Postoperative nursing management, as discussed in chapter 19, is crucial for ensuring patient safety, comfort, and optimal recovery after a surgical procedure. This involves a comprehensive approach encompassing pain management, wound care, monitoring vital signs, and preventing complications. Effective postoperative nursing management, guided by the principles outlined in chapter 19, plays a vital role in minimizing risks and promoting positive patient outcomes.
Understanding the Importance of Postoperative Nursing Management (Chapter 19)
Chapter 19 emphasizes the multifaceted nature of postoperative care. It highlights the nurse’s role as a patient advocate, educator, and coordinator of care. This period, immediately following surgery, is when patients are most vulnerable to complications like infections, respiratory issues, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Proper management based on chapter 19’s guidelines can significantly reduce these risks.
Key Aspects of Postoperative Care as Detailed in Chapter 19
Chapter 19 details several crucial aspects of postoperative care. Pain management is paramount, as uncontrolled pain can hinder recovery and increase the risk of complications. Wound care is equally important, focusing on preventing infection and promoting healing. Monitoring vital signs helps identify potential problems early on, allowing for timely interventions. Additionally, chapter 19 stresses the importance of patient education, empowering individuals to actively participate in their recovery.
- Pain Management: Administering analgesics as prescribed, assessing pain levels regularly, and utilizing non-pharmacological pain relief methods.
- Wound Care: Changing dressings as ordered, monitoring for signs of infection, and educating patients on proper wound care techniques.
- Monitoring Vital Signs: Regularly checking blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature to detect any deviations from the norm.
- Preventing Complications: Implementing strategies to prevent deep vein thrombosis, respiratory infections, and other potential postoperative complications.
Implementing Postoperative Care Principles from Chapter 19
Putting chapter 19’s principles into practice requires a collaborative approach involving the entire healthcare team. Clear communication, meticulous documentation, and ongoing assessment are essential for ensuring continuity of care. Regularly reviewing the patient’s medical history, surgical procedure, and individual needs helps tailor the care plan to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Addressing Common Postoperative Challenges
Postoperative care often presents challenges such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, and difficulty mobilizing. Chapter 19 provides guidance on managing these issues effectively. Proactive interventions, combined with patient education, can minimize discomfort and promote a smoother recovery.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Administering antiemetics as prescribed and encouraging patients to consume small, frequent meals.
- Constipation: Encouraging fluid intake, high-fiber foods, and administering stool softeners as needed.
- Mobilization: Assisting patients with early ambulation to prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis and pneumonia.
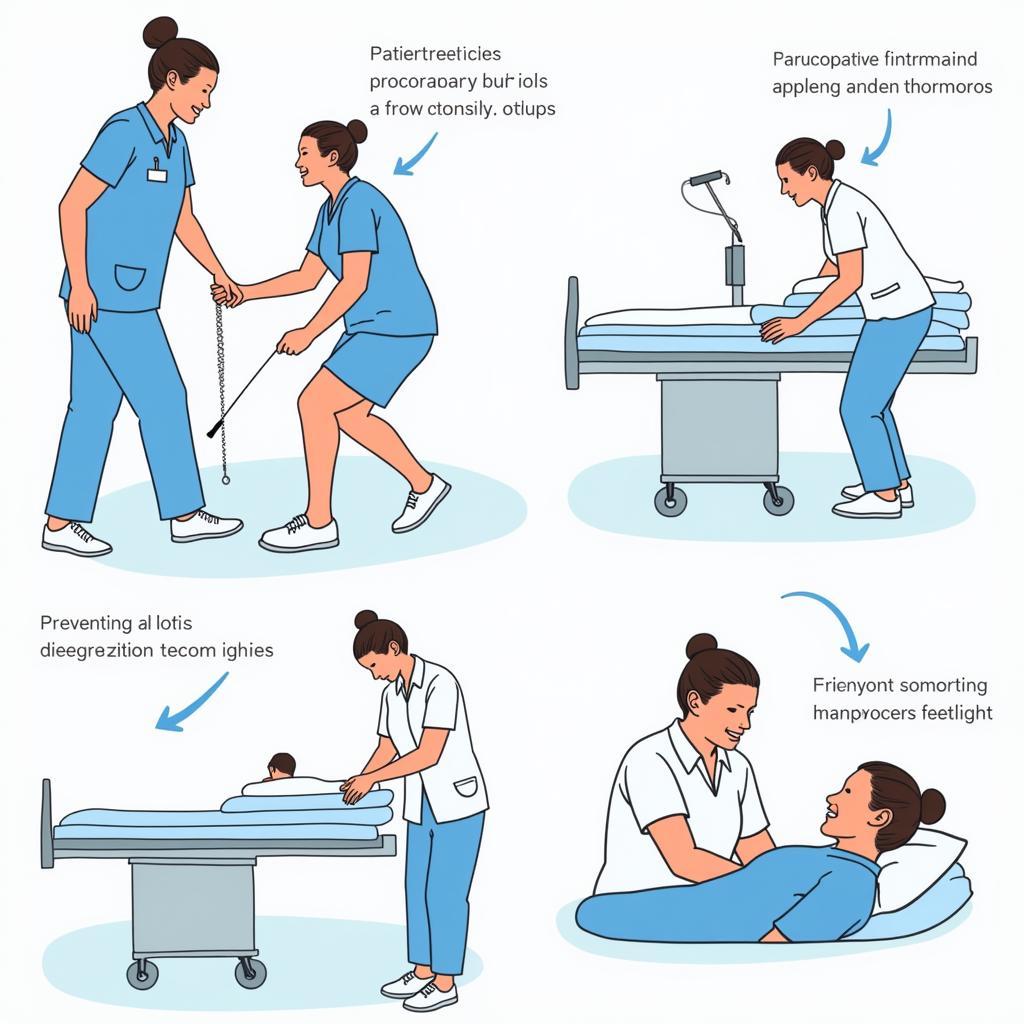 Postoperative Complication Prevention
Postoperative Complication Prevention
“Effective postoperative care is a continuous process of assessment, intervention, and evaluation. It requires a holistic approach that considers the patient’s physical, emotional, and psychological well-being,” says Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a leading expert in postoperative nursing.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of Postoperative Nursing Management (Chapter 19)
Postoperative nursing management, as outlined in chapter 19, is essential for ensuring optimal patient recovery and minimizing complications. By adhering to the principles of pain management, wound care, monitoring vital signs, and preventing complications, nurses play a crucial role in facilitating a smooth transition from surgery to recovery.
“Chapter 19 provides a valuable framework for delivering comprehensive postoperative care. By applying these principles, nurses can empower patients to regain their independence and achieve their optimal level of health,” adds Dr. Nguyen.
FAQ
- What is the primary goal of postoperative nursing management? (To promote healing, prevent complications, and ensure patient comfort.)
- What are some common postoperative complications? (Infection, deep vein thrombosis, respiratory issues, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.)
- How often should vital signs be monitored postoperatively? (Frequency depends on the patient’s condition and the type of surgery, but typically every 15 minutes initially, then gradually less frequent as the patient stabilizes.)
- What are some non-pharmacological pain relief methods? (Deep breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, cold or heat therapy.)
- When can a patient typically resume normal activities after surgery? (The timeframe varies depending on the type of surgery and individual patient factors.)
Common Scenarios and Questions:
- Scenario: Patient experiences sudden increase in pain after surgery. Question: What immediate actions should a nurse take?
- Scenario: Patient develops a fever postoperatively. Question: What are the possible causes and necessary interventions?
- Scenario: Patient experiences difficulty breathing after surgery. Question: What emergency measures should be implemented?
Related Articles and Further Information:
- Postoperative Pain Management Strategies
- Preventing Surgical Site Infections
- Early Ambulation After Surgery
Need further assistance? Contact us at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: [email protected] or visit our address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.