The demand for cooling solutions is rapidly increasing across Southeast Asia, driven by factors like population growth, urbanization, and rising temperatures. While air conditioners and refrigeration are essential for comfort and economic development, they rely on refrigerants, which can contribute to climate change if not managed responsibly. That’s where refrigerant recovery and recycling come into play, offering a sustainable approach to cooling in the ASEAN region.
Understanding the Importance of Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling
Refrigerants, often potent greenhouse gases, can significantly impact global warming if released into the atmosphere. Recognizing this, ASEAN countries have made commitments to phase down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), a common type of refrigerant, under the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol. This commitment underscores the need for effective refrigerant management strategies, including recovery and recycling.
Refrigerant recovery involves collecting used refrigerants from equipment like air conditioners and refrigerators before disposal or servicing. This process prevents the release of harmful gases into the environment. Recycling takes it a step further by cleaning and processing recovered refrigerants, making them suitable for reuse in new or existing equipment.
Key Benefits of Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling in ASEAN
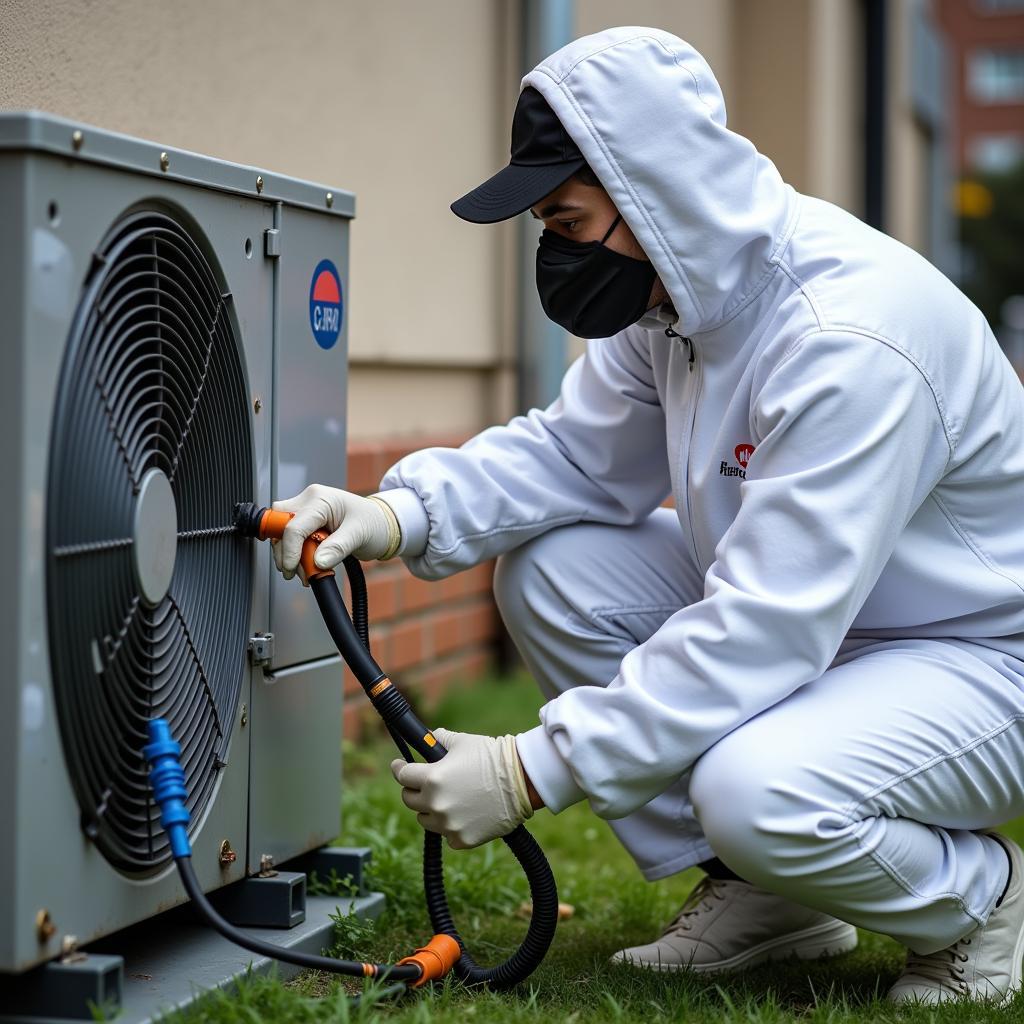 Refrigerant Recovery Process in Action
Refrigerant Recovery Process in Action
Implementing robust refrigerant recovery and recycling programs offers numerous benefits for ASEAN countries:
- Environmental Protection: By preventing refrigerant leaks and emissions, these practices contribute significantly to mitigating climate change and protecting the ozone layer.
- Economic Advantages: Recycling refrigerants reduces the need to manufacture new ones, saving resources and energy. This can lead to cost savings for businesses and consumers.
- Compliance with International Standards: ASEAN nations are actively working towards fulfilling their commitments under international agreements like the Kigali Amendment. Effective refrigerant management is crucial for achieving these goals.
Addressing Challenges and Promoting Best Practices
While ASEAN countries have made strides in refrigerant management, challenges remain:
- Lack of Awareness: Many consumers and businesses are unaware of the environmental impact of refrigerants and the importance of proper disposal.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Setting up efficient recovery and recycling facilities requires significant investment and technological expertise.
- Enforcement of Regulations: Consistent implementation and enforcement of regulations related to refrigerant management are crucial for effectiveness.
To overcome these challenges, ASEAN nations can focus on:
- Raising Public Awareness: Educational campaigns can inform the public about proper refrigerant handling and disposal practices.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Supporting the development of advanced recycling facilities and technologies is essential.
- Strengthening Regulations: Implementing clear and stringent regulations, along with effective enforcement mechanisms, can ensure compliance.
“The successful implementation of refrigerant recovery and recycling programs in ASEAN requires a collaborative effort,” says Dr. Nguyen Van Minh, a leading environmental engineer specializing in sustainable cooling solutions. “Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to adopt environmentally sound practices and promote a circular economy for refrigerants.”
ASEAN’s Path Towards Sustainable Cooling
ASEAN’s commitment to phasing down HFCs presents a unique opportunity to transition towards sustainable cooling solutions. By investing in refrigerant recovery and recycling, the region can mitigate the environmental impact of cooling systems while ensuring economic growth and improving the well-being of its citizens. The journey towards a cooler and more sustainable future for ASEAN begins with responsible refrigerant management.