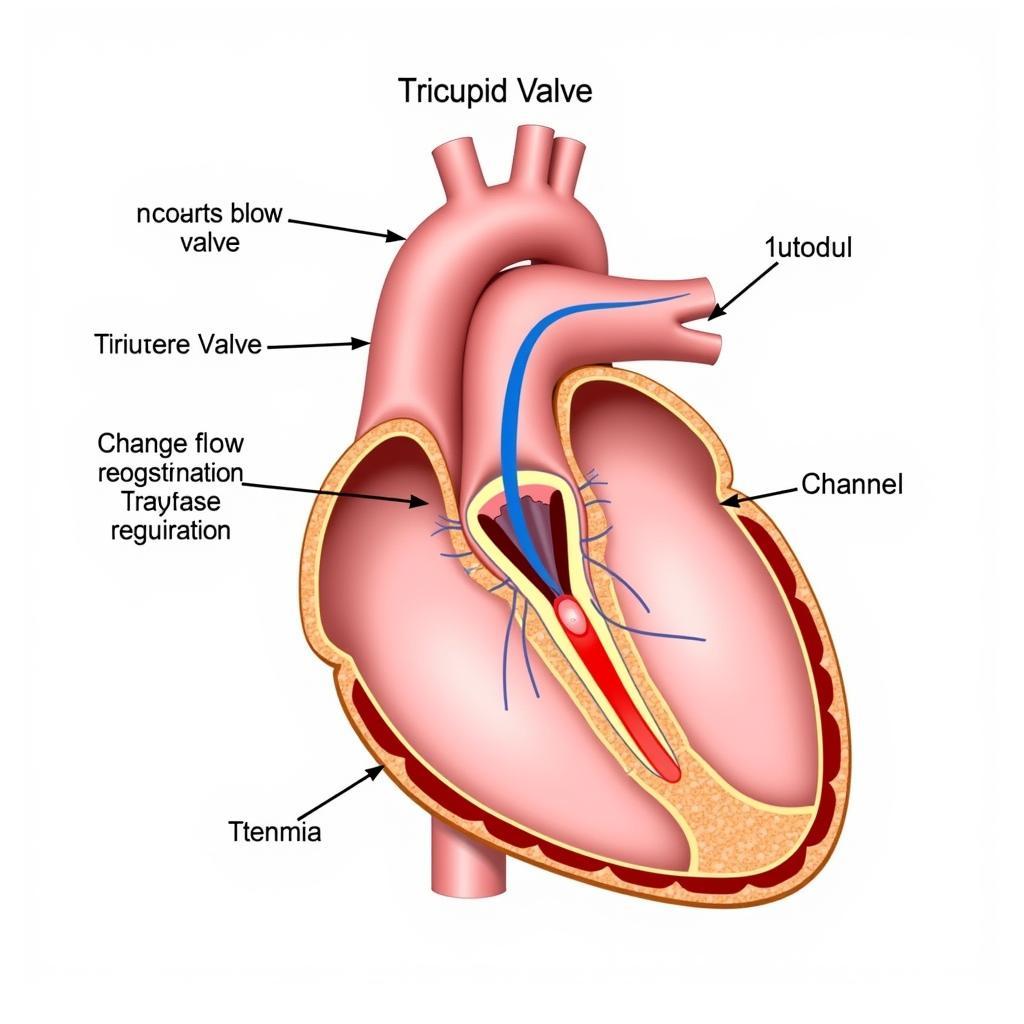 Tricuspid Valve Anatomy and Function
Tricuspid Valve Anatomy and Function
Conclusion
The ASE guidelines tricuspid valve recommendations provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating this important heart valve. Adhering to these guidelines is essential for ensuring accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and improved patient outcomes. By standardizing assessment techniques, the ASE guidelines facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, ultimately contributing to better patient care. This knowledge is invaluable for healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases. For further information on related topics, see our articles on ase echo guidelines prosthetic valve, ase regurgitation, and ase guidelines diastolic function 2016 ppt.
FAQ
- What is the role of echocardiography in assessing the tricuspid valve? Echocardiography is the primary imaging modality for evaluating the tricuspid valve’s structure and function.
- How is tricuspid regurgitation quantified using the ASE guidelines? The ASE guidelines recommend using multiple parameters, including vena contracta width, PISA, and hepatic vein flow patterns, to quantify TR.
- What are the key parameters for diagnosing tricuspid stenosis? Mean pressure gradient and valve area are the primary parameters for assessing TS.
- Why is it important to follow the ASE guidelines for tricuspid valve assessment? The guidelines ensure consistency and accuracy in diagnosis, facilitating communication and improving patient care.
- What are the different types of echocardiography used for evaluating the tricuspid valve? 2D, Doppler, and 3D echocardiography can be used to assess the tricuspid valve.
- How can I find more information about the ASE guidelines for tricuspid valve assessment? The complete guidelines are available on the American Society of Echocardiography website. You can also read more about related topics like ase guidelines native valvular regurgitation and ase guidelines constrictive pericarditis.
- What are the latest updates in the ASE guidelines for tricuspid valve? Refer to the ASE website for the most current version of the guidelines.
You might also be interested in these related articles:
- ASE Guidelines for Valvular Heart Disease
- Echocardiography Techniques for Evaluating Heart Valves
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, or visit us at: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam.