The Ase Radial Distribution Function (RDF) is a crucial tool for analyzing the structure of materials at the atomic level. Within the first 50 words, we’ve established our focus: using the Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE) to calculate and interpret radial distribution functions. This function provides valuable insights into the arrangement and interactions of atoms within a material, helping researchers understand properties and behavior.
Delving into the ASE Radial Distribution Function
The radial distribution function, often denoted as g(r), describes the probability of finding an atom at a distance r from a reference atom. It essentially provides a snapshot of the average atomic arrangement around any given atom in the system. This information is essential for understanding various material properties, such as density, phase transitions, and transport phenomena. 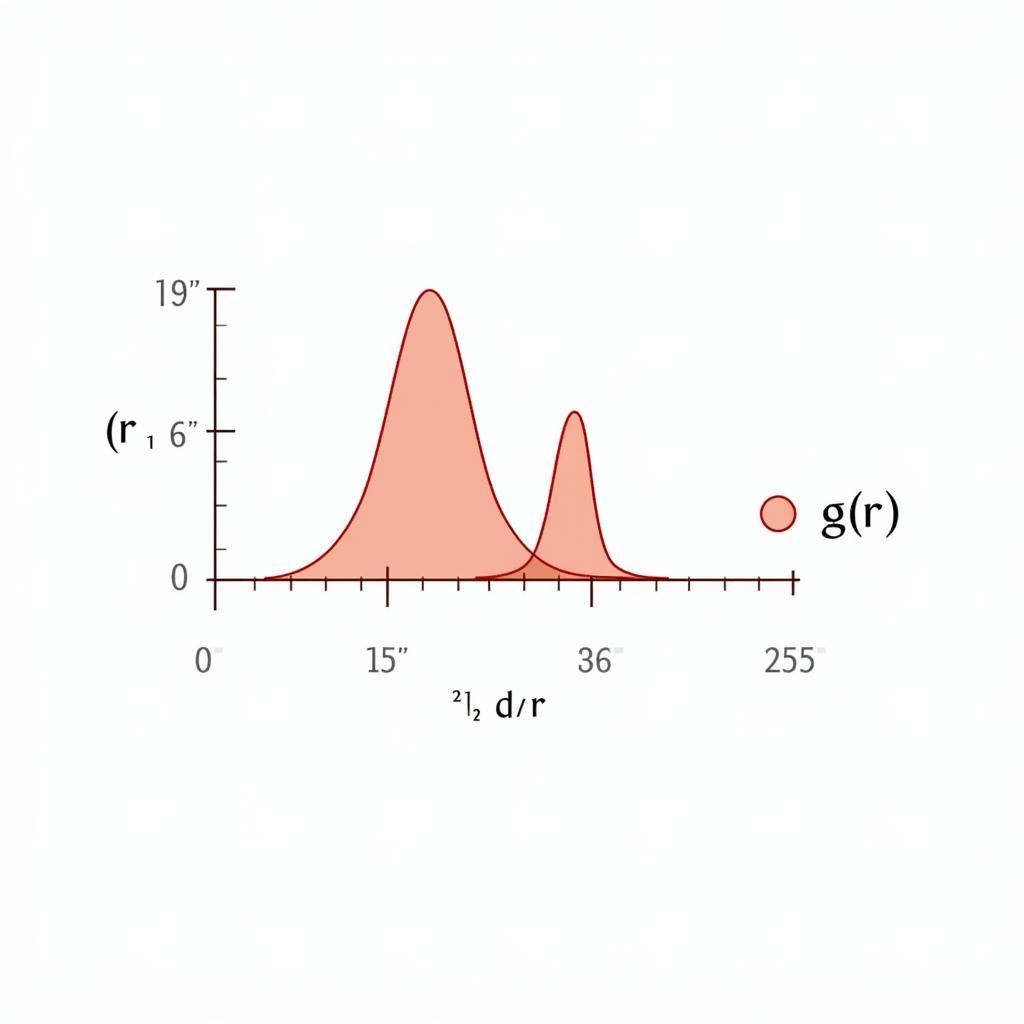 Visualizing the RDF in ASE
Visualizing the RDF in ASE
Using ASE, calculating the RDF becomes a streamlined process. The package offers built-in functions to compute g(r) directly from atomic configurations obtained from simulations or experimental data. This allows researchers to easily analyze their systems and extract valuable structural information. ase plot trajectory traj
Why is the ASE Radial Distribution Function Important?
The RDF’s importance lies in its ability to bridge the gap between microscopic atomic arrangements and macroscopic material properties. By analyzing the peaks and valleys of the RDF, researchers can identify preferred interatomic distances, coordination numbers, and the degree of order or disorder within the material. This information can then be used to explain and predict a wide range of material behaviors.
For instance, a sharp peak in the RDF at a specific distance indicates a strong preference for atoms to be separated by that distance. This can be indicative of strong bonding or specific structural motifs within the material. Conversely, a broad, flat RDF suggests a lack of long-range order, characteristic of amorphous materials like glasses. ase md simulation
“The ASE radial distribution function is an indispensable tool in my research,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a materials scientist at the National University of Singapore. “It allows me to quickly analyze the structure of complex materials and gain valuable insights into their properties.”
Calculating the RDF with ASE: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the RDF using ASE is relatively straightforward:
- Import necessary modules: Begin by importing the necessary modules from the ASE library.
- Define your atomic structure: Create an
Atomsobject representing your material’s atomic structure. - Use the
get_rdf()function: Call theget_rdf()function, providing the necessary parameters such as the cutoff distance and the number of bins. - Visualize the RDF: Plot the obtained RDF data to visualize the structural information.
 Example of RDF Calculation in ASE
Example of RDF Calculation in ASE
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the RDF requires careful analysis of the peaks and their positions. The first peak typically corresponds to the nearest-neighbor distance, while subsequent peaks represent further coordination shells. The height and width of the peaks provide information about the strength of the interactions and the degree of structural order.
“Understanding the radial distribution function is crucial for any materials scientist,” adds Dr. Kenji Tanaka, a researcher at the University of Tokyo. “It provides a fundamental link between the atomic structure and the observable properties of a material.” ase atoms distance
Conclusion: Unlocking Material Secrets with the ASE Radial Distribution Function
The ASE radial distribution function is a powerful tool for understanding the structure of materials at the atomic level. Its ease of use within the ASE package makes it an invaluable asset for researchers in various fields. By leveraging the RDF, scientists can gain critical insights into material properties and design new materials with tailored characteristics.
FAQ
- What is the radial distribution function?
- How do I calculate the RDF using ASE?
- What do the peaks in the RDF represent?
- How can I interpret the RDF results?
- What are some common applications of the RDF?
- What are the limitations of the RDF?
- How does the RDF relate to other structural analysis techniques?
Need assistance? Contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com or visit us at Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.